[Day 111] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Cisco FTD Advanced Enforcement
Table of Contents
Introduction
In modern enterprise security, the days of static firewalls and isolated NAC enforcement are long gone. Today’s threats are adaptive, user devices are mobile, and applications live everywhere — from on-premises data centers to SaaS platforms. This demands dynamic, context-aware enforcement, where security decisions are not just based on IP addresses or ports, but on who the user is, what device they are using, its posture, and the risk level at that moment.
This is where Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) integrated with Cisco Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) becomes a game-changer. By combining the identity and policy intelligence of ISE with the threat detection, intrusion prevention, and advanced firewalling of FTD, organizations gain end-to-end adaptive access control.
Unlike traditional integrations where a firewall only inspects packets, FTD + ISE delivers identity-based, security group tag (SGT) aware, and posture-driven enforcement across the fabric. This means:
- VPN users can be allowed/denied based on ISE posture status.
- Segmentation policies can be enforced in FTD using SGTs pushed by ISE.
- Threat responses can be automated: if ISE detects a compromised endpoint, FTD can instantly quarantine it.
- Security events are correlated: ISE provides the “who/what” context, FTD provides the “what happened” forensic trail.
This integration is not just a checkbox — it’s the pinnacle of next-gen Zero Trust enforcement. In this masterclass, we’ll go step-by-step (GUI + CLI validation) through how Cisco ISE integrates with Cisco FTD for advanced enforcement, how to configure and verify it in the lab, and how enterprises can use it for real-world Zero Trust outcomes.
Problem Statement
Real-world problems this integration solves:
- Identity Blindness: FTD sees IPs/ports but not “who” is connecting. Without identity, access is coarse, and privileged access cannot be differentiated.
- Inflexible enforcement: Static ACLs require manual changes; remediation / quarantine is slow or manual.
- Limited incident response: SOC needs user context (who, device, posture) tied to events to act quickly.
- Policy drift & scale: Multiple firewalls require centralized policy orchestration tied to identity taxonomy.
Goal: Provide automated, identity-aware enforcement where ISE supplies identity, posture, and SGTs; FMC consumes that context and pushes targeted enforcement to FTD devices — with measurable, validated outcomes.
Solution Overview
Core building blocks
- ISE — author identity & posture policies; publish SGTs and user-to-IP mappings via pxGrid; generate Authorization Profiles that can drive remediation metadata.
- FMC / FTD — consumes identity context (pxGrid) to build Access Control Rules (identity conditions), applies Threat/Access rules, and enforces dynamic remediation (quarantine) on FTD.
- Flow: Endpoint authenticates → ISE identifies & evaluates posture → ISE publishes identity mappings/SGTs to pxGrid → FMC consumes pxGrid → FMC Access Control Policies use identity/SGT to allow/deny or apply remediation → FMC deploys to FTD → enforcement occurs at packet level.
Key capabilities achieved
- User-aware access control (e.g., allow finance users to app X; block contractors).
- Posture-based quarantine (ISE tags endpoint non-compliant → FMC/FTD restricts).
- SGT/TrustSec integration (where SXP or TrustSec supported) to unify policy across devices.
- Rapid SOC response via automation (ISE pxGrid events → FMC policy changes).
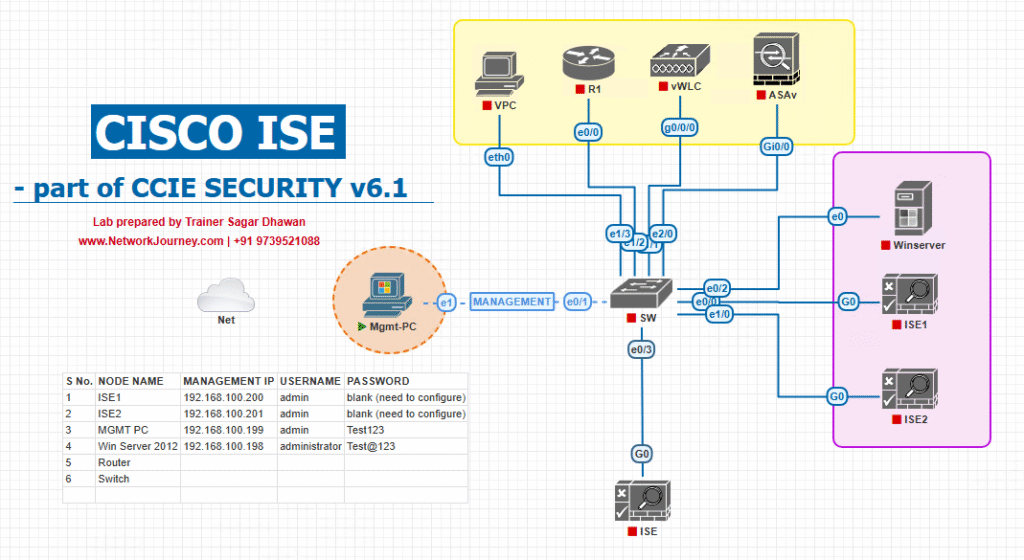
Sample Lab Topology (VMware/EVE-NG + devices)
VMs / Appliances
- Cisco ISE cluster (PAN, MnT, PSN1, PSN2) — VMware
- FMC appliance (or FDM for single-panel labs) — VMware/EVE-NG
- One or more FTD devices (managed by FMC) — virtual/physical
- AD + PKI (Active Directory / AD CS), NTP, DNS — VMs
- Test endpoints: Windows 10/11 (AnyConnect), Linux attacker VM, IoT simulator VM
- Optional SIEM for log correlation
Topology diagram:
Lab assumptions
- FMC and ISE can reach each other on management network.
- FTDs are managed by FMC and accessible to test hosts.
- NTP and DNS properly configured.
- Short TTLs and single domain lab to simplify certificate trust.
Step-by-Step GUI Configuration Guide
PRECHECKS (must pass before any change)
Checklist
- DNS: FMC & ISE FQDNs resolve both ways.
- NTP: clocks aligned across ISE, FMC, FTDs, endpoints.
- Certificates: ISE and FMC must trust each other’s CA chain for pxGrid (if using TLS).
- Admin accounts & RBAC prepared:
pxgrid-clientuser or service account as needed.
CLI / Jump host checks
# DNS & reachability nslookup ise-pan.lab nslookup fmc.lab ping -c3 fmc.lab curl -k https://<fmc>/api/fmc_platform/v1/info # FMC API check (see Step 5.6)
STEP 1 — Prepare ISE for pxGrid & SGT (ISE GUI)
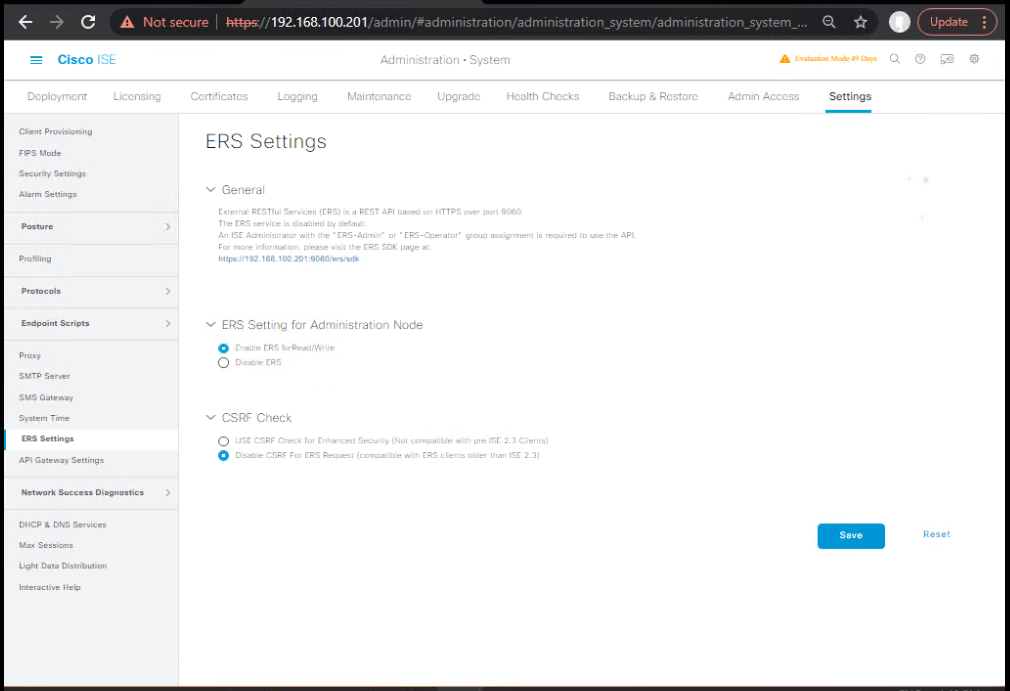
- Enable pxGrid & ERS
Administration → System → Settings → pxGrid Services→ Enable pxGrid; ensure Service is started.Administration → System → Settings → ERS Settings→ Enable ERS (if FMC needs to CRUD endpoints).
- Certificates
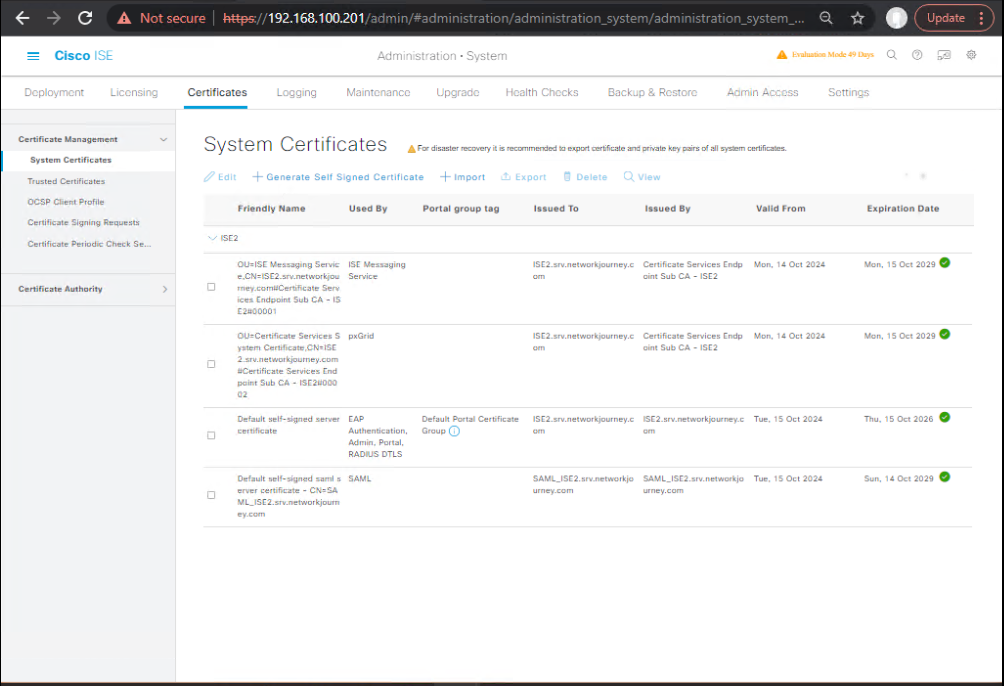
Administration → System → Certificates→ Ensure node certificate is valid and includes FQDN SANs. Export the ISE CA chain.
- pxGrid client approval or automatic trust
- Optionally configure pxGrid auto-approve for FMC (for lab).
- Optionally configure pxGrid auto-approve for FMC (for lab).
VALIDATION (ISE CLI)
show application status ise show logging application pxgrid.log tail 50
Expect pxGrid service running with no errors.
STEP 2 — Register FMC as pxGrid Client in ISE (ISE GUI + FMC)
- On FMC GUI (or FDM): go to System → Integration → pxGrid (menu names vary by FMC version). Choose to Register to ISE. FMC will generate a CSR or initiate pxGrid registration flow to ISE IP/FQDN. Provide credentials (if prompted).
- On ISE: Accept the pxGrid client registration (if manual).
Work Centers → pxGrid Services → All Clients→ ConfirmFMCshows Online / Allowed.
VALIDATION (ISE CLI & FMC GUI)
# ISE show logging application pxgrid.log tail 100 # FMC System → Integration → pxGrid → Status shows connected
Evidence: FMC is listed as pxGrid client on ISE; ISE logs registration event.
STEP 3 — Configure Identity Source / User-to-IP Mapping in FMC
- FMC GUI:
System → Integration → pxGrid→ enable Identity features; configure the relevant ISE domains. - FMC GUI:
Objects & Settings → Object Management → Users/Identity(or Identity Source configuration) → verify ISE is available as a source. - FMC GUI: Under Policies → Access Control → Identity Sources ensure ISE is part of the Identity Source Sequence for Access Control rules.
VALIDATION (FMC GUI)
- In FMC, go to Analysis → Users (or Analysis → Connections → Users) and confirm that authenticated users from ISE appear with user→IP mappings.
STEP 4 — Publish SGT or SXP Mappings (Optional / Advanced)
Use this if your design needs SGTs enforced in devices that require SXP.
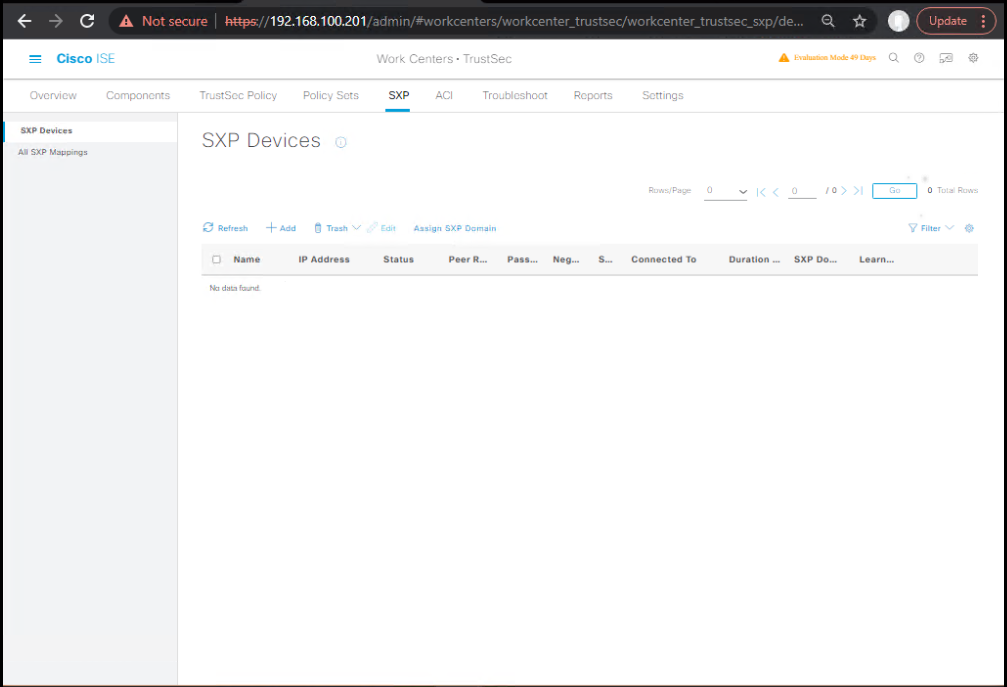
- ISE GUI:
Work Centers → TrustSec → SXP→ configure SXP connections (if FTD/FMC supports SXP or you have SXP servers). Export SGT-IP bindings.
- FMC/FTD: If using SXP, configure SXP peer on devices that accept SGT mappings. (Implementation may be platform dependent.)
VALIDATION
- Verify SGT mapping table in devices using device GUI or logs. On ISE:
show trustsec sgt(CLI). - Evidence: SGT mapping entries present and consistent.
STEP 5 — Create ISE Authorization Profiles (that FMC can consume)
- Create Authorization Profiles in ISE that include metadata FMC/FTD will use: e.g., attributes indicating
Quarantine,FullAccess, orVPN-User. Use RADIUS AVPairs if firewall expects those, or simply use pxGrid identity and tags for FMC.
Policy → Policy Elements → Results → Authorization → Add- Example:
AC-QUARANTINEwith attributes:Filter-Id = ACL_QUARANTINE(if passing via RADIUS), AND setSGTtag in the profile if needed. - ISE Policy Sets: Add rules to return those Authorization Profiles based on AD groups or posture.
Policy → Policy Sets→ CreateFTD-VPNpolicy set matching NAD =FMC / FTDor network device group.
VALIDATION (ISE CLI / GUI)
show running-config ise | include Authorization show logging application ise-radius.log tail 50
Evidence: Authorization profiles listed and active.
STEP 6 — Create FMC Identity-Aware Access Control Rule
- In FMC GUI:
Policies → Access Control → Access Policy→ Edit Policy (or create new Access Control Policy) and add Rule:- Name:
Allow Finance Apps for Finance Users - Conditions: Source Identity — match
USER: finance_group(ISE identity). Destination: Finance App Servers. Actions: Allow + Log + apply IPS policy. - Quarantine Rule: create a rule at top
IF identity = ISE:Endpoint.Quarantine THEN Block (or Apply Quarantine ACL)
- Name:
- Order & Precedence: Ensure Quarantine rule is at top with immediate action to prevent other rules’ matches.
- Deploy Policy to FTD device(s) (Deploy → select devices → Deploy).
VALIDATION (FMC GUI)
- Verify Deploy status:
System → Dashboards → Device Management → Deployment Statusshows success. - FMC shows last deployment time and devices updated.
STEP 7 — Trigger Authentication & Validate End-to-End Enforcement
Scenario A — User identified as Finance (Allowed)
- From Endpoint: log in to network / start an app connection that will match policy (e.g., access finance server).
- ISE: check
Operations → RADIUS → Live Logs→ look for Access-Request, Access-Accept, Authorization Profile assigned (FullAccess), and pxGrid publish events. - FMC:
Analysis → Connectionsfilter by user or IP. You should see the flow and identity column populated withuser@domainand SGT (if applicable). - FTD enforcement check: On FMC, view Device → Health/Events to see policy hits; or use
Analysis → Networkto show policy hits.
Evidence: connection allowed, policy hit counters increased.
Scenario B — Non-compliant / Quarantine
- Simulate non-compliant endpoint (e.g., disable AV or tag in ISE as noncompliant). ISE will publish the change via pxGrid.
- FMC should receive the event and the top Quarantine rule should match; FTD will apply Quarantine ACL on the host IP.
- Verify: In FMC Analysis or Events, you will see the Quarantine action and policy hit. On endpoint, attempt to reach finance server — blocked.
VALIDATION (evidence checklist)
- ISE Live Log showing Authorization change + pxGrid publish.
- FMC Analysis showing user→IP mapping and policy hit.
- FTD enforcement (blocked requests) verified by client inability to reach server and FMC logs showing DACL or block action hit.
STEP 8 — Troubleshooting & Diagnostics (CLI / API checks)
ISE checks (CLI)
# pxGrid service status & logs show application status ise show logging application pxgrid.log tail 100 show logging application ise-psc.log tail 50
FMC API sample checks (get auth token then query identity objects)
Note: FMC API endpoints vary by version; adapt using FMC API docs.
# 1) generate token (FMC) curl -k -u admin:Password https://<fmc>/api/fmc_platform/v1/auth/generatetoken -i # Extract token from response headers (X-auth-access-token) # 2) sample query (identity/user list - endpoint path may vary) curl -k -H "X-auth-access-token: <token>" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ https://<fmc>/api/fmc_config/v1/domain/default/identity/users | jq .
FMC GUI checks
Analysis → Usersshows user→IP mapping.Analysis → Connectionsshows policy events.Policies → Access Control → Policy Viewershows rule hit counts.
FTD CLI basics (on FTD device via SSH)
show version show managers # shows FMC manager if applicable show running-config # view local config (limited) # For troubleshooting, use 'system support diagnostic-cli' to access deeper commands on FTD
Note: FTD has a different CLI model than ASA; deep troubleshooting often relies on FMC GUI and syslogs.
STEP 9 — Evidence Pack (what to capture)
For each test case produce:
- ISE Live Log (Access-Request / Authorization / pxGrid publish).
- FMC Analysis showing user→IP and policy hit.
- FMC policy deploy log showing device updated.
- FTD packet captures or event entries showing blocked/allowed attempts (if required).
- CLI outputs saved:
ise_pxgrid_logs.txt,fmc_deploy_status.txt,ftd_show_version.txt. - Test matrix CSV entry for each scenario with pass/fail.
Evidence CSV columns
TestCase,StartTS,EndTS,User,EndpointIP,ISE_Log_File,FTD_Event_File,Result,Notes
Expert-Level Use Cases
- User-aware Microsegmentation: Use ISE identities to implement fine-grained access rules in FMC so finance/devops/dev have distinct access to services without touching VLANs.
- Posture-driven Quarantine: ISE posture noncompliance triggers pxGrid event → FMC deploys temporary Quarantine rules to FTD; SOC receives alert and remediation flow begins.
- Automated Incident Response: SIEM detects anomaly → invokes FMC API to block the user IP; ISE revokes user session via pxGrid/CoA to neighboring devices.
- SGT Federation Across Regions: ISE publishes SGTs; SXP syncs SGT→IP bindings to legacy devices; FMC uses identity to maintain consistent policy globally.
- Just-In-Time Privilege: ISE approves temporary elevation for an admin; FMC applies an allow rule for that user for a limited time window and automatically reverts.
- Scale-tested Identity-Aware NAT: For remote users, FTD applies identity tags to translated sessions; policies follow users across NAT boundaries for consistent auditing.
- Threat Containment Playbook: Malware detection via CTR on FTD → FMC triggers ISE to quarantine device (via pxGrid) and block related lateral flows.
- Regulatory Evidence Bundles: Generate ISE + FMC logs and policy hit counters for auditors showing “who accessed what when” with supporting logs.
- Cloud Edge Enforcement: FMC managing cloud-deployed FTDs uses ISE identity via pxGrid to apply consistent rules across on-prem and cloud edge.
- Multi-tenant MSP Model: ISE multitenant identity mapped to tenant policies in FMC; FTD enforces per-tenant microsegmentation while a central SOC aggregates alerts via pxGrid.
FAQs – Cisco ISE AnyConnect Posture Enforcement for Remote Users
1. What’s the difference between AnyConnect Posture and NAC Agent?
- Answer: Cisco has deprecated the NAC Agent; AnyConnect (now Secure Client) Posture Module is the standard. It supports more OS types, integrates seamlessly with ISE, and allows more granular posture checks (AV, firewall, disk encryption, etc.).
- Validation: In ISE Work Centers → Posture → Client Provisioning, confirm “AnyConnect Posture Agent” package is uploaded.
- CLI Check (ASA):
show vpn-sessiondb detail anyconnect→ Look for Posture Status: Compliant/Non-Compliant.
2. Do I need separate AnyConnect licenses for Posture?
- Answer: Yes. You need AnyConnect Plus or Apex licenses depending on feature set. For Posture Enforcement with ISE, Apex is required.
- Validation: On ASA or FTD:
show activation-keyEnsure “AnyConnect Apex” is enabled.
3. How does ISE determine if a device is compliant?
- Answer: Through Posture Policies (Work Centers → Posture → Policy Sets). Each rule checks for conditions like antivirus, OS patch level, registry keys, or firewall status. If all required conditions match, the device is marked Compliant. Otherwise, it goes into Non-Compliant and can be redirected.
- Validation: On ISE Live Logs, filter by Posture Status.
4. What happens if a device is non-compliant?
- Answer: ISE can apply:
- Remediation VLAN/ACL (for updates).
- Web redirection to remediation portal.
- Limited access until compliance is met.
- Validation: On ASA, use:
show vpn-sessiondb anyconnect filter name <username>Look for applied Dynamic ACL or VLAN tag.
5. How are Posture Policies pushed to endpoints?
- Answer: Through Client Provisioning Policies. When a user first connects, ISE provisions the AnyConnect Posture module and compliance rules. The agent enforces them locally and reports status to ISE.
- Validation (GUI):
- ISE → Client Provisioning → Verify AnyConnect package & compliance modules uploaded.
- Check endpoint’s log:
C:\ProgramData\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client\ISEPosture.log.
6. How do I troubleshoot if posture checks are failing?
- Answer:
- Check AnyConnect posture logs on endpoint.
- Validate ASA is redirecting to ISE with correct redirect ACL.
- Check ISE Live Logs → Look for Failure Reason.
- CLI Validation (ASA):
show running-config webvpnEnsureanyconnect module postureis enabled.
7. Can Posture be used for split-tunnel VPNs?
- Answer: Yes, but ensure the ISE posture redirect traffic is excluded from split-tunnel. Otherwise, the agent may fail to communicate with ISE.
- Validation: Check ASA split-tunnel ACL includes ISE PSN IP.
8. How long does posture re-check (reauth) take?
- Answer: Default is 1 hour, configurable in ISE under Posture Settings → Compliance Module. You can set shorter or longer re-check timers depending on security requirements.
- CLI Validation:
show vpn-sessiondb anyconnectLook for “Posture Token Lifetime.”
9. Can I integrate 3rd-party antivirus/firewall checks with ISE posture?
- Answer: Yes. ISE uses OPS (Opportunistic Posture Service) and the Posture Compliance Module which has built-in vendor checks for major AV vendors (McAfee, Symantec, Windows Defender, etc.).
- Validation: ISE → Posture Policies → Conditions → AV checks.
10. What’s the difference between ISE posture and Secure Endpoint (AMP) posture checks?
- Answer:
- ISE Posture: Checks compliance before granting full network access. Reactive and policy-driven.
- Secure Endpoint (AMP/EDR): Provides continuous endpoint monitoring, malware detection, and behavioral analysis. Proactive and threat-driven.
- Best practice: Use both together for layered Zero Trust endpoint security.
YouTube Link
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to my YouTube channel Network Journey and join my instructor-led classes for hands-on, real-world ISE experience
Closing Notes
- Identity is the force multiplier for firewall policy: when ISE and FMC collaborate, policies become precise, auditable, and automation-ready.
- pxGrid is the key — ensure cert trust, NTP, and network reachability first.
- Test with evidence: log ISE Live Logs, FMC Analysis, and FTD event records for each scenario. Keep an evidence pack for audits.
- Operationalize: schedule periodic pxGrid health checks and synthetic identity tests to ensure continuous mapping.
Upgrade Your Skills – Start Today
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to Network Journey on YouTube and join my instructor-led classes.
Fast-Track to Cisco ISE Mastery Pro
I run a focused 4 months of instructor-led CCIE Security training (ISE, TrustSec/SGT, SDA, pxGrid, FTD/FMC integrations, HA/DR).
Course & outline: https://course.networkjourney.com/ccie-security/
Book a readiness call; enroll to get lab configs, runbooks, and the full FTD Enforcement Runbook Pack (templates, API snippets, evidence CSV).
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088

![[Day 38] – Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Wired Supplicant Configuration for Windows](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-38-–-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Wired-Supplicant-Configuration-for-Windows.png)
![[Day 41] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Wireless 802.1X Authentication Overview](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-41-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Wireless-802.1X-Authentication-Overview.png)
