Ultimate Comparison: NetFlow vs sFlow – Insights [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
I know firsthand how critical choosing the right traffic monitoring tool is—be it for CCNA/CCNP preparation, network optimization, or troubleshooting. Today, we’ll decode two powerful technologies: NetFlow and sFlow. We’ll break down what they are, how they work, and which one suits your network—all in clear, human-friendly language.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief
What is NetFlow?
NetFlow, developed by Cisco, observes flows in your network—unique combinations of five elements (source/destination IPs and ports, protocol, and interface). Routers and switches aggregate packets into flow records and export them to a collector for analysis. This allows for detailed insights into who’s communicating, with what, and how much.
What is sFlow?
sFlow uses sampling: every Nth packet or time interval, one packet is captured and exported along with device counters. Standardized across vendors, it uses UDP for lightweight exporting. This sampling approach offers scalable visibility without overburdening the device.
Key Differences
- NetFlow is flow-based: accurate but resource-intensive.
- sFlow is packet-sampled: scalable and low-overhead.
- Use NetFlow for deep troubleshooting, sFlow for high-speed, broad visibility.
Comparison : NetFlow vs sFlow
| Feature | NetFlow (v5/v9/IPFIX) | sFlow (v5) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Flow records | Sampled packets + counters |
| Accuracy | High | Approximate |
| Overhead | High on device | Low |
| Vendor Support | Cisco mainly (others via IPFIX) | Multi-vendor, open standard |
| Use Case | Detailed flow analysis, security forensics | General traffic trends, capacity planning |
| Export Protocol | UDP | UDP |
| Setup Complexity | Moderate to high | Simple |
| Real-Time Visibility | Near real-time | Near real-time |
| Historical Analysis | Accurate counts | Estimated but scalable |
| Scalability | Good for moderate loads | Excellent for high-scale environments |
Essential CLI Commands (Cisco IOS)
| Task | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable NetFlow on interface | ip flow ingress / ip flow egress | Starts collecting flow data |
| Set Flow exporter | flow exporter EXPORTER | Defines where flow records are sent (collector IP, port, version) |
| Set Flow monitor | flow monitor MON | Defines matching and exporting policies |
| Attach monitor to interface | interface Gig0/1 → ip flow monitor MON input/output | Applies monitoring |
| Enable sFlow on interface | sflow agent-address <IP> / sflow collector-ip | Sets sFlow source and dest collector |
| Show NetFlow status | show flow monitor MON cache | View active flows |
| Show sFlow statistics | show sflow | Displays packet sampling rate and counts |
| Debug sFlow export | debug sflow packet | Real-time view of sampled packets |
Real-World Use Case
| Scenario | NetFlow Use Case | sFlow Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| DDoS detection | Identify top talkers & flows | Identify traffic spikes via sampling |
| Capacity planning | Exact bandwidth per application | Trends via sampled data |
| VoIP/QoS troubleshooting | Detailed per-call flow visibility | Broad call patterns with low overhead |
| Data center east-west traffic | Per-VM and flow analysis | Network-wide traffic sampling in switches |
| Multi-vendor monitoring | Cisco/OpenFlow/IPFIX supported | Works across diverse hardware |
EVE‑NG LAB: NetFlow vs sFlow
Lab Diagram
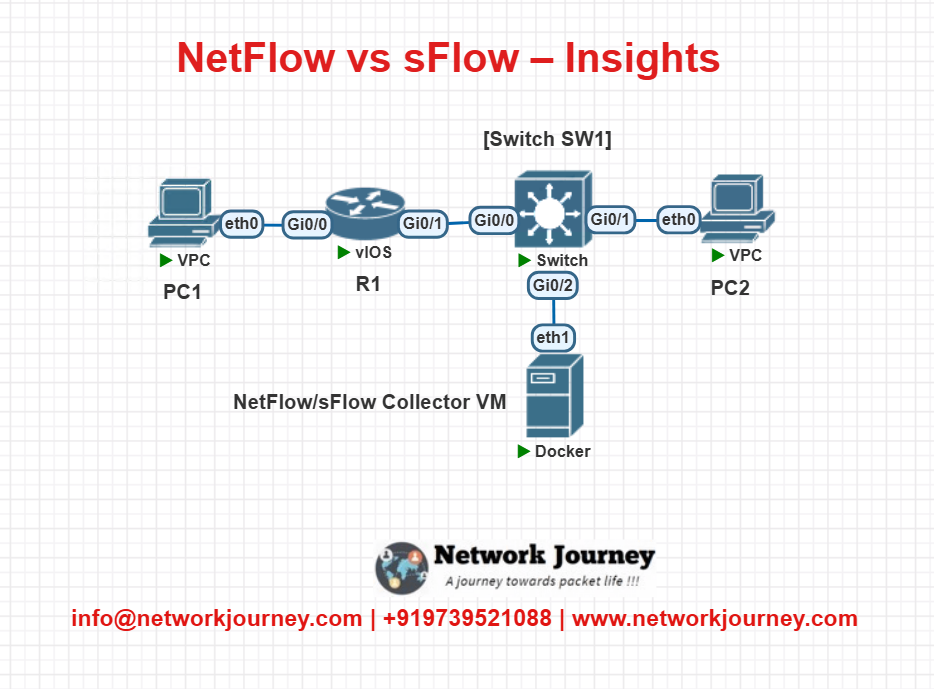
Configurations
On R1 (NetFlow):
conf t interface Gig0/0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 ip flow ingress exit flow exporter EXP1 destination 10.0.99.10 transport udp 2055 template data timeout 60 exporter EXP1 flow monitor MON1 record netflow ipv4 original-input exporter EXP1 exit interface Gig0/0 ip flow monitor MON1 input end
On R1 (sFlow):
conf t sflow agent-address 10.0.0.1 sflow collector-ip 10.0.99.10 sflow collector-port 6343 interface Gig0/0 sflow sampler 10 end
Lab Steps
- Generate traffic from PC1 to PC2 (ping, HTTP, etc.).
- On collector: check flows (NetFlow) or sampled data (sFlow).
- Use
show flow monitor MON1 cache(NetFlow) orshow sflowto verify.
Troubleshooting Tips
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No NetFlow records on collector | Exporter misconfigured or UDP blocked | Verify flow exporter, ACLs, and UDP port 2055 |
| sFlow shows 0 packets sampled | Sampling not enabled or wrong sampler rate | Check sflow sampler on interface |
| Inconsistent flow data | Network time mismatch | Synchronize device and collector clocks (NTP) |
| High CPU due to NetFlow on device | Overloaded monitor or high traffic | Adjust sampling rate or use sFlow or IPFIX |
| Missing application data | Incorrect flow record template | Use record ipv4 original-input |
FAQs – NetFlow vs sFlow
1. What is the key difference between NetFlow and sFlow?
Answer:
The core difference lies in how data is collected:
- NetFlow tracks entire flows (a unidirectional sequence of packets) and provides complete statistics for each flow.
- sFlow, on the other hand, uses statistical sampling of packets and interface counters to offer a scalable and lighter-weight monitoring solution.
NetFlow gives more granular visibility, while sFlow is more efficient for high-throughput networks.
2. Which protocol is better suited for high-speed data center environments?
Answer:
sFlow is preferred in high-speed or cloud-scale environments because it uses sampling, which significantly reduces CPU and memory overhead on devices. NetFlow can become resource-intensive when monitoring massive volumes of traffic, making sFlow the more scalable choice.
3. Does NetFlow provide more accurate data than sFlow?
Answer:
Yes. NetFlow provides detailed and accurate per-flow data, including byte counts, durations, and source-destination details. In contrast, sFlow estimates traffic based on sampled packets, which may miss short-lived or low-volume flows.
4. Is sFlow supported on Cisco devices?
Answer:
Yes, many Cisco switches and routers support sFlow, especially in platforms that are focused on Layer 2 switching or data center applications. However, NetFlow (and its standardized form, IPFIX) is more widely supported across Cisco routing platforms.
5. Can I use both NetFlow and sFlow in the same network?
Answer:
Absolutely. Many network designs use NetFlow at aggregation or core routers for detailed insights, and sFlow at access or distribution layers for scalable visibility. This hybrid approach balances performance and detail.
6. What kind of analytics tools support NetFlow and sFlow?
Answer:
Popular monitoring tools include:
- NetFlow: SolarWinds NTA, nfdump/nfsen, PRTG, ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer
- sFlow: sFlowTrend, ntopng, InMon, Grafana (via collectors)
Some tools support both protocols for centralized analysis and visualization.
7. What is IPFIX and how is it related to NetFlow?
Answer:
IPFIX (IP Flow Information Export) is an IETF standard that evolved from Cisco’s NetFlow v9. It provides a vendor-neutral format for exporting flow data and supports custom fields and templates, offering more flexibility than traditional NetFlow.
8. How much bandwidth does NetFlow or sFlow consume on the network?
Answer:
- NetFlow typically generates more traffic (1-2% of total bandwidth), depending on flow volume and export rate.
- sFlow uses far less bandwidth, as it samples packets and exports data periodically. It’s ideal where network overhead must be minimized.
9. Can I detect DDoS attacks using NetFlow or sFlow?
Answer:
Yes. Both NetFlow and sFlow can identify DDoS patterns by detecting:
- Sudden spikes in traffic
- High number of flows from the same source
- Unusual port or protocol usage
NetFlow offers better precision for forensic analysis, while sFlow provides real-time snapshots to detect anomalies quickly.
10. Which protocol is easier to configure and deploy?
Answer:
sFlow is generally easier and quicker to deploy, especially on multi-vendor hardware. It requires fewer configurations and less processing overhead. NetFlow involves setting up flow exporters, monitors, records, and may need tuning to prevent performance issues.
YouTube Link
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Ultimate Comparison: NetFlow vs sFlow is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Ultimate Comparison: NetFlow vs sFlow – Insights [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Ultimate-Comparison_NetFlow-vs-sFlow-–-Insights_networkjourney.png)
![Version Control for Network Configs – Bring Git-Like Power to Your Routers! [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Version-Control-for-Network-Configs-–-Bring-Git-Like-Power-to-Your-Routers-1.png)

![MAC Address Table Lookup Deep Dive: Mastering Switch-Level Visibility [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/MAC-Address-Table-Lookup-Deep-Dive_networkjourney.png)