[Day 18] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Configuring Wired 802.1X on a Cisco Switch
Table of Contents
Introduction
Wired 802.1X is the standard method to authenticate users and devices before they gain access to a wired LAN port. In a Cisco ISE + switch deployment, 802.1X provides per-port enforcement (user identity, device posture, or machine identity), dynamic VLANs, and downloadable ACLs — all centrally controlled by ISE. Mastering wired 802.1X is essential for secure enterprise NAC, compliant network design, and real-world troubleshooting.
Problem Statement
Enterprises face these recurring problems on the wired LAN:
- Unknown devices or rogue machines can plug in and access internal resources.
- Static VLANs don’t provide per-user policy (so every user on a port has identical access).
- Guest/contractor access is difficult to segregate and audit.
- Manual changes are slow and error prone; you need centralized policy & auditability.
This lab solves that by configuring switches to use ISE for authentication and authorization, giving you identity-aware, dynamic access control.
Solution Overview
Cisco ISE acts as RADIUS to:
- Authenticate user/device (802.1X or fallback MAB),
- Authorize access (dynamic VLAN, downloadable ACLs, CoA),
- Log events (RADIUS logs / Live Logs),
- Integrate with AD for user/Group mapping.
Now—jump into the lab.
Sample Lab Topology
Run platform: VMware Workstation / ESXi or EVE-NG (either works; EVE-NG is great for IOSv/L2 and WLC images).
VMs/devices:
- Cisco ISE (PSN/PAN or single node for lab) — IP 10.10.10.5/24
- Windows Server 2019 (AD, DNS, DHCP) — IP 10.10.10.10/24
- Catalyst switch (IOS-XE or IOSv-L2) — mgmt IP 10.10.10.2/24
- CSR1000v router (for routing/internet simulation) — IP 10.10.10.1/24
- Windows 10 client wired — gets DHCP / tests supplicant
- (Optional) WLC + Wi-Fi laptop for wireless parity tests
Logical diagram:
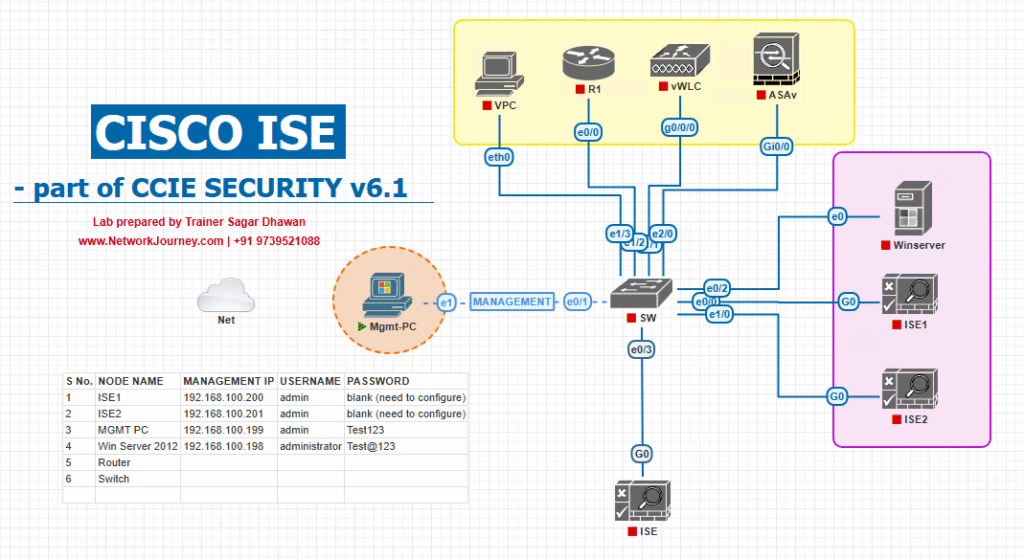
VLANs:
- Corp VLAN = 20 (192.168.20.0/24)
- Guest VLAN = 30 (192.168.30.0/24)
- Mgmt = 10.10.10.0/24
Step-by-Step GUI + CLI Configuration Guide
(Do everything in the lab environment. Exact GUI labels may vary slightly by ISE/WLC version — I use current 3.x/4.x menu names.)
Part A — Pre-reqs & planning (1–3 minutes)
- Ensure NTP is correct on ISE, AD, Switch (time skew breaks auth).
- Ensure DNS resolution between ISE and AD.
- Identify management IPs and shared secret to use between switch and ISE (example secret: cisco123).
- If using EAP-TLS later, stand up a small PKI (AD Certificate Services).
Part B — ISE: Add Switch as a Network Device (GUI)
- Login to ISE GUI (Admin).
- Go to Administration → Network Resources → Network Devices.
[Screenshot: ISE Add Network Device Screen]
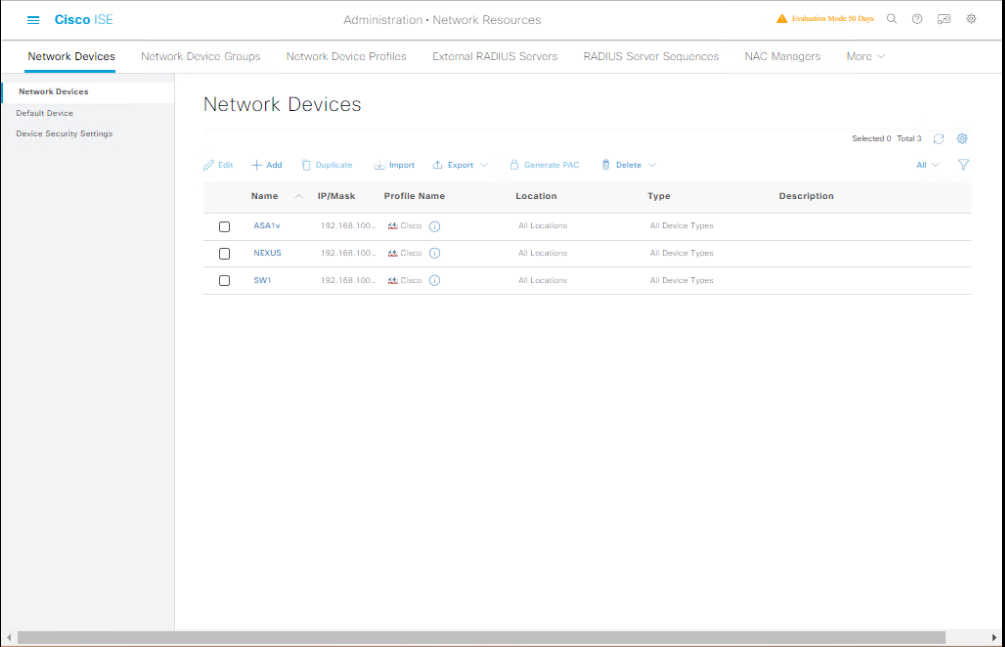
- Click Add. Fill:
- Name:
SW-Access1 - IP address:
10.10.10.2(or range) - Device Type:
Switch - Shared Secret:
cisco123
- Name:
- Save.
Why: This tells ISE which devices are allowed to query it and which shared secret to use.
Part C — ISE: Integrate Active Directory (GUI)
- Administration → Identity Management → External Identity Sources → Active Directory.
[Screenshot: ISE AD Join Screen]
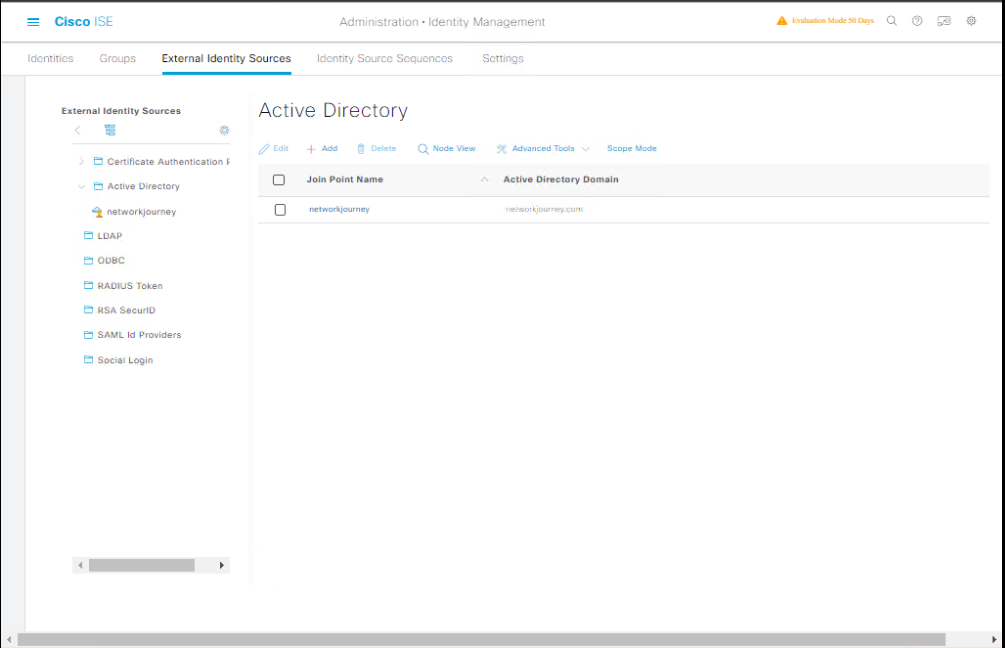
- Click Add / Join: Provide domain name and AD join credentials (a domain account with permission to join computers).
- Validate group sync (pull a test AD group such as
ISE_TEST_USERS). - Verify:
Administration → System → Diagnostics → AD Statusshows joined.
Why: ISE uses AD for user authentication and group lookup.
Part D — ISE: Create Authentication & Authorization Policies (Policy Sets)
- Policy → Policy Sets → Add new Policy Set
Wired_8021X_Default.
[Screenshot: ISE Policy Set Screen]
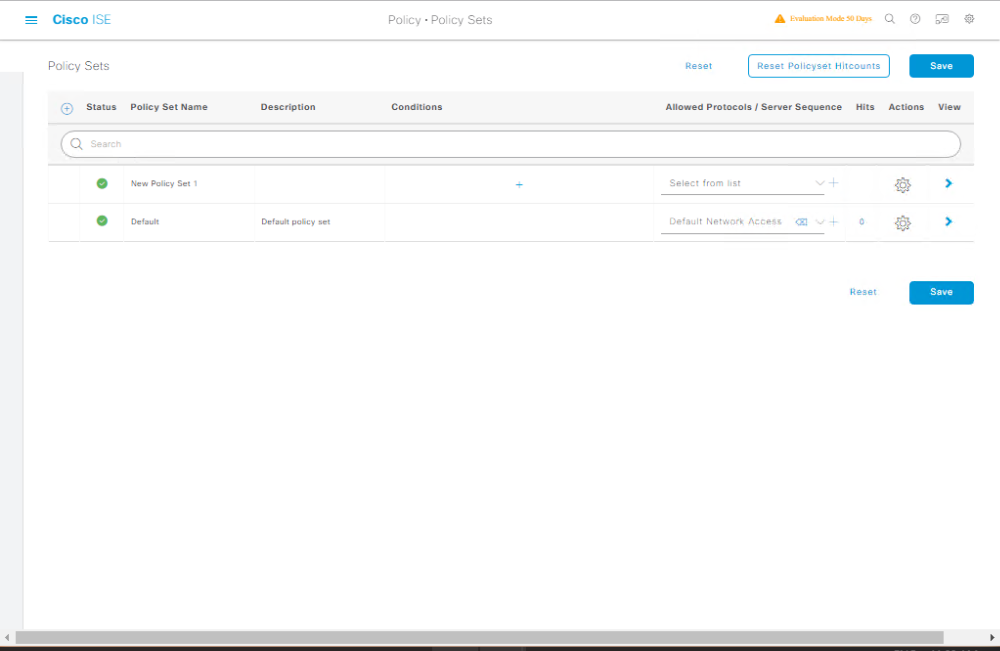
- Conditions (top):
Network DeviceisSW-Access1(optional),Timeif needed. - Under Authentication Policy (within the set):
- First rule:
If Protocol == EAP (802.1X)→ Select EAP methods (PEAP/MSCHAPv2) and identity source =Active Directory. - Add fallback:
If MAB→ Identity Source =Internal Endpoints(or AD mapping if you register MACs).
[Screenshot: ISE Authentication Policy]
- First rule:
- Under Authorization Policy: create Authorization Profiles:
Corp_Authz→ Access: Permit; VLAN =20(dynamic VLAN assignment) OR set Downloadable ACL as needed.- In GUI: Authorization Profile → Allowed Protocols → VLAN Assignment: VLAN ID 20.
Guest_Authz→ VLAN =30with restricted access.Deny_Authz→ Reject.
[Screenshot: ISE Authorization Profiles]
Notes: Order matters. Place explicit user/group rules above broader catches.
Part E — Switch configuration (IOS CLI)
Below is a tested IOS-style config snippet. Adjust interface names and details to your platform.
! 1) Define RADIUS server (IOS XE / modern) radius server ISE address ipv4 10.10.10.5 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key cisco123 ! 2) (Optional) place server in group for AAA: aaa group server radius ISE_GROUP server name ISE ! 3) Enable AAA and point dot1x auth to radius aaa new-model aaa authentication dot1x default group ISE_GROUP aaa authorization network default group ISE_GROUP ! 4) Enable 802.1X globally dot1x system-auth-control ! 5) Configure interface (example Gi1/0/24) interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24 description Wired-User-Port switchport mode access switchport access vlan 1 ! Temporary until auth authentication port-control auto dot1x pae authenticator mab spanning-tree portfast ! Optional: if auth fails, put into guest VLAN authentication event fail action authorize vlan 30
Important: On some switches you must set ip radius source-interface Vlan1 so RADIUS packets use the right source address.
Part F — Windows 10 Client: Configure Wired 802.1X supplicant (GUI)
- Network Connections → Right-click the Ethernet adapter → Properties → Authentication tab.
- Check Enable IEEE 802.1X authentication.
- Choose Protected EAP (PEAP) → Settings:
- Validate server certificate: ON (recommended) and select the ISE server certificate root CA, OR temporarily turn off validation for lab testing (not recommended for production).
- Select EAP method: Secured password (EAP-MSCHAP v2).
- Enter AD user credentials when prompted (username@domain or domain\username).
[Screenshot: Windows wired supplicant settings]
Tip: For certificate-based auth (EAP-TLS) import client cert into Personal store and choose EAP-TLS.
Part G — Validate & Test (GUI + CLI checks)
1) On the switch (CLI)
- Check port session and VLAN:
show authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/24
Expected output snippet:
Interface: Gi1/0/24
MAC Address: 00:11:22:33:44:55
Authentication: SUCCESS
Method: dot1x
Authenticator: enabled
Session status: Authenticated
VLAN assigned: 20
IP address: 192.168.20.15
- See dot1x global status:
show dot1x all
- Verify RADIUS server and counters:
show running-config | section radius show radius statistics
2) In ISE GUI
- Operations → RADIUS → Live Logs — filter by switch IP or endpoint MAC. You should see Access-Request, Access-Accept with the authorization profile assigned.
[Screenshot: ISE Live Logs showing Accept]
- Operations → Authentications or Operations → Endpoints — verify endpoint profile (MAC, authentication status).
3) On Windows client
- Confirm IP in correct VLAN subnet (192.168.20.x). Use
ipconfig /all. - Event Viewer → System/Security logs will show 802.1X authentication events.
4) Packet capture (troubleshooting)
- Mirror client port to capture with Wireshark OR on ISE PSN run a short tcpdump (lab only):
# On PSN node (requires appropriate privileges) tcpdump -i any -s 0 -w /tmp/radius.pcap udp port 1812 or udp port 1813
Open capture in Wireshark to see Access-Request / Access-Accept flows.
Part H — Test Fallback (MAB) and Guest flow
- Disable 802.1X on client or plug a non-supplicant device; switch will use MAB.
- ISE will match MAC to
Internal Endpointsor apply theGuest_Authzprofile. - Validate in Live Logs for MAB request and assigned profile.
Part I — CoA (Change of Authorization) test
- Create an Authorization Profile that includes a downloadable ACL or changes VLAN.
- In ISE Operations find the successful session → choose Change of Authorization and push a new profile.
- Validate the switch shows updated session attributes (
show authentication sessions interface ...).
Feature / Criteria, Description, Pros, Cons, Configuration Steps, and Validation.
| Feature / Criteria | Description | Pros | Cons | Configuration Steps (CLI + GUI) | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Wired 802.1X using Cisco Switch + Cisco ISE for authentication and authorization. | Strong port-level security, prevents unauthorized access, integrates with AD & certificates. | Requires endpoint supplicant support, adds complexity to deployment. | CLI:aaa new-modelaaa authentication dot1x default group radiusradius-server host <ISE-IP> key <secret>dot1x system-auth-controlint g0/1switchport mode accessauthentication port-control automabdot1x pae authenticatorspanning-tree portfastGUI:1. Add switch in ISE > Admin > Network Devices.2. Configure RADIUS shared secret.3. Create Policy Set for Wired 802.1X.4. Link to AD & VLAN assignment policies. | CLI: show authentication sessionsGUI: ISE > Operations > RADIUS Live Logs |
| Lab Topology | Switch connected to ISE (Mgmt VLAN), Endpoint connected to Access Port, ISE connected to AD. Can be virtualized in VMware/EVE-NG. | Easy to simulate in virtual lab, cost-effective for learning. | Limited performance in virtual switches vs physical. | 1. Create VLANs & IP addressing.2. Configure trunk between switch and ISE.3. Enable AAA and 802.1X.4. Connect test PC with 802.1X supplicant enabled. | Ping test to ISE.802.1X login success in logs. |
| Authentication Method | IEEE 802.1X (user-based or machine-based) via RADIUS to ISE. | Granular access control, supports dynamic VLANs & downloadable ACLs. | Dependent on RADIUS server availability, fallback required for non-802.1X devices. | 1. Enable 802.1X globally.2. Configure per-interface authentication.3. Map to ISE authentication rules. | Successful “Authorized” status in show auth sessions. |
| Authorization Method | ISE applies policies based on user/device identity (VLAN, ACL, TrustSec SGT). | Highly flexible — different users/devices get different permissions. | Requires policy planning to avoid conflicts. | In ISE: Policy Sets → Authorization Rules → Assign VLAN/ACL. | Packet capture shows correct VLAN assignment post-authentication. |
| Fallback (MAB) | MAC Authentication Bypass when 802.1X is unsupported. | Ensures non-802.1X devices still get network access. | Less secure — relies on MAC address (can be spoofed). | mab command under interface config. Add MAC to ISE endpoint DB. | ISE logs show MAB authentication events. |
| Integration with AD | ISE queries AD to validate domain user/machine credentials. | Centralized user management, reuses existing AD groups. | Requires AD connectivity and sync health. | ISE → Administration → External Identity Sources → AD → Join Domain. | ISE logs show successful AD lookup during auth. |
| Security Mode | Low-impact or Closed Mode. | Closed Mode gives maximum security; Low-impact allows pre-auth services. | Closed Mode may disrupt existing connections during cutover. | Configure authentication open for low-impact; default is closed mode. | Endpoint connectivity test pre/post authentication. |
| Certificates | Used for EAP-TLS or device identity. | Strong security, mutual authentication. | Requires PKI infrastructure & certificate lifecycle mgmt. | Generate/import certs into ISE & endpoint. | Successful EAP-TLS handshake in logs. |
| Troubleshooting | Process to fix auth issues. | Speeds up resolution, improves confidence in deployment. | Requires knowledge of both switch & ISE logs. | debug dot1x all, show radius statistics on switch. Check ISE Live Logs. | Resolve failed attempts & verify in logs. |
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between Wired 802.1X and Wireless 802.1X?
Wired 802.1X controls access at the physical Ethernet port level on a switch, while Wireless 802.1X controls access to the WLAN on a WLC or AP. Both use the same RADIUS/EAP authentication flow with ISE, but the configuration on the network device differs.
2. Do I need a special license in Cisco ISE for Wired 802.1X?
Yes. At minimum, you need an ISE Base license for authentication. If you plan to use advanced features like Posture Assessment or Profiling, you will also need Plus or Apex licenses.
3. What happens if the endpoint does not support 802.1X?
You can configure MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) as a fallback method. The switch will send the device’s MAC address to ISE for authentication. This is less secure but ensures non-802.1X devices (printers, IP phones, IoT) still get network access.
4. Should I use Low Impact Mode or Closed Mode for deployment?
In Closed Mode, all traffic is blocked until authentication succeeds — maximum security, but risky during migration.
Low Impact Mode allows limited pre-auth traffic, easing the cutover process. Most engineers start in Low Impact Mode and later switch to Closed Mode.
5. Which EAP method is recommended for Wired 802.1X?
EAP-TLS is the most secure, as it uses mutual certificate-based authentication. PEAP-MSCHAPv2 is easier to deploy but relies on username/password, making it less secure.
6. Can I integrate 802.1X with Active Directory?
Yes. ISE can query AD to validate domain users or machines. This allows you to create authorization rules based on AD group membership.
7. How do I verify if Wired 802.1X is working on the switch?
Run:
show authentication sessions show dot1x all
Look for Authorized status for the interface. You can also check RADIUS Live Logs in ISE.
8. How do I troubleshoot failed authentications?
- On the switch: enable
debug dot1x alland checkshow radius statistics. - On ISE: check Operations → RADIUS Live Logs for failure reason (bad credentials, unknown device, cert issue, etc.).
9. Do I need to enable spanning-tree portfast on 802.1X ports?
Yes. Without spanning-tree portfast, 802.1X can be delayed due to STP listening/learning states, causing authentication timeouts.
10. Is Wired 802.1X suitable for all access ports?
It’s best for user-facing and guest access ports. For uplinks, trunk ports, or management-only ports, 802.1X is typically not used — instead, other security controls like ACLs and device hardening are applied.
YouTube Link
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to my YouTube channel Network Journey and join my instructor-led classes for hands-on, real-world ISE experience
Closing Notes
Key takeaways
- Wired 802.1X + ISE centralizes authentication and authorization and drastically improves security posture.
- The lab flow: add network device → join AD → create policy sets → configure switch → configure client → validate in ISE Live Logs.
- Common failures are certificate issues, RADIUS secret mismatch, AD connectivity, and supplicant misconfig.
Upgrade Your Skills – Start Today
Take Your Cisco ISE Skills to Expert Level
I run a focused 4-Month Instructor-Led CCIE Security Mastery Program where you’ll go from ISE basics to advanced deployments including TrustSec, BYOD, Guest Portals, Posture, and more.
- Course Outline: course.networkjourney.com/ccie-security
- Hands-On Labs
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day 18] Configuring Wired 802.1X on a Cisco Switch](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-18-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Configuring-Wired-802.1X-on-Cisco-Switch.png)
![[Day 6] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Initial Setup Wizard & GUI Tour](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-6-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Initial-Setup-Wizard-GUI-Tour.png)

