Cisco Debug vs Show Commands: Deep Dive for Network Troubleshooting [CCNP Enterprise]
If you’ve ever been stuck troubleshooting a stubborn routing issue or chasing down why BGP isn’t forming, you know that sometimes a simple show command gives you just the picture—but not the full story. That’s where debug steps in. In this guide, I’ll break down the key differences, benefits, and best practices for using show and debug commands on Cisco devices. Whether you’re preparing for your CCNA, CCNP, or battling issues in a production environment, this article will give you clarity and confidence to use these tools like a pro.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief
What are ‘show’ and ‘debug’ commands in Cisco IOS?
In Cisco networking, show and debug are essential commands used to gather information about the device’s current state and its live processes. They help engineers analyze and verify configurations, protocols, interfaces, and ongoing operations.
Show Commands – The Snapshot Tool
Show commands are non-intrusive. They pull current system data like routing tables, interface statuses, ARP tables, or BGP sessions. These are safe to run on production devices at any time because they do not consume excessive CPU or log data in real time.
Debug Commands – The Live Monitor
Debug commands display live, real-time events as they happen on the device. They are incredibly useful during protocol handshakes, route advertisements, or NAT translations. However, they consume CPU and should be used cautiously, especially on production routers.
When to Use What?
- Use
showfor verification and periodic checks. - Use
debugfor real-time troubleshooting and protocol-level issues.
For example, to check if OSPF is configured: useshow ip ospf neighbor.
To see why it’s failing: usedebug ip ospf adj.
Summary / Comparison / Pros and Cons
Feature Comparison
| Feature | show Command | debug Command |
|---|---|---|
| Output Type | Snapshot / current state | Real-time live output |
| Performance Impact | Low | High (especially with high traffic) |
| Use in Production | Safe | Risky unless filtered |
| Examples | show ip route, show interface | debug ip icmp, debug ip ospf events |
| Log Destination | Console/terminal | Console/terminal, can be logged with syslog |
| Syntax Simplicity | Easy to use | Requires specific protocol knowledge |
Pros and Cons
| Command Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
show | Safe for production, easy to read, scriptable | Doesn’t show live or internal behavior |
debug | Real-time view, ideal for protocol-level issues | CPU-intensive, risky in production, floods terminal if misused |
Essential CLI Commands
| Purpose | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Show interface details | show ip interface brief | Displays IP, status, and protocol of all interfaces |
| Check routing table | show ip route | Shows learned/static routes |
| OSPF neighbors | show ip ospf neighbor | Verifies OSPF adjacencies |
| Live ICMP traffic debug | debug ip icmp | Shows ICMP packets (e.g., ping traffic) in real time |
| BGP session troubleshooting | debug ip bgp events | Displays BGP events like opens and keepalives |
| Turn off all debugs | undebug all or u all | Stops all running debug processes |
| Log debug to buffer | logging buffered 100000 debugging | Logs debug messages to buffer instead of console |
| View debug buffer logs | show logging | Displays messages in the log buffer |
Real-World Use Case
| Scenario | Command(s) Used | Reason & Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| OSPF not forming neighbor adjacency | debug ip ospf adj | Showed Hello packets not received—mismatched timers |
| Interface up but no traffic | show interface, debug ip icmp | Discovered input drops due to duplex mismatch |
| NAT not working for users | show ip nat translations, debug ip nat | Tracked address mapping and found missing ACL |
| BGP neighbor stuck in Idle state | debug ip bgp + show ip bgp summary | Helped identify misconfigured BGP remote-as |
| DHCP server not assigning IP | debug ip dhcp server packet | Observed offer packets blocked by upstream firewall |
EVE-NG Lab – Debug vs Show Demo
Lab Topology
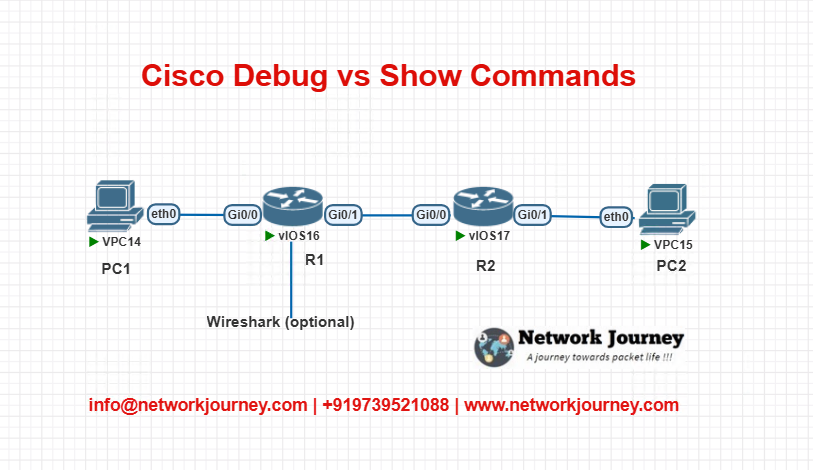
Objective:
- Troubleshoot OSPF adjacency issue using both
showanddebugcommands. - Simulate ping failures and analyze via ICMP debug.
Configuration (R1 and R2):
R1:
router ospf 1 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 interface Gig0/0 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
R2:
router ospf 1 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 interface Gig0/0 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
Verification Commands:
R1# show ip ospf neighbor R1# debug ip ospf adj R1# show ip route R1# ping 192.168.12.2 R1# debug ip icmp
Troubleshooting Tips
| Symptom | Cause | Suggested Show/Debug Commands |
|---|---|---|
| OSPF neighbor stuck in INIT state | Hello packet mismatch | debug ip ospf hello, show ip ospf interface |
| NAT translation not occurring | ACL or interface missing | debug ip nat, show ip nat translations |
| High CPU usage after debugging | Excessive debug logging | undebug all, show process cpu |
| DHCP not assigning IPs | Upstream blocks DHCPOFFER | debug ip dhcp server, show ip dhcp binding |
| Interface flapping | Duplex mismatch or bad cable | show interface, debug interface |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between show and debug commands in Cisco IOS?
Answer:
The show command provides a snapshot of the current status or configuration of a device component, such as interfaces, routing tables, or protocols. It’s static and non-intrusive. The debug command, on the other hand, offers real-time logging of dynamic events (like OSPF hello packets, BGP updates, or ICMP messages), which is essential for live troubleshooting. While show is safe for use in production, debug should be used with caution due to its potential CPU impact.
2. Is it safe to run debug commands on a production network device?
Answer:
Not always. debug commands can be CPU-intensive, especially on devices handling heavy traffic. If not scoped properly, they can overload the CPU, causing slowness or even crashes. In production environments, it’s recommended to:
- Use specific
debugcommands (notdebug all) - Log output to buffer (
logging buffered) - Immediately stop it using
undebug allwhen done
3. How do I stop a debug session that is overwhelming the terminal?
Answer:
If your console is flooded with debug output, press Ctrl+C to interrupt it and enter the command:
undebug all
or simply:
u all
This stops all active debug processes. It’s a good practice to always run undebug all after using any debug command.
4. Can I redirect debug output to a log file or buffer instead of the console?
Answer:
Yes. To avoid overwhelming the terminal, use:
logging buffered 100000 debugging
Then view the logs using:
show logging
This stores debug output in memory (buffer), letting you review it safely without flooding your screen.
5. What are some common debug commands used in routing protocol troubleshooting?
Answer:
Here are useful protocol-specific debug commands:
- OSPF:
debug ip ospf adj,debug ip ospf hello - EIGRP:
debug eigrp packets,debug ip routing - BGP:
debug ip bgp,debug ip bgp events
These help capture events such as neighbor formation, route advertisements, or protocol errors in real time.
6. What does show ip interface brief tell me?
Answer:
This command gives a concise summary of all interfaces on a device, showing:
- Interface name (e.g., Gig0/1)
- Assigned IP address
- Status (up/down)
- Protocol (up/down)
It’s typically the first command used to verify if interfaces are correctly configured and operational.
7. How can I troubleshoot ping (ICMP) issues with debug?
Answer:
Use:
debug ip icmp
It shows each ICMP echo request and reply as it enters or leaves the router. Combine it with a ping command to verify if ICMP traffic is reaching its destination and returning successfully. This helps identify ACL issues or unreachable hosts.
8. What should I do if debug output isn’t showing anything?
Answer:
If no output appears, check:
- Is the related event actually happening? For example,
debug ip ospfwon’t show anything if OSPF isn’t running or there are no neighbors. - Is logging enabled to the correct destination? Use
show loggingto verify. - Did you filter too narrowly with a specific
debug?
Sometimes using a broader debug variant or initiating related traffic (like ping or routing updates) can help trigger visible output.
9. What are some best practices for using debug safely?
Answer:
- Never use
debug all—it enables all debugs and can crash a device. - Use protocol-specific or event-specific debug commands.
- Enable buffered logging to review logs without flooding your console.
- Monitor CPU usage with
show process cpu. - Always end your session with
undebug all.
Following these practices minimizes the risk of downtime during debugging.
10. Can I use show and debug together for end-to-end troubleshooting?
Answer:
Absolutely! That’s actually the best approach:
- Start with
showcommands to verify basic configurations and interface/routing status. - If the issue is not visible or intermittent, use
debugto monitor real-time behavior. - Example flow:
show ip ospf neighbor→ to verify OSPF adjacency- If stuck, use
debug ip ospf adjto see Hello packet exchanges
This combination gives both static and live views of the issue, improving diagnosis accuracy.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: Cisco Debug vs Show Commands: Deep Dive for Network Troubleshooting Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Cisco Debug vs Show Commands: Deep Dive for Network Troubleshooting is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Cisco Debug vs Show Commands: Deep Dive for Network Troubleshooting [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Cisco-Debug-vs-Show-Commands-Deep-Dive-for-Network-Troubleshootingnetworkjourney.png)
![OSPF Area Types Explained: Stub, Totally Stubby & NSSA with CLI, Lab & Real-World Use Cases. [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/OSPF-Area-Types-Explained_Stub_Totally-Stubby_NSSA_networkjourney.png)
![[Day #28 Pyats Series] SNMP configuration consistency check using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/SNMP-configuration-consistency-check-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![Ticket#10 - NAT Overload Failure: Why Users Couldn't Access the Internet – A Real Fix [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/nj-blog-post-Ticket-10.jpg)