[Day #71 Pyats Series] Create CI/CD pipeline with pyATS (Jenkins + GitLab) using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction on the Key Points
In today’s fast-paced networking world, automation is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity.
When we talk about Python for Network Engineer workflows, pyATS stands out as Cisco’s powerful network testing and validation framework that fits beautifully into a CI/CD pipeline.
Imagine this: You make a configuration change to a Cisco router, push it to GitLab, and—without manually logging into devices—your Jenkins job kicks in, runs pyATS tests, validates your change, and gives you a pass/fail result within minutes. That’s exactly what we’re building today.
In this Day #71 PyATS Series guide, you will learn:
- How to integrate pyATS with Jenkins for automated network testing.
- How to use GitLab repositories for storing test scripts and configurations.
- How to trigger pyATS jobs automatically after code commits.
- How to catch configuration errors before they cause network outages.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a fully functional CI/CD pipeline for network validation—something most network engineers still think is “only for software developers.”
Topology Overview
Here’s the setup we’ll be working with for our CI/CD automation:
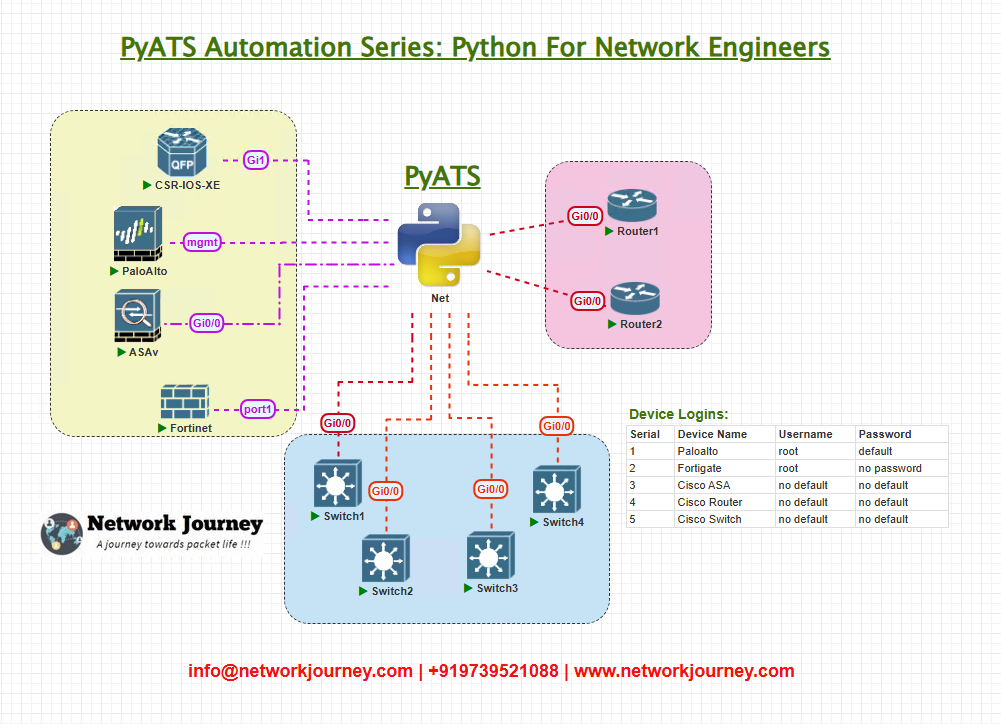
- GitLab Server – Hosts the pyATS scripts and configuration files.
- Jenkins Server – CI/CD orchestrator that triggers pyATS tests automatically on commits.
- Cisco Routers (R1, R2) – Devices under test (DUTs).
- Communication: Jenkins pulls scripts from GitLab → Executes pyATS → Validates against Cisco devices.
Topology & Communications
Key communication flows:
- Developer Pushes Code
You commit a new test case or configuration change to GitLab. - GitLab → Jenkins Webhook
GitLab notifies Jenkins via a webhook that new code is available. - Jenkins Pipeline Execution
Jenkins pulls the latest pyATS code from GitLab and runs the validation script. - pyATS → Cisco Devices
pyATS connects via SSH or API to execute tests. - Results Reporting
Jenkins collects pyATS test results and updates the pipeline dashboard.
Why this matters for network engineers:
Instead of running manual tests after every config change, this pipeline makes sure every commit is validated automatically—reducing outages and giving you confidence in your network deployments.
Workflow Script
Below is a simplified Jenkins pipeline script that integrates pyATS:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Clone Repository') {
steps {
git branch: 'main',
credentialsId: 'gitlab-cred',
url: 'https://gitlab.example.com/network/pyats-tests.git'
}
}
stage('Install Dependencies') {
steps {
sh 'pip install pyats genie'
}
}
stage('Run pyATS Tests') {
steps {
sh 'pyats run job job_file.py --testbed-file testbed.yml'
}
}
stage('Archive Results') {
steps {
archiveArtifacts artifacts: 'results/**', followSymlinks: false
}
}
}
}
Explanation by Line
pipeline {}– Declares the Jenkins pipeline syntax.agent any– Tells Jenkins to run the pipeline on any available agent.stage('Clone Repository')– Fetches pyATS scripts from GitLab.stage('Install Dependencies')– Installs pyATS and Genie libraries.stage('Run pyATS Tests')– Executes the pyATS job file against Cisco devices.stage('Archive Results')– Saves pyATS HTML/XML test results for future reference.
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: cisco_lab
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: Cisco123
devices:
R1:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.1
R2:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.2
Post-validation CLI (Expected Output)
Example pyATS output after a successful run:
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | pyATS Test Report | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ Testbed: cisco_lab Devices: R1, R2 [INFO] Connecting to devices... [PASS] R1: Interface status check passed. [PASS] R2: OSPF neighbor adjacency verified. Overall Result: PASS Execution Time: 12 seconds +------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
FAQs
1. What is the benefit of integrating pyATS into a Jenkins + GitLab CI/CD pipeline for network automation?
By integrating pyATS into a Jenkins + GitLab workflow, you bring continuous testing principles to network configurations.
- Automation: Every commit or merge in GitLab can trigger pyATS test jobs in Jenkins.
- Error Prevention: Ensures that faulty configuration changes are caught before deployment.
- Scalability: Supports multi-vendor devices but here, we focus on Cisco.
- Visibility: Jenkins provides real-time pass/fail dashboards and historical trend graphs.
2. How does the workflow look from code commit to test execution?
- Developer pushes config/test script to GitLab → triggers webhook.
- Jenkins pipeline starts → pulls latest code from GitLab.
- pyATS runs test jobs → connects to Cisco devices in lab or production.
- Results are published → Jenkins stores them, and notifications are sent to the team (Slack/Email).
3. Can pyATS test jobs in Jenkins be executed in parallel?
Yes. Jenkins supports parallel stages. For example:
- Stage 1: Connectivity check (
ping,traceroute) - Stage 2: Routing table validation (
show ip route) - Stage 3: Interface status checks (
show interfaces status)
Running them in parallel reduces total test time significantly.
4. How do I handle Cisco device credentials in this setup?
- Best practice: Store them in Jenkins Credentials Manager and reference them in pipeline scripts.
- Alternative: Use environment variables or encrypted
testbed.yaml. - Never store plain-text passwords in GitLab repositories.
5. Can I trigger pyATS tests automatically after a network config change?
Yes. You can set GitLab Merge Request events as pipeline triggers in Jenkins.
- Example: When a network engineer submits a config change script for review, Jenkins automatically runs pyATS validation before merging.
- This is similar to “unit testing” in software development but for network configurations.
6. How can I visualize pyATS results in Jenkins?
- JUnit XML Export: pyATS can export results in JUnit format, which Jenkins natively understands.
- HTML Reports: Publish pyATS HTML logs in Jenkins post-build actions for detailed drill-down.
- Trend Graphs: Jenkins can graph pass/fail over time, helping spot recurring issues.
7. What happens if pyATS detects a failure in the pipeline?
- Jenkins marks the build as FAILED.
- GitLab Merge Request can be blocked until the failure is fixed.
- Notifications can be sent to the responsible engineer via email, Slack, or MS Teams.
- This enforces a “test-before-deploy” culture.
8. Is this CI/CD pipeline limited to Cisco devices only?
No. While this example focuses on Cisco IOS/IOS-XE/IOS-XR/NX-OS, pyATS is vendor-agnostic.
- The same Jenkins + GitLab pipeline can validate Arista, Juniper, Palo Alto, Fortigate, etc., by updating the testbed YAML and parsing logic.
- This ensures scalability for multi-vendor networks in the future.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Create CI/CD pipeline with pyATS (Jenkins + GitLab) using pyATS for CiscoLab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
If you’re a network engineer who wants to master Python for Network Engineer workflows like this CI/CD pipeline, you’ll love our 3-Month Instructor-Led Training by Trainer Sagar Dhawan (14+ years of industry experience).
We go deep into:
- Python for Network Engineers
- Ansible Automation
- pyATS & Genie
- Cisco DevNet APIs
- CI/CD Pipelines for Network Automation
- Multi-vendor Automation (Cisco, Arista, Palo Alto, FortiGate)
Next Batch: Check Course Page
Limited Seats Available – Book your slot today and future-proof your career!
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #71 Pyats Series] Create CI/CD pipeline with pyATS (Jenkins + GitLab) using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Create-CI-CD-pipeline-with-pyATS-Jenkins-GitLab-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)

![Ansible Playbook for VLAN Configuration – Automate Smarter, Not Harder! [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Ansible-Playbook-for-VLAN-Configuration-–-Automate-Smarter-Not-Harder-1.png)
![[Day #32 PyATS Series] Tracing End-to-End Path (Multi-Hop Traceroute Validation) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-32-PyATS-Series-Tracing-End-to-End-Path-Multi-Hop-Traceroute-Validation-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)