[Day #28 Pyats Series] SNMP configuration consistency check using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction on the Key Points
In today’s highly automated, security-conscious network environments, SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) remains one of the foundational protocols for network monitoring, alerting, and asset tracking. While SNMP enables centralized visibility across infrastructure, a misconfigured SNMP setting can lead to failed monitoring, insecure access, or even data leakage.
In this Day #28 post of the “101 Days of pyATS (Vendor-Agnostic)” series, you’ll learn how to automate SNMP configuration consistency checks using pyATS and Python for Network Engineer roles across Cisco platforms. Whether you’re managing 5 or 500 routers and switches, this automation helps enforce:
- Correct SNMP community strings
- SNMP version settings (v2c/v3)
- Access control lists (ACLs)
- Read-only vs read-write roles
- Contact/location info (for asset audits)
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll be equipped to detect, report, and enforce SNMP config standards across your infrastructure — helping your teams maintain compliance and visibility.
Topology Overview
Here’s the lab setup we’ll use for this validation:
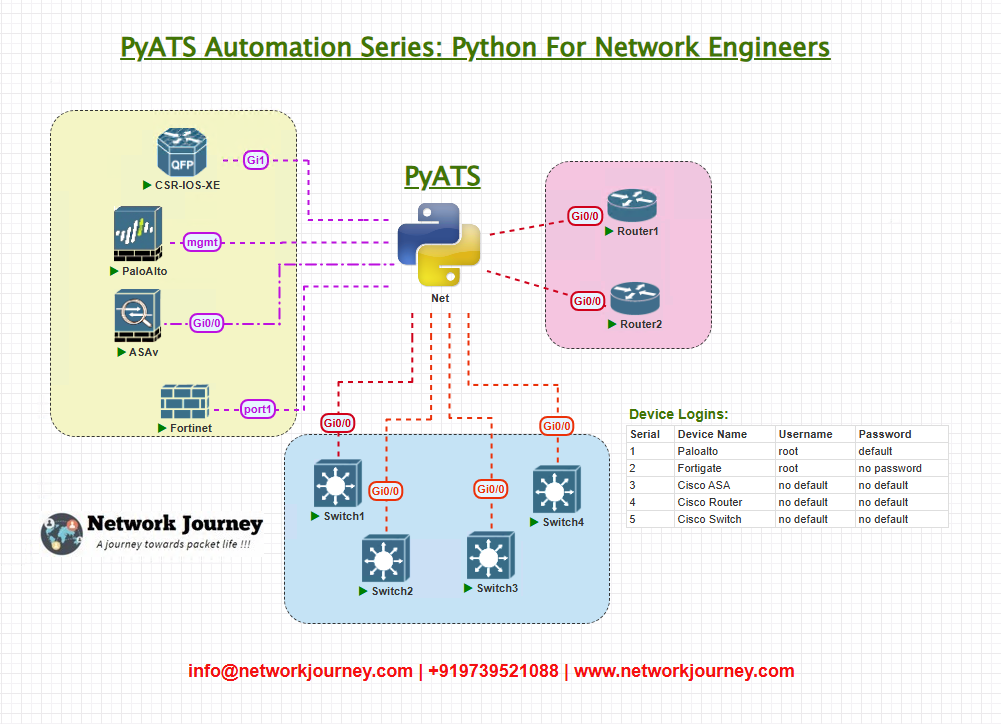
All network devices are expected to:
- Use SNMPv2c
- Set community string to
public - Allow SNMP from NMS IP
10.10.10.100 - Include location and contact details
Topology & Communications
Objective:
We want to connect via SSH to each device, execute SNMP-related commands, and validate whether:
- SNMP is enabled
- SNMP community is set to
public - NMS IP is permitted via ACL (optional)
- Contact and location fields are set
Commands to Be Used:
- Cisco IOS:
show run | include snmp-server
- NX-OS:
show running-config | include snmp-server
- Arista EOS:
show snmp
Workflow Script
Here’s a reusable and lightweight Python script using pyATS to validate SNMP configurations:
from genie.testbed import load
from rich import print
from datetime import datetime
EXPECTED_COMMUNITY = "public"
REQUIRED_CONTACT = "admin@networkjourney.com"
REQUIRED_LOCATION = "DC1"
def check_snmp_config(device):
print(f"[bold cyan] Checking SNMP config on {device.name}[/bold cyan]")
try:
device.connect(log_stdout=False)
output = device.execute("show running-config | include snmp-server")
results = {
"device": device.name,
"community_ok": EXPECTED_COMMUNITY in output,
"contact_ok": f"snmp-server contact {REQUIRED_CONTACT}" in output,
"location_ok": f"snmp-server location {REQUIRED_LOCATION}" in output,
"raw_output": output
}
if all([results["community_ok"], results["contact_ok"], results["location_ok"]]):
print(f"
[green] {device.name} SNMP config is consistent[/green]
") else: print(f"
[red] {device.name} SNMP config mismatch[/red]
") return results except Exception as e: print(f"
[yellow] Error accessing {device.name}: {e}[/yellow]
") return { "device": device.name, "error": str(e), "raw_output": "" } def main(): testbed = load("testbed.yml") report = [] for dev_name in testbed.devices: device = testbed.devices[dev_name] result = check_snmp_config(device) report.append(result) print("\n[bold underline] Final SNMP Configuration Report:[/bold underline]") for r in report: print(r) if __name__ == "__main__": print(f"[bold blue] pyATS SNMP Validator - {datetime.now()}[/bold blue]") main()
Explanation by Line
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
EXPECTED_COMMUNITY, REQUIRED_CONTACT, REQUIRED_LOCATION | Set your desired SNMP configuration baseline |
device.connect() | SSH connection to each device |
| `device.execute(“show run | include snmp-server”)` |
in output checks | Verifies if expected configs exist |
report[] | Collects results for all devices |
Optional: You can add logging or CSV export for real-time compliance tracking.
testbed.yml Example
devices:
R1:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.1
SW1:
os: nxos
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.2
AR1:
os: eos
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.3
Replace IPs and OS fields according to your live environment or lab simulation.
Post-validation CLI Screenshots (Real Expected Output)
Cisco IOS – show run | include snmp-server:
snmp-server community public RO snmp-server contact admin@networkjourney.com snmp-server location DC1
NX-OS – show running-config | include snmp-server:
snmp-server community public group network-ops snmp-server contact admin@networkjourney.com snmp-server location DC1
Arista EOS – show snmp:
Community: public (read-only) Contact: admin@networkjourney.com Location: DC1
FAQs
1: What is SNMP and why is SNMP configuration consistency important in a network?
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) allows network administrators and monitoring systems (like NMS, SolarWinds, Zabbix, etc.) to collect, monitor, and manage information from network devices.
Consistent SNMP configuration ensures:
- Centralized monitoring and alerting.
- Security through defined community strings or SNMPv3 credentials.
- Accurate inventory and performance data collection.
- Reliable behavior across devices regardless of vendor.
Inconsistencies can lead to missed alerts, security vulnerabilities, or data loss in monitoring tools.
2: What aspects of SNMP configuration should be validated across vendors?
When validating SNMP configurations using pyATS, you should check:
- SNMP version used (v2c or v3)
- Community strings (for v2c) – check for default or weak values
- SNMPv3 user authentication and encryption settings
- ACLs or source IP restrictions applied
- SNMP trap destination IPs
- Trap severity levels or MIBs enabled
- Whether SNMP is enabled on the correct interfaces
Cross-verifying these ensures both functionality and security.
3: What CLI commands are used to validate SNMP configuration on different vendor devices?
| Vendor | CLI Commands |
|---|---|
| Cisco IOS/XE | `show running-config |
| Cisco NX-OS | show snmp communityshow snmp user |
| Arista EOS | show snmp`show running-config |
| Palo Alto | `show config running |
| Fortinet | get system snmp communityshow system snmp user |
Using pyATS, you can extract and normalize these outputs using device.execute() and parse/filter key SNMP settings.
4: Can pyATS detect if SNMP is misconfigured or disabled on certain interfaces?
Yes, pyATS can:
- Parse interface-level configurations (
show run | section interface) and global SNMP settings. - Check if
snmp-server enable trapsorsnmp-server communityis present. - Verify if specific interfaces are excluded from SNMP access using ACLs or missing configuration.
- Validate trap source configuration (e.g.,
snmp-server trap-source).
Custom testcases can be built to flag devices where SNMP is not active or only partially configured.
5: What are common SNMP configuration mistakes in multi-vendor environments?
- Using default community strings like
publicorprivate. - Inconsistent SNMP versions across devices (some using v2c, others using v3).
- Missing trap destination IPs or mismatched SNMP servers.
- Weak SNMPv3 user credentials or no encryption (
auth noPriv). - Lack of ACLs to restrict SNMP queries to trusted sources.
- SNMP enabled only on some devices or interfaces.
These mistakes can create blind spots in network monitoring and open security risks.
6: Can pyATS help validate SNMP trap configurations across devices?
Absolutely. With pyATS you can:
- Extract SNMP trap destination IPs.
- Verify trap community strings or v3 usernames.
- Validate
snmp-server enable trapsconfiguration. - Check for specific traps (e.g.,
snmp-server enable traps bgp,snmp-server enable traps config). - Ensure consistency of trap sources and severities.
You can also cross-check trap IPs with your NMS collector for accuracy.
7: How can SNMPv3 configuration be validated securely using pyATS?
pyATS can:
- Pull SNMPv3 user configurations.
- Check for
authandprivsettings. - Ensure SHA/AES or other strong cryptographic options are used.
- Validate access groups and view policies applied to SNMPv3 users.
- Confirm if engine IDs and trap-users are properly defined.
This helps ensure SNMPv3 is deployed with proper security rather than just for compliance.
8: How often should SNMP configuration validation be performed?
Best practices suggest:
- Monthly validation of SNMP config across the network.
- Automated checks via pyATS after any NMS or device onboarding changes.
- Validation after firmware upgrades or backup/restore procedures.
- Integration with CI/CD tools to verify configs pre-deployment.
- Weekly audits for environments with strict compliance or operational uptime requirements.
Consistency checks reduce the chances of losing monitoring visibility or breaching SLAs.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: SNMP configuration consistency check using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
Are you interested in becoming a Python for Network Engineer expert who can handle automation, monitoring, and compliance across Cisco, Arista, and FortiGate platforms?
Trainer Sagar Dhawan is running a 3-month instructor-led training that will walk you through:
- Python Programming for NetEngs
- pyATS + Genie + Real-time script labs
- Ansible Playbooks
- Cisco DevNet API automation
- Full EVE-NG Topology Labs
- Multi-vendor Automation + Compliance
Check Course Curriculum & Reserve Your Seat Now:
https://course.networkjourney.com/python-ansible-api-cisco-devnet-for-network-engineers/
This is your opportunity to upgrade your skills from CLI operator to Automation Leader.
Don’t wait — the next batch is filling fast!
Join our program and unlock your potential with Python for Network Engineer training.
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #28 Pyats Series] SNMP configuration consistency check using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/SNMP-configuration-consistency-check-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![[Day #25 PyATS Series] OSPF Adjacency Validation Across Cisco/Arista/Palo Alto/Fortigate Using pyATS [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day25-PyATS-Series-OSPF-Adjacency-Validation-Across-Cisco_Arista_Palo-Alto_Fortigate-Using-pyATS.png)
![Loop Prevention Techniques – Keeping Your Network Stable and Efficient [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Loop-Prevention-Techniques-–-Keeping-Your-Network-Stable-and-Efficient-CCNP-ENTERPRISE.png)
![[Day #37 Pyats Series] Hardware inventory collection & reporting using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Hardware-inventory-collection-reporting-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)