Ticket#15 – Multicast Video Freezes Randomly: PIM DR Election Misconfiguration Found [CCNP Enterprise]
Table of Contents
Problem Summary
In a large campus network using multicast video for digital signage and corporate streaming, users began reporting intermittent video freezing across multiple access switches. The issue was not tied to any specific time, user, or content, and only affected a subset of devices at any given point.
The video stream originated from a server behind the core, using multicast group 239.1.1.1. The network was running PIM Sparse Mode, with multiple access and distribution switches connected via Layer 3.
Symptoms Observed
- Video freezes for 5–10 seconds every few minutes.
- Stream continues normally after the freeze—no manual intervention needed.
- Affected users change every hour (random pattern).
- Logs showed intermittent (register stop) messages on RP.
- No interface drops, no CPU spikes, no routing flaps.
Root Cause Analysis
After checking the multicast routing, RP mapping, RPF lookups, and interface stats, we found that:
- Multiple downstream L3 interfaces were part of the same subnet.
- Two access-layer switches connected to the same VLAN both participated in PIM DR election.
- DR role kept flipping due to incorrect PIM priority settings (default on all).
- Whenever DR flipped, multicast flow briefly interrupted as new DR tried to register source with RP.
Misconfiguration:
PIM DR election priority was default (1) across interfaces on access switches, causing tie and random DR flips.
The Fix
- Set deterministic DR priority on access switches:
interface Vlan20 ip pim dr-priority 10 - Ensure only one device per segment is eligible to be DR:
- Either use HSRP active interface.
- Or explicitly configure priorities.
- Restarted PIM on both interfaces to trigger fresh election:
clear ip pim neighbor
EVE-NG Lab Topology
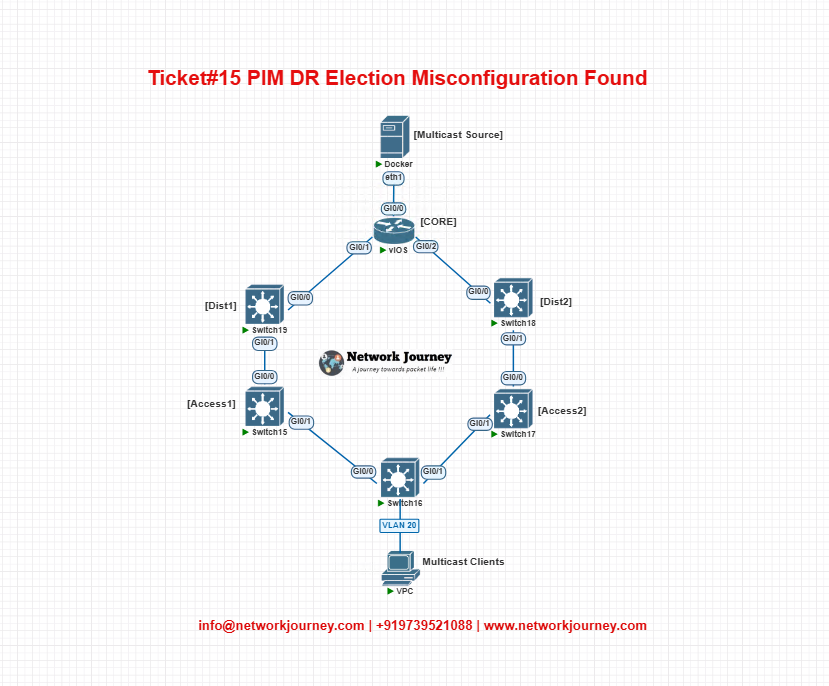
- PIM Sparse Mode enabled across all links.
- RP configured on CORE.
- Access1 and Access2 were in same VLAN—both tried to become DR.
Verification
Run the following checks post-fix:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
show ip pim interface | Confirm DR priority settings |
show ip pim neighbor | Confirm PIM neighbors seen correctly |
show ip mroute | Ensure proper (S,G) entries |
show ip igmp groups | Confirm client joins reaching router |
debug ip pim dr | DR election messages for confirmation |
ping 239.1.1.1 repeat 100 | Test stream reachability |
Key Takeaways
- DR flipping in multicast = flow interruption.
- Never leave DR election to default values.
- PIM Sparse Mode needs stability in DR roles.
- Multicast requires attention to control-plane behavior (DR, RP, RPF).
- EVE-NG is a perfect way to simulate this for practice!
Best Practices / Design Tips
- Always configure PIM DR priority explicitly in L3 access segments.
- Prefer a single DR per LAN segment.
- Align DR role with HSRP/GLBP active gateway.
- Use Bidirectional PIM or PIM-SSM if multicast traffic patterns allow.
- Monitor RP and DR logs periodically.
- Simulate multicast failover in test labs before going live.
FAQs
1. What is a PIM DR (Designated Router)?
Answer: In a multicast-enabled network, the PIM DR is the router on a multi-access segment (like Ethernet) that is responsible for:
- Sending IGMP joins from receivers toward the Rendezvous Point (RP)
- Receiving multicast traffic from directly connected sources
2. Why is PIM DR election important?
Answer: Only one router per LAN segment should perform source registration and receiver join operations. If the wrong router becomes DR due to misconfiguration, multicast traffic may not be forwarded correctly.
3. How is the PIM DR elected?
Answer: Among all PIM-enabled routers on a LAN segment, the router with the highest IP address on the interface becomes the Designated Router.
4. What causes multicast video to freeze intermittently?
Answer: Common reasons include:
- Wrong PIM DR not forwarding joins to RP
- Duplicate/missing IGMP joins
- RP unreachable from DR
- Multicast routing table inconsistencies
5. How do I check who the PIM DR is?
Answer: Use:
show ip pim interface <interface>
It displays the DR and the router’s own IP on the segment.
6. How can I influence PIM DR election?
Answer: You can manually control DR election by assigning IP addresses:
- Give the preferred DR a higher interface IP
- Or, manipulate DR priority in PIM BSR (Cisco IOS-XR/Multicast BGP)
7. What happens if a non-optimal router becomes DR?
Answer:
- It may lack reachability to RP
- It may not handle source registration
- IGMP joins might be dropped or misrouted
This leads to no multicast stream reaching the receivers.
8. Is there a way to manually assign DR in PIM?
Answer: Not directly with a priority value (unlike OSPF). DR election depends on highest IP address among PIM routers on the subnet.
9. Does the DR role affect multicast source or receivers?
Answer: Yes.
- DR registers sources with the RP
- DR forwards IGMP joins from receivers upstream
A misconfigured DR disrupts both operations.
10. How do I check IGMP joins on a router?
Answer: Use:
show ip igmp groups
This displays all joined multicast groups and their source interfaces.
11. What is the difference between IGMP and PIM?
Answer:
- IGMP operates between hosts and routers to join multicast groups
- PIM operates between routers to build multicast forwarding trees
12. How do I verify multicast routing on a router?
Answer: Use:
show ip mroute
This shows multicast source and group entries, interfaces involved, and tree type (shared or shortest path).
13. What tools help simulate or verify multicast flow?
Answer:
- ip igmp join-group for simulating joins
- ping / mcast client/server tools for multicast traffic
- Wireshark to capture and verify PIM, IGMP packets
14. What is a Rendezvous Point (RP) in PIM Sparse Mode?
Answer: The RP is a centralized router used for initial multicast source registration and group joins. It’s a critical part of PIM Sparse Mode multicast tree.
15. How do I prevent multicast disruptions in DR scenarios?
Answer:
- Always ensure routing reachability between DR and RP
- Assign a stable, reachable DR on each segment
- Use Loopback interfaces with higher IPs on preferred DR routers
- Monitor DR with
show ip pim interfaceandshow ip mroute
YouTube Video
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Multicast Video Freezes Randomly: PIM DR Election Misconfiguration Found is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career
![Ticket#15 - Multicast Video Freezes Randomly: PIM DR Election Misconfiguration Found [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Ticket15_Multicast-Video-Freezes-Randomly_PIM-DR-Election-Misconfiguration-Found_networkjourney-1.png)
![Ticket#7 - Multicast Video Freezes in Conference Room – Troubleshoot IGMP and PIM [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/nj-blog-post-Ticket-7.jpg)
![Multicast Basics and PIM Overview – Smarter Traffic Delivery in Modern Networks [CCNP Enterprise]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Multicast-Basics-and-PIM-Overview-–-Smarter-Traffic-Delivery-in-Modern-Networks.png)
![Troubleshooting Multicast in Enterprise – From Chaos to Clarity [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Troubleshooting-Multicast-in-Enterprise-–-From-Chaos-to-Clarity.png)