[Day 22] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: MAB (MAC Authentication Bypass) Configuration
Table of Contents
Introduction
MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) lets network devices authenticate endpoints by their MAC address when 802.1X fails or isn’t possible (non-802.1X devices such as printers, IP phones, cameras, unmanaged endpoints). In Cisco ISE deployments, MAB is commonly used as a fallback to 802.1X or as the primary method for legacy devices. Proper MAB configuration in tandem with ISE policies gives you predictable VLAN assignment, role-based access, and a way to quarantine unknown devices — but it needs careful policy design and validation to avoid security gaps (MAC spoofing, misclassification).
Problem statement (what this solves)
Real networks contain many devices that cannot do 802.1X (printers, badge readers, cameras). Without a secure fallback you either:
- Blanket allow these devices on production VLANs (bad), or
- Block them completely (operational issues).
MAB + ISE lets you: detect device MACs, check ISE endpoint database or profiling information, and then map each device to a targeted authorization result (VLAN, dACL, redirect to remediation, or guest). This gives operational access while retaining centralized policy control and logging.
Solution overview (how ISE solves it)
- Network Device (switch/WLC) sends RADIUS Access-Request with username set to MAC.
- ISE authenticates the MAC against an Endpoint identity store (Internal Endpoints or external DB) or uses profiling to decide.
- ISE returns an Authorization Profile (Access-Accept) containing attributes (VLAN, ACL, dACL, downloadable ACL, CoA target) which the NAD applies.
- Live logs + session views let you validate every step.
Sample lab topology
Text topology (keep it simple for VMware/EVE-NG):
- ISE VM (ISE1) — running on VMware or EVE-NG VM (2 vCPU/8–16GB for lab)
- Switch (Catalyst 9k/3850/3650) — L2 switch acting as NAD (RADIUS client)
- WLC (optional) — for wireless MAB tests (optional)
- DHCP Server — for endpoints to get IPs (could be a Windows/Linux VM)
- Endpoint(s) — PC (802.1X capable), IP camera / printer (non-802.1X)
- Admin PC — used to access ISE GUI and Switch console
Topology Layout:
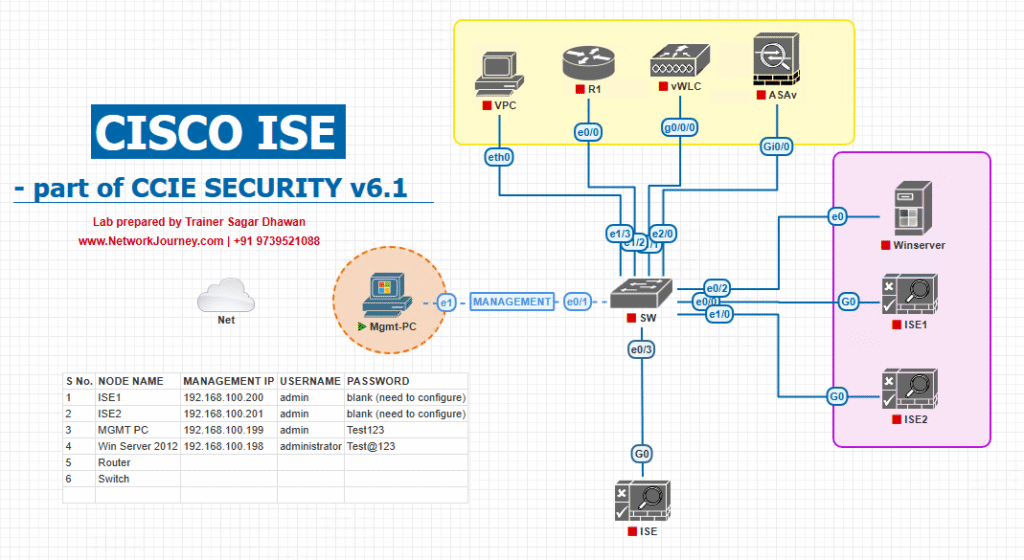
Notes:
- Lab environment: ISE VM on VMware Workstation/ESXi or EVE-NG. Switch can be virtual (CML/IOSvL2) or physical.
- If testing wireless MAB, add WLC between APs and ISE (WLC as RADIUS client).
Step-by-Step GUI Configuration Guide (ISE)
Important prechecks: ISE has correct time (NTP), server certificate trusted by NAD (or use shared secret in lab), and licensing allows MAB (MAB uses Network Access licensing). Also make sure ISE node is reachable from NAD and firewall permits UDP 1812/1813.
A — Add Network Device (Switch / WLC) in ISE
- Login to ISE GUI → Administration > Network Resources > Network Devices.
[Screenshot: ISE Network Device List]
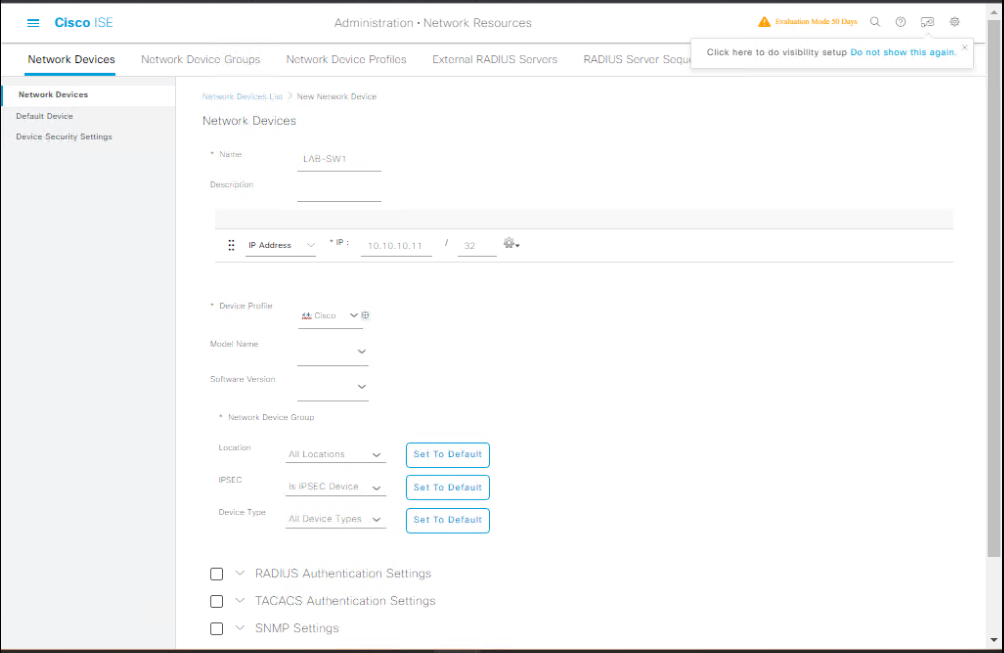
- Click Add. Fill fields:
- Name: LAB-SW1
- IP Address: 10.10.10.11 (NAD IP)
- Shared Secret:
MabSecret123(this must match on switch) - Device Type / Location: (optional)
- SNMP settings: (optional for profiling)
[Screenshot: ISE Add Network Device]
- Save.
B — Add known endpoints (optional but recommended)
- ISE: Administration > Identity Management > Identities > Endpoints > Add.
[Screenshot: ISE Add Endpoint]
- Add endpoint by MAC (format
00:11:22:33:44:55). Assign Endpoint Identity Group (e.g.,Printers,Cameras,Unknown). - Save.
Why: Known endpoints (pre-populated MACs) allow ISE to immediately match and authorize appropriately. For unknown MACs you can map to a guest/quarantine policy.
C — Create Authorization Profiles (ISE)
- Policy > Policy Elements > Results > Authorization > Authorization Profiles > Add.
[Screenshot: Add Authorization Profile]
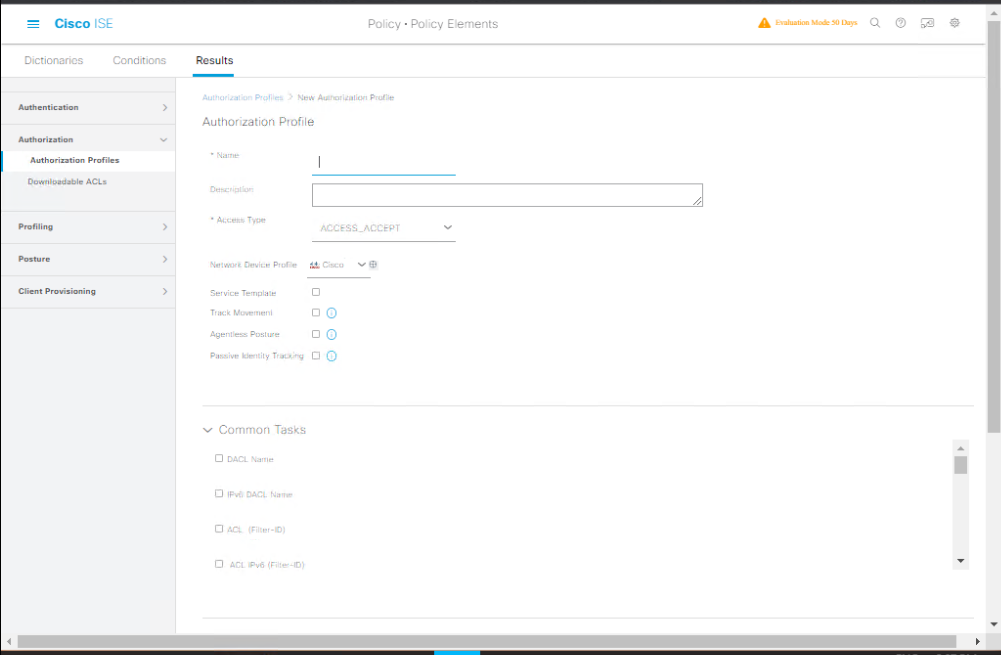
- Create profiles you need:
- MAB-Allow-VLAN100
- Common Tasks → Access Type: Permit
- Common Tasks → Use VLAN: enable → VLAN ID: 100
- (Optional) dACL / Filter-ID to limit traffic.
- MAB-Guest-Quarantine
- Redirect to captive portal or assign quarantine VLAN.
- MAB-Allow-VLAN100
- Save.
D — Create Policy Set (Authentication & Authorization)
- Policy > Policy Sets. Either update the Default policy set or create a new policy set for lab (recommended).
[Screenshot: Policy Sets]
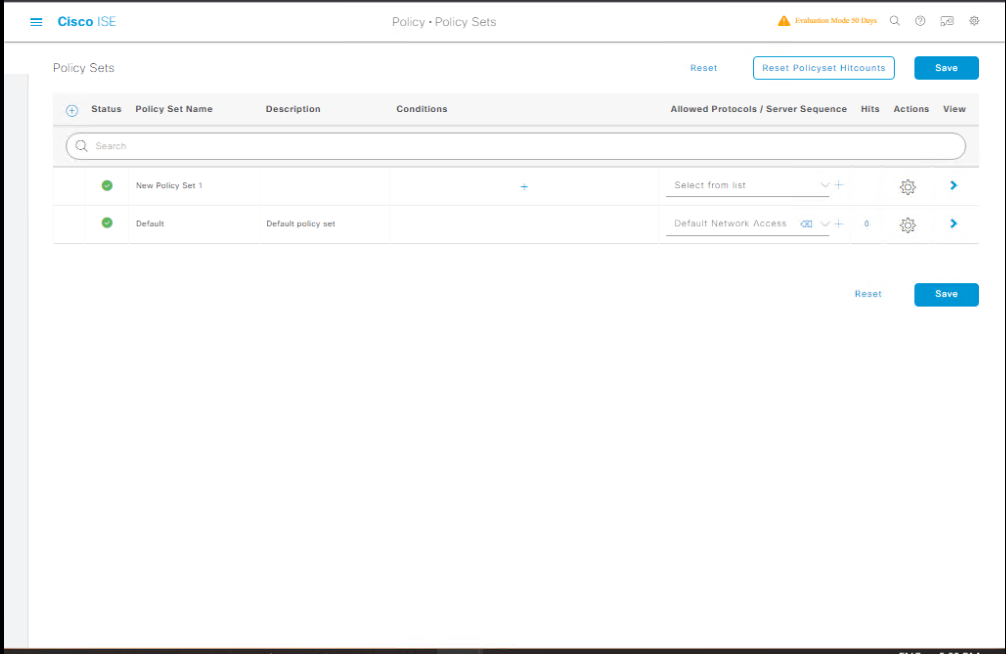
- Add Condition to match NAD(s): e.g., If NAD IP equals 10.10.10.11 or If NAD identity is LAB-SW1. This lets you control policies per device/location.
- Under the selected Policy Set:
- Authentication Policy:
- Add rule: If Protocol = MAB (or if
Identity Sourceis MAC Address) → Then use Internal Endpoints as the Identity Source (so ISE matches MAC entries).
[Screenshot: Policy Set > Authentication Policy: Add MAB rule]
- Add rule: If Protocol = MAB (or if
- Authentication Policy:
- Fallback: If not found in Internal Endpoints → use Guest or Profiling method.
- Authorization Policy:
- Add rule: If Endpoint:IdentityGroup ==
Printers→ Then Authorization Profile =MAB-Allow-VLAN100. - Add rule: If Endpoint:IdentityGroup ==
Unknown→MAB-Guest-Quarantine.
[Screenshot: Policy Set > Authorization Policy: Add rules]
- Add rule: If Endpoint:IdentityGroup ==
- Save and test.
Tip: Keep authZ rules order tight — put explicit known device rules above generic rules.
E — Switch configuration (Catalyst IOS example)
Global configuration
enable configure terminal ! Radius server (old IOS style) radius-server host 10.10.10.20 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key MabSecret123 aaa new-model aaa authentication dot1x default group radius aaa authorization network default group radius ! Enable dot1x globally (works with MAB fallback) dot1x system-auth-control end
Interface configuration (access port — example Gi1/0/1)
configure terminal interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 description LAB - PC / Printer switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 spanning-tree portfast authentication host-mode single-host authentication port-control auto authentication order dot1x mab ! Alternatively, on some IOS versions: ! authentication priority dot1x mab mab dot1x pae authenticator exit end write memory
Notes about authentication order vs authentication priority:
authentication order dot1x maborauthentication priority dot1x mabdepends on IOS version. If one cmd errors, try the other.mabalone enables MAC auth fallback.
F — Wireless (WLC) MAB outline (optional)
- On WLC: Security > RADIUS > Authentication Servers → add ISE (10.10.10.20) with same shared secret.
- On WLAN → Security → Layer 2 → set to Open or Layer 2/MAC Auth depending on controller. Configure MAC authentication/filtering to point to RADIUS server.
- In ISE, add WLC as Network Device (same as switch) and use Policy Sets to treat wireless MAB requests (you can match
Called-StationorSSID).
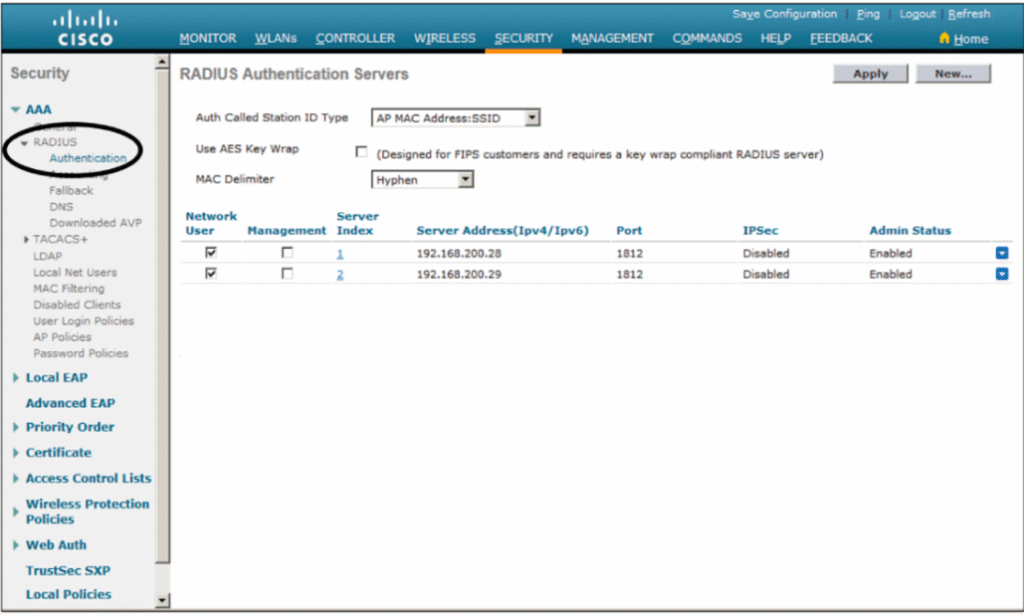
(WLC GUIs differ by version — adapt accordingly.)
G — Validation (GUI + CLI) — do this step by step
1) ISE Live Logs validation (GUI)
- In ISE GUI: Operations > RADIUS > Live Logs (or Operations > SLA depending on version).
[Screenshot: ISE Live Logs]
- Filter for your NAD or the endpoint MAC. You should see:
- Access-Request from NAD containing Username =
001122334455(MAC) - ISE decision: Authentication: MAB → Identity Source = Internal Endpoints (or Profiler)
- ISE Authorization response: Access-Accept with attributes (e.g., Tunnel-Private-Group-ID: 100 or Filter-ID).
- Access-Request from NAD containing Username =
What to look for: If ISE returns Access-Reject, the RADIUS shared secret or NAD match may be wrong. If ISE authenticates but no VLAN change occurs, check Authorization Profile attributes.
2) Switch CLI validation
Run:
show authentication sessions interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 details
Expected snippet (example):
Interface: Gi1/0/1 MAC Address: 00:11:22:33:44:55 Method: mab Auth State: AUTHORIZED Authorized VLAN: 100 Authentication Server: ISE1 (10.10.10.20)
If the device is 802.1X then method may show dot1x. If MAB used, method should show mab.
Useful debug commands:
debug radius authentication debug dot1x all debug aaa authentication show radius statistics show running-config | section radius
Interpretation: Debugs show RADIUS Access-Request/Response and any errors (timeout, shared secret mismatch, attribute missing).
3) DHCP / IP test
- Confirm the endpoint gets IP on assigned VLAN (if ISE assigned VLAN).
- From switch,
show mac address-table interface gi1/0/1to see learned MAC.
4) ISE endpoint database verification
- In ISE: Administration > Identity Management > Identities > Endpoints → search the MAC → verify endpoint group and attributes.
FAQs
1. What is an Identity Source Sequence in Cisco ISE?
An Identity Source Sequence is a logical list of identity stores (like AD, LDAP, Internal DB, or certificate-based repositories) that Cisco ISE checks in a specific order during authentication. It allows fallback to alternative sources if the primary source is unreachable or doesn’t have the user/device.
2. Why should I use an ISS instead of pointing directly to one identity source?
If you directly point to AD and AD goes down, authentication will fail entirely. An ISS ensures that if AD is unavailable, ISE will automatically try the next source, such as Internal Users or Internal Endpoints, reducing downtime.
3. Can I mix internal and external sources in the same ISS?
Yes. For example:
- Primary: Active Directory
- Secondary: Internal Users (for guest accounts)
- Tertiary: Internal Endpoints (for MAB)
This is the most common deployment strategy.
4. What happens if a user exists in multiple sources in the ISS?
ISE stops checking as soon as it finds a matching identity, provided the “Stop if found” option is enabled. If not enabled, it will check all sources and use the first match in priority order.
5. Does the order of sources affect authentication speed?
Yes. If the first source is slow to respond or unreachable, authentication delays occur until ISE times out before moving to the next source. Best practice: put the most frequently used and fastest sources first.
6. Can ISS be used for both wired and wireless 802.1X authentication?
Absolutely. ISS is independent of the access type. You can apply it to any authentication policy in ISE, including wired, wireless, and VPN authentications.
7. How do I troubleshoot when ISS is not working as expected?
- Check RADIUS Live Logs in ISE for the “Identity Source” column.
- Enable
debug radius authenticationon the switch/WLC. - Verify that the external source (like AD) is reachable via System → Logging → Test Connectivity.
8. Can ISS be used for MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB)?
Yes. For MAB, you can use ISS where the primary source is the Internal Endpoints database, with fallback to other sources if the MAC address is not found.
9. What’s the difference between an ISS and multiple separate authentication rules?
Multiple authentication rules can reference different sources, but that approach is less flexible and requires more policy maintenance. ISS lets you have one policy rule that can query multiple sources in a controlled order.
10. What is the best practice order for ISS in enterprise deployments?
- First: AD (for corporate users)
- Second: Internal Users (for guest/fallback accounts)
- Third: Internal Endpoints (for IoT/MAB devices)
- Avoid placing rarely-used or slow sources first to minimize delays.
YouTube Link
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to my YouTube channel Network Journey and join my instructor-led classes for hands-on, real-world ISE experience
Closing notes / Key takeaways
- MAB is a practical fallback and must be used carefully with policies to avoid security gaps.
- Always validate both sides: ISE Live Logs and NAD CLI (
show authentication sessions). - Use endpoint groups in ISE to create precise authorization outcomes (VLANs, dACLs).
- Combine MAB with profiling, port security, and logging to mitigate MAC spoofing risks.
Upgrade Your Skills – Start Today
If you want to master Cisco ISE (complete, hands-on workflows — GUI + CLI + troubleshooting), join 4-month instructor-led CCIE Security / ISE training — live classes, 100+ hours of lab training, real-world lab scenarios and recorded resources. The full course outline, hands-on lab details and registration are on Network Journey’s CCIE Security course page. (Network Journey)
- Want end-to-end, lab-based Cisco ISE mastery (GUI + CLI + real troubleshooting)? Join 4-month instructor-led CCIE Security program — live sessions, 100+ hours of labs, workbook, and 1:1 doubt support.
- Apply / Book a free counselling call: tell us your name, role, years of experience, preferred batch (weekday/weekend) and best contact number — send to info@networkjourney.com or WhatsApp +91 97395 21088 and the team will schedule your call. (Network Journey)
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day 22] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: MAB (MAC Authentication Bypass) Configuration](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-22-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-MAB-MAC-Authentication-Bypass-Configuration.png)
![[Day 14] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Setting Up a Test Switch for Authentication](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-14-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Setting-Up-a-Test-Switch-for-Authentication.png)

