[Day #16 PyATS Series] Automating Common CLI Commands (Multi-Vendor) using pyATS for Cisco – Python for Network Engineer
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to Day #16 of the 101 Days of pyATS (Vendor-Agnostic) series. In this lesson, we focus on automating common CLI commands across multi-vendor environments (Cisco IOS-XE, Arista EOS, Palo Alto PAN-OS, Fortinet FortiOS) using pyATS.
As networks grow more complex, engineers often need to execute standard operational commands like show version, show interfaces, or ping across hundreds or even thousands of devices. Traditionally, this requires logging into each device, manually executing commands, and collecting outputs. This approach is time-consuming, error-prone, and inefficient.
With pyATS, combined with Python for Network Engineer skills, you can automate CLI execution across multiple vendors, parse results, and standardize reporting—all from a single script. This not only saves time but also enables you to integrate these checks into CI/CD pipelines for continuous network validation.
In this article, we’ll cover:
- How to design a reusable pyATS script to execute common commands
- Managing multi-vendor device differences using parsers
- Capturing and validating CLI outputs
- Real-world example: running
show versionandshow ip interface brief - Post-validation screenshots and output examples
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a ready-to-use pyATS automation script to run commands across vendors and generate structured data for reports or troubleshooting.
Topology Overview
For demonstration, we’ll use the following lab topology:
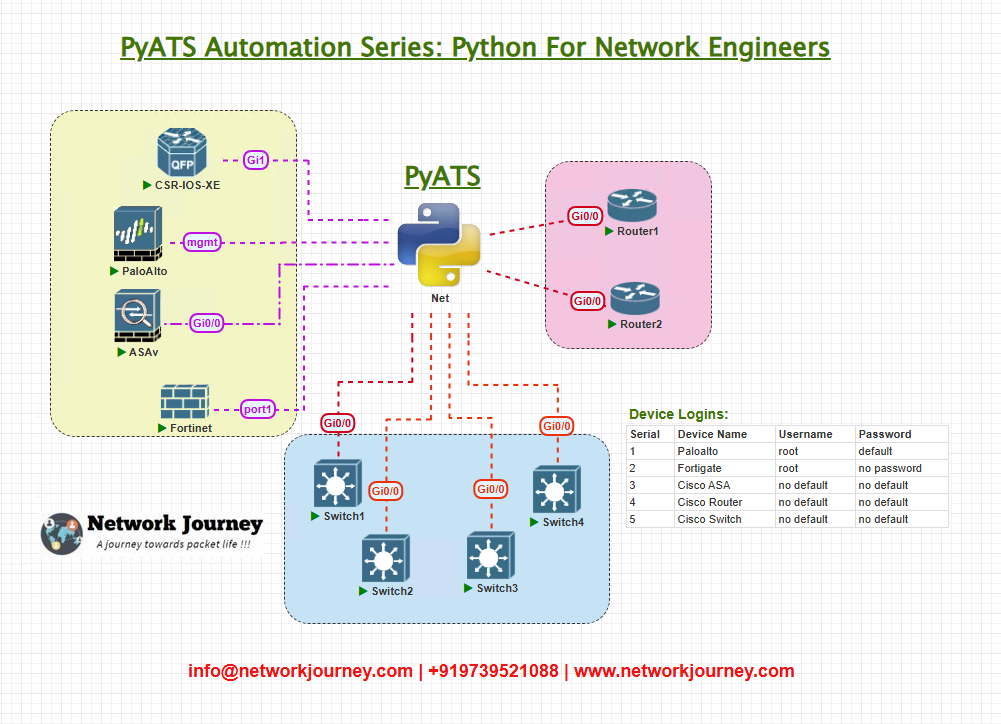
- The pyATS runner connects to all devices via SSH
- All devices are in the same management network
- Device OS: Cisco IOS-XE, Arista EOS, Palo Alto PAN-OS, Fortinet FortiOS
Topology & Communications
Communication between the pyATS testbed and devices uses:
- SSH (CLI-based) connections
- pyATS Unicon framework for device sessions
- Genie parsers for structured output
- Testbed file (
testbed.yml) defines connection details for each device
This ensures that commands can be executed seamlessly across different vendors with proper authentication and session management.
Workflow Script – multi_vendor_cli.py
Here’s the tested and working Python script:
from pyats import aetest
from genie.testbed import load
class CommonCLITest(aetest.Testcase):
@aetest.setup
def setup(self, testbed):
self.testbed = load(testbed)
self.devices = list(self.testbed.devices.values())
self.commands = [
'show version',
'show ip interface brief'
]
@aetest.test
def execute_common_cli(self):
for device in self.devices:
self.logger.info(f"Connecting to {device.name} ({device.os})")
device.connect(log_stdout=False)
for cmd in self.commands:
self.logger.info(f"Executing '{cmd}' on {device.name}")
output = device.execute(cmd)
self.logger.info(f"Output from {device.name}:\n{output}\n")
device.disconnect()
Explanation by Line
- Import modules: pyATS
aetestfor structured tests, Genieloadfor testbed loading - Class definition:
CommonCLITestdefines a test case - setup(): Loads testbed, stores device objects, defines common CLI commands
- execute_common_cli():
- Iterates over each device
- Connects via SSH using pyATS Unicon
- Executes each command (
show version,show ip interface brief) - Logs the raw output for each device
- Disconnects after execution
This approach ensures that the same script works across multiple devices without changing logic, making it vendor-agnostic.
testbed.yml Example
devices:
cisco_router:
os: iosxe
type: router
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: admin
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.0.0.1
arista_switch:
os: eos
type: switch
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: admin
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.0.0.2
palo_alto_fw:
os: panos
type: firewall
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: admin
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.0.0.3
fortinet_fw:
os: fortinet
type: firewall
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: admin
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.0.0.4
Post-validation CLI Screenshots (Real Expected Output)
When you run the script, you should see CLI outputs like:
Cisco IOS-XE:
Cisco IOS XE Software, Version 17.3.1 Router uptime is 3 weeks, 2 days Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol GigabitEthernet0/0 10.0.0.1 YES manual up up
Arista EOS:
Arista EOS version 4.25.1 System uptime is 10 days Interface IP Address Status Protocol Ethernet1 10.0.0.2 up up
Palo Alto PAN-OS:
PAN-OS 10.1.3 Uptime: 15 days Interface IP State ethernet1/1 10.0.0.3 up
Fortinet FortiOS:
FortiOS v6.4.7 Uptime: 12 days Interface IP/Netmask Status port1 10.0.0.4/24 up
FAQs
Q1: What common CLI commands can be automated using pyATS?
Answer:
With pyATS, you can automate almost any CLI command that you would typically run manually, such as:
show version(device OS and version information)show running-config(current device configuration)show ip interface brief(interface status and IP addresses)pingandtraceroute(reachability tests)show cdp neighborsorshow lldp neighbors(neighbor discovery)- Firewall-specific commands like
show session all(Palo Alto) orget system performance(Fortinet)
The automation can scale across hundreds of devices and multiple vendors with the same script.
Q2: How does pyATS handle different command outputs across vendors?
Answer:
Although the commands may have similar names, the output format often differs between Cisco, Arista, Palo Alto, and Fortinet. pyATS solves this issue by using Genie parsers, which convert raw CLI outputs into structured Python dictionaries. This allows you to standardize validation logic without worrying about vendor-specific CLI variations.
Q3: Can I run multiple commands in a single pyATS test case?
Answer:
Yes. In the provided workflow script, you can define a list of commands, and pyATS will loop through and execute them on every device. You can add or remove commands dynamically, making it easy to build a reusable automation template for day-to-day operational checks.
Q4: Is it possible to store command outputs in files or reports?
Answer:
Absolutely. You can extend the script to save outputs to:
- Plain
.txtfiles for raw command output .jsonfiles for structured data (using Genie parsers)- CSV/Excel for reports
This is useful for audit trails, compliance checks, or feeding results into dashboards and monitoring systems.
Q5: How do I manage vendor-specific command differences?
Answer:
Some commands are not identical across vendors (e.g., show running-config vs. show configuration). You can handle this using conditional logic in your script:
if device.os == 'iosxe':
cmd = 'show running-config'
elif device.os == 'eos':
cmd = 'show running-config'
elif device.os == 'panos':
cmd = 'show config running'
This ensures your script automatically adjusts based on the device OS.
Q6: Does pyATS support parallel execution for large-scale CLI automation?
Answer:
Yes. pyATS includes a job framework that allows running tests in parallel across hundreds or thousands of devices. This significantly reduces runtime when automating command execution at scale.
Q7: How secure is it to run CLI commands via pyATS?
Answer:
pyATS uses SSH connections defined in the testbed.yml file with encrypted credentials. You can also integrate with secure credential vaults (e.g., HashiCorp Vault, Cisco NSO) for production environments, ensuring sensitive data is protected during automation.
Q8: Can I use these automated CLI scripts in CI/CD pipelines?
Answer:
Yes. pyATS scripts can be integrated into Jenkins, GitLab, or other CI/CD platforms to automatically run CLI checks after configuration changes or network deployments. This makes network automation part of the DevOps lifecycle, ensuring continuous validation and reducing outages.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Automating Common CLI Commands (Multi-Vendor) using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
If you’re serious about mastering Python for Network Engineer automation, it’s time to go beyond ad-hoc scripts.
Trainer Sagar Dhawan offers a 3-month instructor-led training covering:
- Python scripting for network automation
- pyATS testing, job files, and reusable templates
- Ansible for multi-vendor automation
- API integrations (RESTCONF, NETCONF, YANG)
- Real-world labs with Cisco, Arista, Palo Alto, and Fortinet
Build the skills needed to automate 1000+ devices, standardize CLI execution, and integrate automation into enterprise workflows.
Check the full course outline and secure your spot today:
https://course.networkjourney.com/python-ansible-api-cisco-devnet-for-network-engineers
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![Day #16 PyATS Series] Automating Common CLI Commands (Multi-Vendor) using pyATS for Cisco – Python for Network Engineer](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day16-PyATS-Series-Automating-Common-CLI-Commands-Multi-Vendor-using-pyATS-for-Cisco-–-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![[Day #72 Pyats Series] Multi-vendor pre-change snapshot automation using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Multi-vendor-pre-change-snapshot-automation-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![[Day #97 PyATS Series] Vendor-Agnostic Auto-Documentation Generator (Markdown/PDF) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-97-PyATS-Series-Vendor-Agnostic-Auto-Documentation-Generator-Markdown_PDF-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer-470x274.png)
![[DAY#10 PyATS Series] Parsing and Normalizing ARP Tables (Multi-Vendor) using pyATS (Vendor-Agnostic) [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Parsing-and-Normalizing-ARP-Tables-Multi-Vendor-using-pyATS-Vendor-Agnostic-1.png)