[Day 136] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Industrial Switch OT Security
Table of Contents
Introduction
Industrial switches (Cisco IE, Hirschmann, Moxa, Aruba Industrial, etc.) connect PLCs, HMIs, cameras, sensors and other OT gear. These devices rarely support modern endpoint management or 802.1X, are often safety-critical, and require non-disruptive security controls.
Cisco ISE becomes the control plane: it identifies OT devices (profiling), decides access (policy), and enforces segmentation (VLANs, dACLs, SGTs, CoA). This Article teaches you how to integrate industrial switches with ISE while preserving OT availability
Problem Statement
Real world OT constraints:
- Many OT devices lack supplicants (no 802.1X).
- Devices may use static IPs, use non-standard ports/protocols (Modbus, Profinet) and be intolerant to active scans.
- A misapplied CoA/port-shutdown can halt production.
- Switches come from different vendors with different CoA/attribute expectations.
- Teams need asset inventory, firmware tracking and safe quarantine workflows.
We need a repeatable, low-risk approach to authenticate and segment OT endpoints and provide visibility for SOC and OT ops teams.
Solution Overview (how Cisco ISE addresses the problem)
Key elements:
- Non-disruptive discovery & profiling: Combine passive probes (DHCP, SNMP, syslog, NetFlow, HTTP UA) and PIC templates to identify OT devices and extract model/firmware. Use multi-probe confidence to avoid false positives.
- Safe authentication policy: Default to MAB for OT devices, use MAC + profiling → map to Endpoint Identity Groups. Use 802.1X only where supported.
- Policy mapping & enforcement: Use Authorization Profiles to place devices into OT VLANs/dACLs or SGTs. Use CoA only where tested and safe (no port-shutdown for critical devices).
- Operational guardrails: Change control, pre-production testing, allow list / emergency fail-open, and staged rollout.
- Integration & automation: pxGrid to OT visibility tools (Cisco Cyber Vision, Nozomi, Forescout), SIEM alerts and automated quarantine orchestration.
Sample Lab Topology
Platform: VMware (ISE OVA) or EVE-NG for NAD images. Use snapshots.
Lab components (recommended):
- Cisco ISE PAN + PSN (Profiler enabled):
10.10.10.11 - Cisco IE switch (IOS-XE based) —
10.10.30.10(or simulate with Catalyst IOS XE) - DHCP server (Linux) —
10.10.20.10 - SNMP emulator / OT sim (snmpsim) —
10.10.40.10 - Syslog generator (Node-RED/logger) —
10.10.50.50 - Test client/IoT emulator (Linux) —
172.16.110.101 - Optional: OT visibility tool (Cyber Vision / Forescout) for pxGrid integration
Topology diagram:
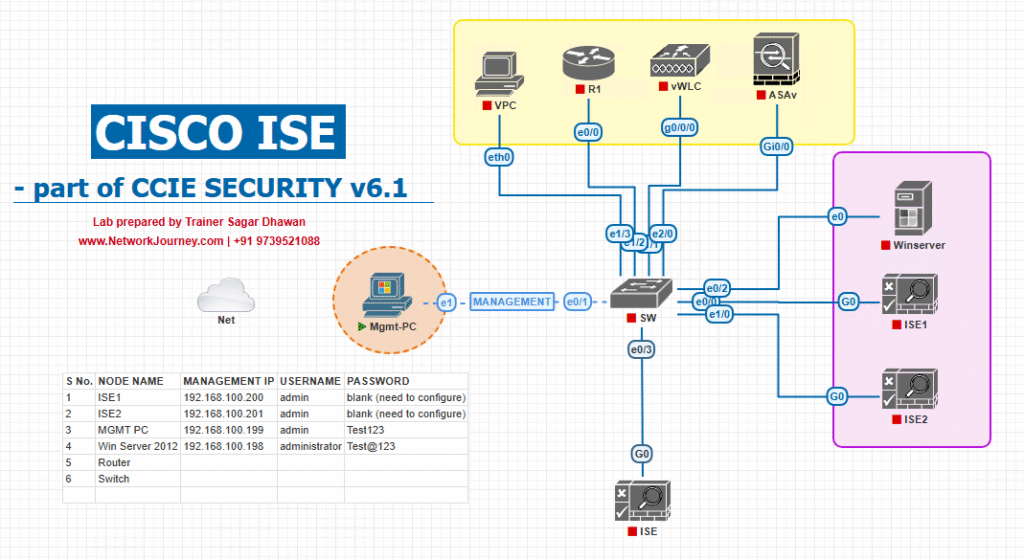
Lab notes: Use a test VLAN for staged rollouts. Do not run destructive tests against real OT hardware—use emulators or lab replicas.
Step-by-Step GUI Configuration Guide
(Complete ISE + sample Cisco IE CLI — with validation steps and screenshot placeholders)
High level plan:
- Add industrial switch to ISE as network device + enable CoA, SNMP;
- Create authentication policy (802.1X + MAB fallback) and authorization profiles for OT VLAN/quarantine;
- Configure switch for dot1x/MAB and RADIUS;
- Test profiling + enforcement and validate with CLI + packet capture.
A — ISE: Add industrial switch as Network Device
- ISE GUI → Administration > Network Resources > Network Devices > Add.
- Name:
IE-SW-1 - IP Address:
10.10.30.10 - Device Profile: choose Cisco Switch or custom profile (if available, choose Cisco IE/Industrial profile).
- Shared Secret:
ISE_SECRET - Enable Radius Authentication, Radius Accounting, and Dynamic Authorization (CoA) (tick any CoA-related boxes).
- Configure SNMP read (if you want SNMP probe or ISE to query the switch).
- [Screenshot: ISE Add Network Device — Network Device Dialog]
- Name:
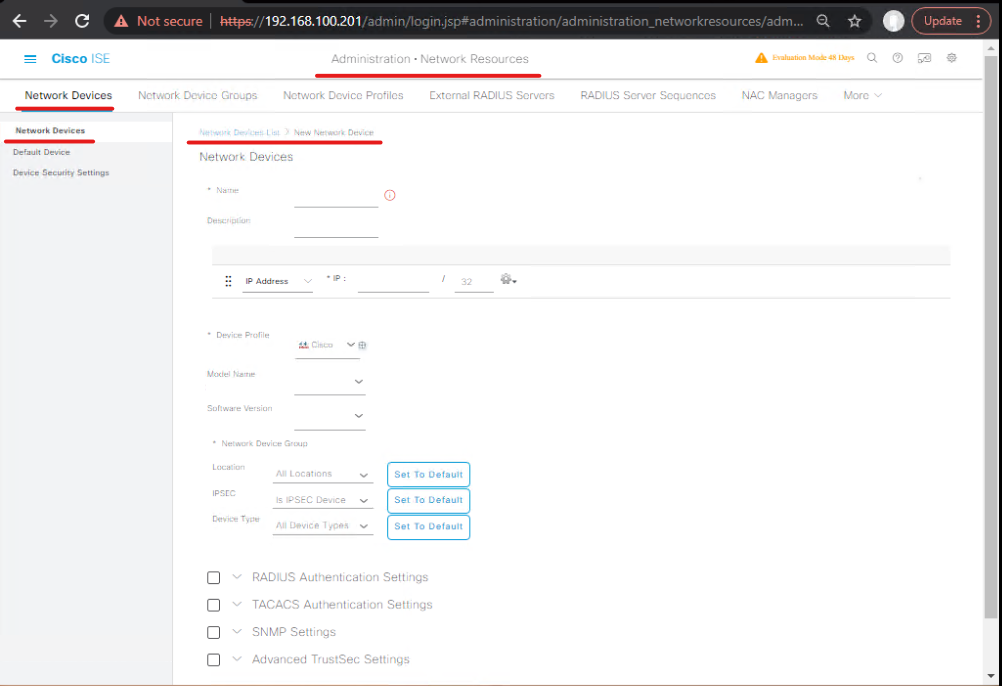
Validation (ISE GUI): After save, in Operations > Network Devices verify the device exists. Use the Test function (if present).
B — ISE: Add Network Device Group (recommended for policy management)
- Administration > Network Resources > Network Device Groups > Add
Industrial_Switchesand placeIE-SW-1into the group.- [Screenshot: ISE Network Device Group]
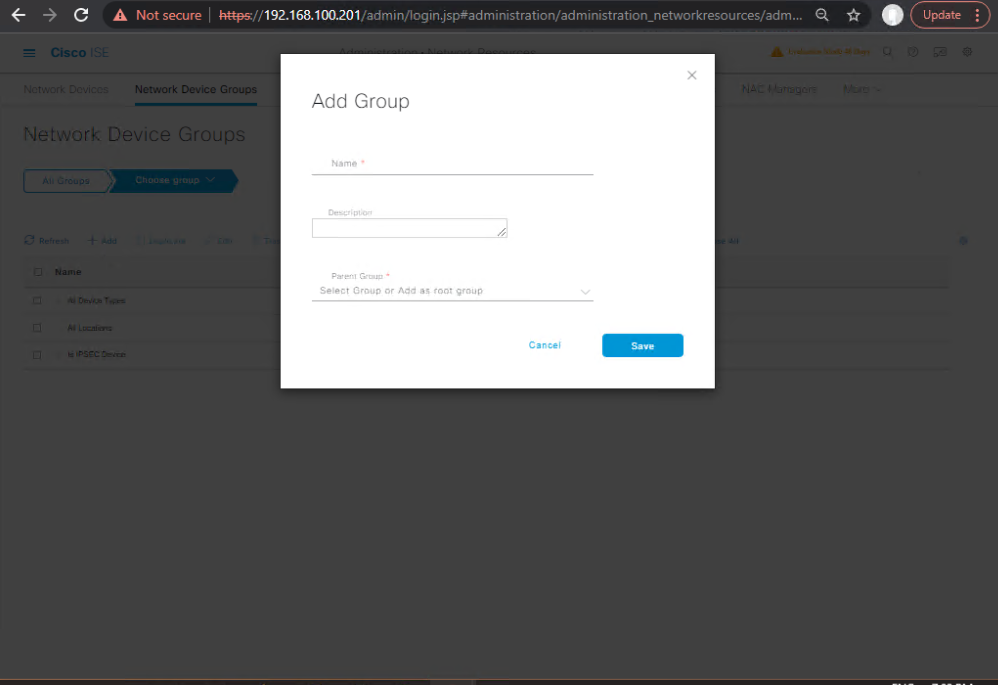
Why: Easier policy targeting (e.g., different authz for industrial switches).
C — ISE: Authentication Policy (802.1X + MAB fallback)
- ISE GUI → Policy > Policy Sets → Edit the policy set for your NAD/SSID.
- Authentication policy: add rule (top) to match the industrial switch group:
- Condition:
Network Device Group == Industrial_Switches - Allowed Protocols: EAP (e.g., PEAP/EAP-MSCHAPv2) and MAB fallback.
- For OT devices that do not do 802.1X, make MAB the fallback. Use order: dot1x then mab.
- [Screenshot: ISE Policy Set — Authentication Rules]
- Condition:
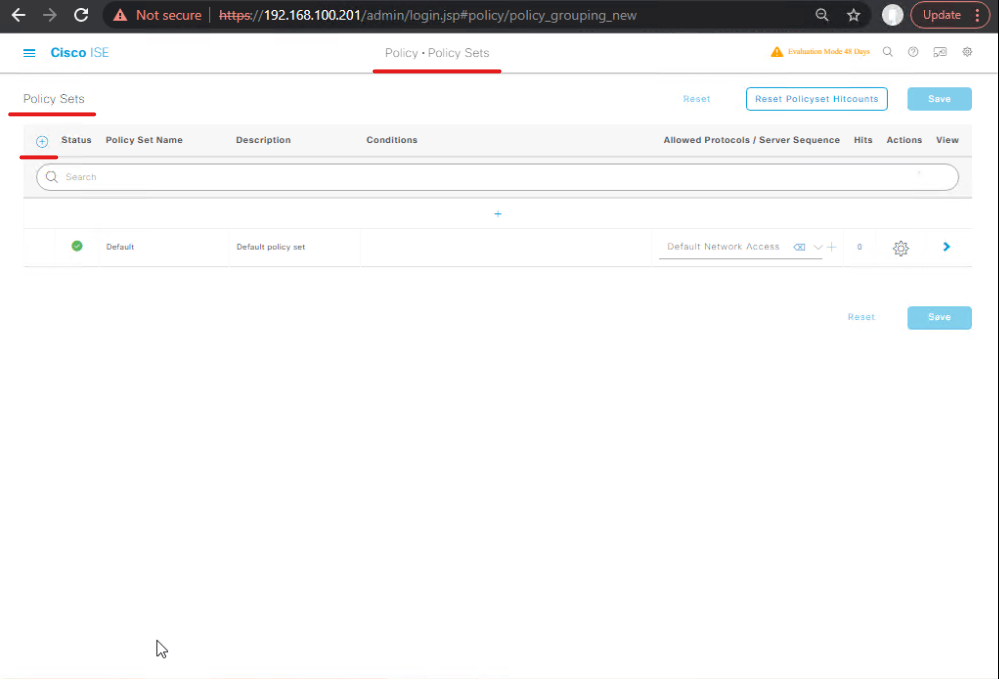
Validation (ISE): Test with a device that does 802.1X; you should see Access-Request and Accept/Reject in Operations > RADIUS > Live Logs.
D — ISE: Authorization Profiles for OT VLAN / Quarantine
- ISE GUI → Policy > Policy Elements > Results > Authorization > Authorization Profiles > Add.
OT_VLAN— Access Type =ACCESS_ACCEPT; set VLAN ID200or set SGT assignment if TrustSec used.OT_Quarantine—ACCESS_ACCEPT; VLAN 999 or dACL limiting traffic.Allow_Admin_Access— for management station; permit specific services.- [Screenshot: ISE Authorization Profile — OT_VLAN]
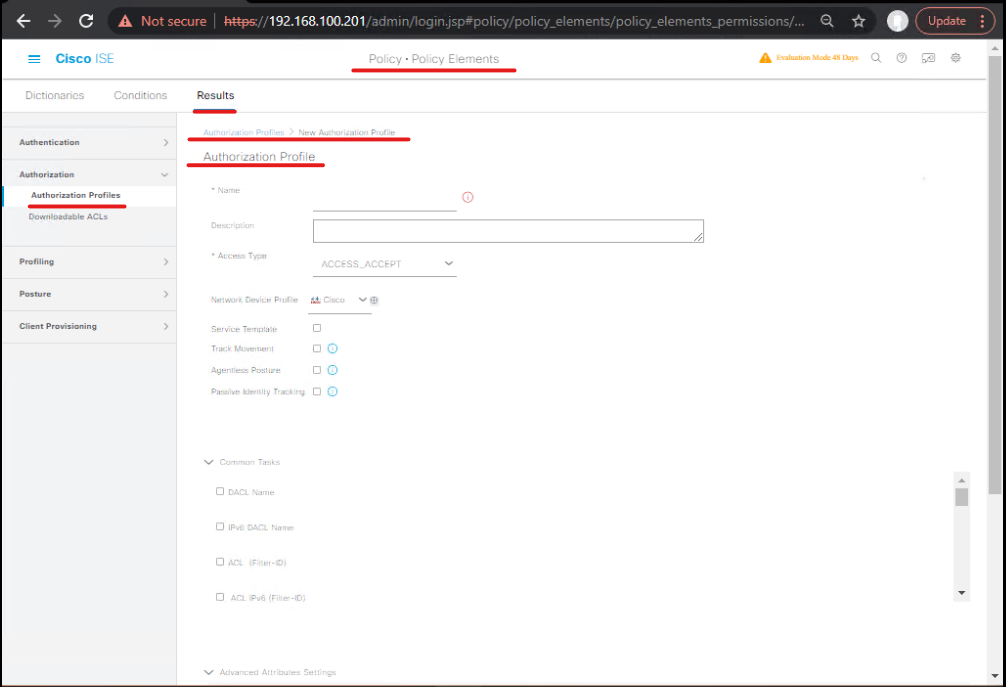
- Policy Set Authorization: Add rules:
- If
Endpoint Identity Group == OT/PLC→ applyOT_VLAN. - If
Endpoint Identity Group == UnknownandMAC not found→ applyOT_Quarantine(use with caution). - [Screenshot: ISE Policy Set — Authorization Rules]
- If
Validation (ISE GUI): Use Policy Testing if available or test live device and inspect Access-Accept attributes in Live Logs for VLAN assignment.
E — Cisco Industrial Ethernet switch sample CLI (IOS-XE style)
Important: these examples are for IOS-XE (Cisco IE 3000/4000). Adjust for vendor specifics and test in lab.
1) Configure RADIUS server:
configure terminal radius server ISE address ipv4 10.10.10.11 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key ISE_SECRET exit aaa new-model aaa group server radius ISE_GROUP server name ISE ! aaa authentication dot1x default group ISE_GROUP aaa authorization network default group ISE_GROUP aaa accounting update periodic 5 ip radius source-interface Loopback0
2) Enable 802.1X & MAB globally
dot1x system-auth-control authentication mac-move permit
3) Configure interface for OT device (Gi1/0/10)
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10 description PLC-Port switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 authentication host-mode multi-auth authentication order dot1x mab authentication priority dot1x mab mab dot1x pae authenticator spanning-tree portfast no shutdown
4) Configure CoA (RFC-3576) support (server must support dynamic auth)
# On IOS XE: configure the RADIUS server to accept dynamic auth radius server ISE address ipv4 10.10.10.11 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key ISE_SECRET # Some platforms require "aaa server radius dynamic-author" syntax aaa server radius dynamic-author server name ISE
(Exact syntax varies; consult switch vendor docs for RFC-3576 enable.)
Validation (switch CLI):
show radius serversorshow running-config | section radiusshow authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/10→ shows dot1x/MAB state and assigned VLANshow accountingandshow loggingfor RADIUS messages
F — Safe OT enforcement guidelines
- Start with monitor mode: on the switch enable logging to ISE but do not enforce VLAN change for first 7–14 days. Use ISE Live Logs and endpoint lists to confirm classification.
- Use soft quarantine first: apply limited dACLs to reduce blast radius (e.g., restrict to Syslog, SNMP to monitoring server) rather than cutting power or shutting port.
- Avoid port-shutdown or immediate reboots: never enable “port shutdown” CoA for critical OT without approvals.
- Define maintenance windows and rollback playbooks.
validation checklist (GUI + CLI + packet capture)
- ISE: Operations → RADIUS → Live Logs shows Access-Request/Access-Accept and Authorization Profile (VLAN ID or Filter-ID). Also inspect Profiler → Endpoints to ensure device is in expected Identity Group. [Screenshot: ISE Live Logs]
- Switch CLI:
show authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/10 details→ VLAN assignment and method (dot1x/mab). - Packet capture (capture on path between switch & ISE):
sudo tcpdump -i eth0 udp and \(port 1812 or port 1813 or port 3799\) -w radius_coa.pcapInspect Access-Request / Access-Accept and CoA (RADIUS code) in Wireshark.
Troubleshooting & Diagnostics
Follow a repeatable triage: (A) Authentication path, (B) Profiling & identification, (C) Enforcement.
A — Authentication path checks
- RADIUS reachability & secrets
- On switch:
show radius statistics/show running-config | include radius - On ISE: Operations > Network Resources → find device, use Test RADIUS (if available).
- On switch:
- Authentication debug (lab only, with caution):
- Switch:
debug aaa authenticationordebug dot1x all(commands vary; debug carefully).
- Switch:
- Live Logs: ISE → Operations > RADIUS > Live Logs — check Access-Request details and failure reason (bad credentials, unknown client, policy reject).
B — Profiling & identification
- If OT device is
Unknown: check probes (DHCP/SNMP/syslog) are enabled in ISE Profiler and that device sends expected telemetry. - Validate raw probe data via
tcpdumpand Operations > Profiler > Probe Activity. - Force a Rescan on the endpoint in ISE: Operations > Profiler > Endpoints → Select → Rescan.
C — Enforcement problems
- If ISE sent Access-Accept with VLAN but switch didn’t apply it: check VLAN exists, switchtrust, and that the switch parsed RADIUS attributes correctly.
show running-config | include vlanshow authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/10 details
- For CoA failures: confirm RFC-3576 is enabled and UDP port (commonly 3799) open. Inspect CoA-NAK reasons in PCAP (Error-Cause attribute).
D — Common OT pitfalls & fixes
- Static IP devices (no DHCP): use SNMP or syslog-based profiling or map MAC OUIs to identity group.
- MAC cloning: use port-binding (switch port controls) and OUI+port correlation to detect clones.
- SNMP credential issues: test
snmpwalkfrom a management host. If SNMPv3, check auth/encryption settings.
Lab Walkthroughs with Validation
Walkthrough 1 — Onboard a PLC via MAB + Profiling → OT VLAN
- Connect PLC (or emulator) to port Gi1/0/10. Configure PLC to use DHCP or static MAC.
- Switch performs MAB (MAC authentication) → sends Access-Request to ISE.
- ISE uses profiling (DHCP Option 60 and HTTP UA) to identify PLC as
OT/PLCand returns Authorization ProfileOT_VLAN. - Switch applies VLAN 200. Validate on switch:
show authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/10shows VLAN 200. Confirm network reachability to allowed services only.
Artifacts to collect: ISE Live Log screenshot, show authentication sessions output, tcpdump of RADIUS.
Walkthrough 2 — Safe Quarantine by SOC Trigger (CoA)
- SOC detects suspicious flow from endpoint (pcap/sample). SOC system calls orchestration which uses pxGrid / ISE REST to mark endpoint for quarantine (set Identity Group
Quarantine). - ISE sends CoA to the switch to change VLAN or apply dACL (Action:
Disconnect / Port Bounceavoided for OT). - Validate switch CLI shows VLAN/dACL change and endpoint restricted. On ISE, Live Logs show CoA Sent/Ack.
Important: Use safe quarantine actions (restrict to monitoring servers and NTP only) rather than port down for OT devices.
Expert Level Use Cases (step-by-step mapping + validation)
- OT Zero Trust Micro-segmentation: Profile device → assign SGT (TrustSec) → use SGTs in firewall for micro segmentation between OT stacks. Validate SGT tags in switch and firewall flow logs.
- Firmware compliance automation: Extract firmware from HTTP UA/syslog → export inventory → feed to vulnerability scanner → initiate patch or compensating control. Validate exported CSV has
firmwarefield and matches actual device. - High-availability ISE + multi-vendor CoA: Deploy multiple PSNs and ensure NAD has the correct CoA reachability to each PSN. Validate CoA to the correct PSN that holds session state; avoid sending CoA to a VIP unless vendor supports session synchronization.
- OT safe-mode during maintenance: During maintenance window, switch ISE policies to monitor-only or apply a maintenance ACL. Validate by changing the policy and performing test authentication.
FAQs
Q1 — Is 802.1X recommended for industrial OT devices?
A: Only when devices support it and vendors guarantee no disruption. Many OT devices can’t do 802.1X — use MAB+profiling for those. If you use 802.1X, do staged testing and certificate management (EAP-TLS) planning.
Validation: On switch, show dot1x all and on ISE live logs check EAP flows.
Q2 — Is CoA safe for OT devices? Can it break them?
A: CoA can be disruptive. Avoid port-shutdown or immediate reboots. Prefer gentle actions: VLAN reassignment to quarantine VLAN that allows monitoring and management ports. Always test the CoA action on a lab replica of the device.
Validation: Use lab test: send a CoA that only changes VLAN and observe device behavior.
Q3 — How to handle static IP OT devices with no DHCP?
A: Use SNMP sysDescr/sysObjectID, netflow-based behavioral signatures, syslog, MAC OUI or port binding. Combine multiple signals (SNMP + NetFlow) for reliable mapping.
Validation: Confirm snmpwalk returns sysDescr and ISE profiler records it.
Q4 — What RADIUS attributes does Cisco IE expect for VLAN assignment?
A: Common attributes: Tunnel-Type, Tunnel-Medium-Type, Tunnel-Private-Group-ID or VLAN ID (depending on NAD). Cisco switches commonly understand VLAN ID returned in Access-Accept (e.g., Tunnel-Private-Group-ID). Validate in ISE by looking at the Access-Accept attributes in Live Logs.
Validation: Inspect Access-Accept in Wireshark from packet capture for Tunnel-Private-Group-ID or VLAN.
Q5 — How should we configure port security (sticky MAC) for OT ports?
A: Use conservative port security: limit maximum MACs to 1 or small number, use sticky MAC cautiously. On OT ports, prefer static MAC binding (in switch config) rather than aggressive automatic learning that could cause false locks.
Validation: show port-security interface Gi1/0/10 and test reconnect behavior.
Q6 — What probes are most useful for OT profiling?
A: SNMP, DHCP (Option 60), HTTP User-Agent, NetFlow, and syslog. For legacy devices, NetFlow patterns (e.g., consistent Modbus TCP 502 traffic) are often the best indicator.
Validation: Use Profiler Probe Activity and Endpoint attributes in ISE.
Q7 — How do I avoid false positives with MAC cloning attackers?
A: Combine MAC with port binding, OUI, behavior signatures and authentication history. Use anomaly detection and compare newly seen MAC on different ports to flag cloning.
Validation: Generate a test where same MAC appears on two ports — check ISE event and switch logs.
Q8 — How do we roll back if authorization breaks OT communication?
A: Have a documented rollback: revert ISE policy to monitor mode, or manually set port to original VLAN on switch. Use maintenance/standby VLAN and a maintenance user to reconfigure if automated actions misfire.
Validation: Confirm manual VLAN change restores connectivity.
Q9 — How to scale OT profiling across many industrial switches?
A: Use ISE Network Device Groups and templates, centralize SNMP creds, use pxGrid integration for third-party telemetry, and run capacity tests for PSNs. Maintain a profile change log and version control for regex/templates.
Validation: Run simulated device onboarding at scale in lab and monitor PSN CPU/memory.
Q10 — Which testing controls should be in change management for OT security changes?
A: Pre-prod validation, scheduled maintenance window, rollback procedure, stakeholder sign-off (OT engineers), and on-call contact list. Test on one cell before enterprise rollout.
Validation: Documented test logs, sign-off screenshots, and successful revert tests.
YouTube Link
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to my YouTube channel Network Journey and join my instructor-led classes for hands-on, real-world ISE experience
Closing Notes
- Safety first: OT environments require non-disruptive, staged changes. Start with monitor mode and use multi-probe profiling.
- Automation with caution: pxGrid/automation accelerate containment, but always provide OT ops manual override.
- Operationalize: export asset inventory, integrate with CMDB/SIEM, and keep profiles & templates tracked in version control.
- Teachability: Use replicas/emulators for demos and avoid running risky commands on production OT switches.
Upgrade Your Skills — Start Today
“For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to my YouTube channel Network Journey and join my instructor-led classes.”
Fast-Track to Cisco ISE Mastery Pro — 4-month instructor-led training. Real EVE-NG/VMware labpacks, weekly live debugging, deep OT & ISE labs. Reserve seats and get the Industrial Switch OT Security lab pack (topology + runbook): https://course.networkjourney.com/ccie-security/
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088



![[Day 48] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: BYOD Wireless Onboarding Overview](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-48-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-BYOD-Wireless-Onboarding-Overview.png)