OSPF Router Types Explained: ABR, ASBR, DR Roles, CLI, Lab & Real-World Examples [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
In today’s blog, we’re diving into one of the most essential concepts that often gets overlooked when learning OSPF—OSPF Router Types: ABR, ASBR, and DR.
I remember back in my early days of CCNP preparation, this topic felt dry—just definitions. But once I started applying it in real labs and client projects, I realized these roles define how OSPF behaves in your topology, how LSAs propagate, and how your network converges. So, if you’ve ever been confused about why one router becomes the DR or when you need an ASBR, stick around.
By the end of this post, you’ll not only know the theory, but also see the CLI in action, build a simple EVE-NG lab, and get real troubleshooting examples.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief – Understanding OSPF Router Roles
1. What is an ABR (Area Border Router)?
An ABR is a router that connects two or more OSPF areas, one of which must be Area 0 (Backbone Area). It serves as a gateway between areas, summarizing and forwarding LSA Type 3 & 4.
Example: A router connecting Area 0 and Area 1 is an ABR.
2. What is an ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router)?
An ASBR is a router that redistributes external routes (from BGP, EIGRP, etc.) into the OSPF domain. It generates LSA Type 5 or 7, depending on whether it’s in a normal or NSSA area.
Example: A router taking in BGP routes and injecting them into OSPF is an ASBR.
3. What is a DR (Designated Router)?
In a multi-access network like Ethernet, OSPF elects a Designated Router (DR) and Backup DR (BDR) to reduce LSA flooding. DR generates LSA Type 2, representing the network to all other routers.
Only one DR and one BDR per segment.
4. Why These Roles Matter
- ABR: Controls inter-area communication
- ASBR: Bridges external networks
- DR: Prevents LSA flooding storms in large subnets
Summary – Router Role Comparison
| Role | Full Form | Purpose | Key LSAs Generated | When It’s Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABR | Area Border Router | Connects multiple OSPF areas | Type 3, Type 4 | Multi-area OSPF design |
| ASBR | Autonomous System Boundary Router | Injects external routes into OSPF | Type 5 (or 7 in NSSA) | Route redistribution |
| DR | Designated Router | Central point in broadcast segment | Type 2 | Multi-access network like Ethernet |
Essential CLI Commands
| Task | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Show OSPF neighbors | show ip ospf neighbor | Shows DR, BDR, and neighbor states |
| Verify ABR status | show ip ospf border-routers | Lists ABRs in the OSPF domain |
| Check ASBR | show ip ospf database external | Lists external LSAs (Type 5) |
| See LSA Types and originators | show ip ospf database | See which router originated which LSA |
| View interface DR/BDR election | show ip ospf interface | Displays current DR and BDR |
| Debug route redistribution | debug ip ospf redistributes | Check if ASBR is redistributing correctly |
Real-World Use Cases
| Scenario | Router Type Involved | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Branch router redistributes BGP into OSPF | ASBR | Required for connecting external BGP to internal OSPF domain |
| Core router connecting Area 0 and Area 1 | ABR | Required to move traffic between backbone and non-backbone areas |
| Switch segment with multiple routers | DR | DR reduces LSA floods; BDR takes over if DR fails |
| OSPF + static route redistribution to Area 2 | ASBR in NSSA | Type 7 LSAs are generated and converted to Type 5 by ABR |
| Fast convergence in multi-access segment | DR/BDR | Prevents unnecessary OSPF adjacency formation between all routers |
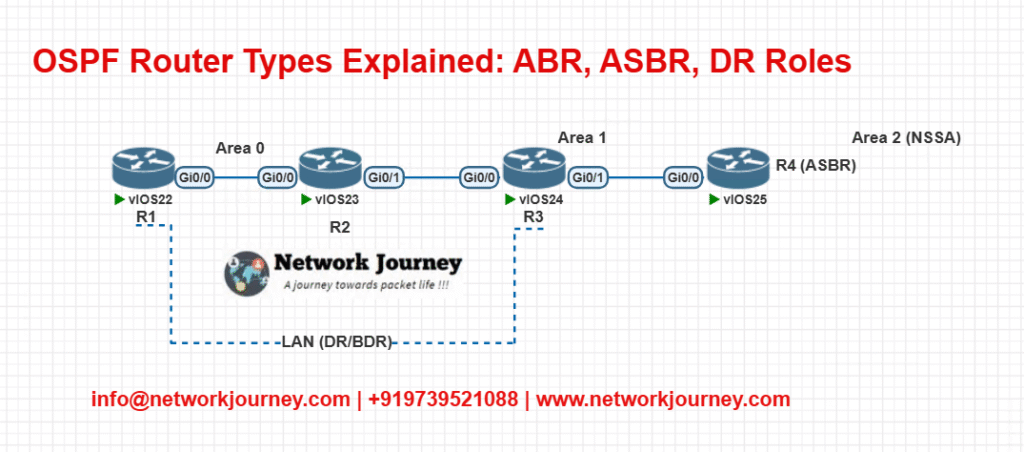
EVE-NG LAB – Demonstrating ABR, ASBR & DR
Lab Objective:
- Simulate an ABR between Area 0 and Area 1
- Configure an ASBR redistributing static routes into Area 2 (NSSA)
- Observe DR/BDR election on a broadcast segment
Topology Diagram
Config Snippets
R2 (ABR)
router ospf 1 network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
R4 (ASBR)
router ospf 1 network 10.2.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 2 area 2 nssa redistribute static subnets
R3 & R2 LAN segment (DR/BDR setup)
interface Gig0/0 ip ospf priority 100 ! For DR
Testing
- Use
show ip ospf neighborto verify DR/BDR election. - Use
show ip ospf databaseto confirm Type 3, Type 5, and Type 7 LSAs. - Add a static route on R4 and check if it appears on R1 (via ASBR > ABR > Area 0).
Troubleshooting Tips
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No external routes seen in Area 0 | ASBR misconfigured | Check redistribution + NSSA Type 7 handling |
| Two routers acting as DR | DR election priority mismatch | Use ip ospf priority or reboot routers |
| ABR not summarizing | Improper area config | Confirm backbone area is connected |
| No LSAs propagated | Passive interfaces or filtering | Check interface status and OSPF filters |
| DR not forming neighbor adjacencies | MTU mismatch or hello timer issue | Verify interface MTU and OSPF timers |
FAQs – ABR, ASBR, DR in OSPF
1. What are the different types of routers in OSPF?
Answer:
In OSPF, routers are categorized based on their role and function in the OSPF domain. The primary router types are:
- Internal Router – All interfaces in the same area.
- ABR (Area Border Router) – Connects two or more OSPF areas.
- ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router) – Redistributes routes from another protocol into OSPF.
- Backbone Router – Any router with at least one interface in Area 0.
- DR/BDR (Designated/Backup Designated Router) – Elected on broadcast/multi-access networks to reduce LSA flooding.
These roles can overlap; for example, a router can be both an ABR and a DR at the same time.
2. What is an ABR (Area Border Router), and what is its role?
Answer:
An ABR connects Area 0 (Backbone) with non-backbone areas (e.g., Area 1, Area 2). It:
- Maintains separate LSDBs per area it connects.
- Generates Type 3 Summary LSAs to share routing info between areas.
- Participates in inter-area route summarization (if configured).
Think of ABRs as “border control officers” — they control what OSPF information enters and leaves their area.
3. What is an ASBR, and when is it used?
Answer:
An ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router) is used when you redistribute external routes (from BGP, EIGRP, static, etc.) into OSPF. It:
- Generates Type 5 LSAs in normal areas.
- Generates Type 7 LSAs in NSSA areas.
- Does not have to connect to Area 0.
It acts like a gateway between OSPF and the rest of the outside world.
4. What is a DR (Designated Router) in OSPF, and why is it important?
Answer:
A DR is elected on broadcast or multi-access networks (like Ethernet) to:
- Reduce LSA flooding by representing the network as a single point.
- Generate Type 2 Network LSAs listing all attached routers.
The DR minimizes unnecessary OSPF overhead by acting as the central communicator.
5. What is a BDR, and how does it function in OSPF?
Answer:
A Backup Designated Router (BDR) is a standby to the DR. It listens to OSPF updates but does not actively advertise LSAs unless the DR fails. It:
- Becomes DR automatically if the current DR goes down.
- Ensures high availability on multi-access segments.
BDRs provide fault tolerance without increasing LSA overhead.
6. How is the DR/BDR elected in OSPF?
Answer:
DR/BDR election occurs per segment based on:
- Highest OSPF priority (default is 1; 0 means ineligible).
- If tie, then highest Router ID wins.
You can manually influence elections using:
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip ospf priority 100
To prevent a router from becoming DR or BDR, set the priority to 0.
7. Can a router be both ABR and ASBR at the same time?
Answer:
Yes, absolutely. A router can serve as:
- An ABR, connecting two OSPF areas.
- An ASBR, redistributing routes into OSPF.
In large enterprise networks, it’s common for edge routers to act as both. The router will generate both Type 3 (summary) and Type 5/7 (external) LSAs.
8. How can I check a router’s OSPF role using CLI?
Answer:
Here are the most useful commands:
- To verify DR/BDR role on an interface:
show ip ospf interface
- To check OSPF neighbors and see who is DR/BDR:
bashCopyEditshow ip ospf neighbor
- To confirm ABR/ASBR roles:
show ip ospf border-routers
- For redistributed routes:
show ip protocols
9. What happens if there is no DR in a broadcast network?
Answer:
If no DR is elected (due to all routers having priority 0 or other misconfigurations), OSPF routers will still form full adjacencies, but the Type 2 Network LSA won’t be generated, leading to:
- Increased LSA flooding.
- Potential instability or slow convergence on large segments.
It’s best to allow a DR/BDR election in broadcast environments.
10. How do router types affect the OSPF LSAs generated?
Answer:
| Router Type | LSAs Generated | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Router | Type 1 | Within the same area |
| DR | Type 2 | Within the same area |
| ABR | Type 3, Type 4 | Inter-area (between areas) |
| ASBR | Type 5 (or Type 7 in NSSA) | To advertise external routes |
Understanding which router generates what type of LSA helps you troubleshoot OSPF behavior effectively in real-world networks.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: OSPF Router Types Explained: ABR, ASBR, DR Roles, CLI, Lab & Real-World Examples Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement OSPF Router Types is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![OSPF Router Types Explained: ABR, ASBR, DR Roles, CLI, Lab & Real-World Examples. [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/OSPF-Router-Types-Explained_ABR_ASBR_DR-Roles_networkjourney.png)
![OSPF Area Types Explained: Stub, Totally Stubby & NSSA with CLI, Lab & Real-World Use Cases. [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/OSPF-Area-Types-Explained_Stub_Totally-Stubby_NSSA_networkjourney.png)