[Day #30 PyATS Series] Checking STP Root Bridge Across Cisco Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a fundamental Layer 2 protocol used to prevent loops in switched networks. One critical aspect of STP is determining the Root Bridge, which plays a central role in defining the active forwarding paths. Manually verifying STP root bridges across multiple switches can be time-consuming and error-prone.
In this tutorial, part of the 101 Days of pyATS (Vendor-Agnostic) series, we automate the process of identifying the STP root bridge across Cisco devices using pyATS. This post is written in the style of Trainer Sagar Dhawan, tailored for Python for Network Engineer learners. You’ll learn how to:
- Connect to multiple Cisco switches using pyATS
- Execute STP-related commands to identify the root bridge
- Validate consistency of root bridge selection across the network
- Generate structured reports for easy troubleshooting
By the end, you’ll have a repeatable, scalable solution that ensures STP stability and aids in proactive network maintenance.
Topology Overview
Our test environment includes three Cisco switches configured for STP:
- Switch1 (Candidate for root)
- Switch2
- Switch3
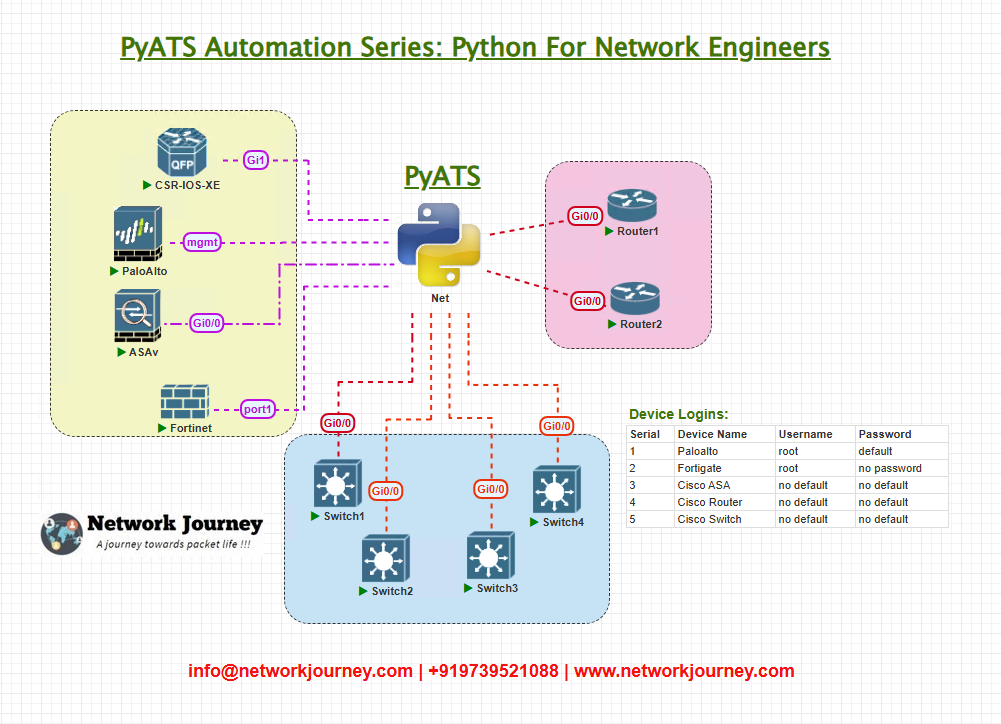
Objective: Verify which switch is the designated STP root bridge and ensure the correct device is serving as root according to network design.
Topology & Communications
- Protocol: STP BPDU-based root bridge election
- Authentication: Managed via
testbed.yml - Execution: CLI connections (SSH)
Steps:
- Connect to each switch
- Execute STP show commands
- Parse output to identify root bridge MAC and priority
- Compare results to the expected root bridge
Workflow Script
from genie.testbed import load
import json
def get_stp_root(device):
device.connect(log_stdout=False)
output = device.parse('show spanning-tree')
device.disconnect()
root_info = {}
for vlan, details in output['vlans'].items():
root_id = details['root_bridge']['address']
root_priority = details['root_bridge']['priority']
root_info[vlan] = {
'Root MAC': root_id,
'Root Priority': root_priority
}
return root_info
if __name__ == "__main__":
testbed = load('testbed.yml')
devices = testbed.devices
report = {}
for name, device in devices.items():
print(f"Checking STP root bridge from {name}...")
report[name] = get_stp_root(device)
with open('stp_root_report.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(report, f, indent=4)
print(json.dumps(report, indent=4))
Explanation by Line
- Imports: Load pyATS testbed and JSON for reporting.
- get_stp_root function:
- Connects to each switch.
- Parses STP details for all VLANs.
- Extracts root bridge MAC and priority.
- Main block:
- Iterates through devices.
- Collects root bridge info.
- Outputs JSON report.
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: stp_root_validation
devices:
Switch1:
os: iosxe
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.100.11
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: cisco123
Switch2:
os: iosxe
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.100.12
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: cisco123
Switch3:
os: iosxe
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.100.13
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: cisco123
Post-validation CLI Screenshots (Expected Output)
Switch1:
Switch1# show spanning-tree
VLAN0001
Root ID Priority 24577
Address 001a.2b3c.4d5e
This bridge is the root
Script Output:
{
"Switch1": {
"VLAN0001": {
"Root MAC": "001a.2b3c.4d5e",
"Root Priority": 24577
}
},
"Switch2": {
"VLAN0001": {
"Root MAC": "001a.2b3c.4d5e",
"Root Priority": 24577
}
},
"Switch3": {
"VLAN0001": {
"Root MAC": "001a.2b3c.4d5e",
"Root Priority": 24577
}
}
}
FAQs
1. How does this script determine the STP root bridge on Cisco switches?
The script connects to each switch, runs show spanning-tree, and parses the output using pyATS Genie parsers to identify the root MAC address and bridge priority for each VLAN.
2. Can I verify the root bridge across multiple VLANs simultaneously?
Yes. The script iterates through all VLANs in the STP output, ensuring you can validate root bridge information for every VLAN configured on the switches.
3. Does this solution support different STP modes like RSTP, PVST, and MST?
Yes. The Genie parser supports multiple STP modes. You can adapt the script to parse outputs from PVST, RSTP, and MST depending on your network configuration.
4. How can I detect if the wrong switch has become the root bridge?
You can define an expected root bridge MAC address in your script. If any switch reports a different root MAC, the script flags it as a mismatch.
5. Is it safe to run STP root bridge checks during production hours?
Yes. The script only executes read-only show commands and does not alter device configurations, making it safe for production networks.
6. Can the output be visualized in a dashboard for easier monitoring?
Absolutely. The generated JSON report can be integrated with dashboards such as Grafana, Kibana, or custom web applications for real-time monitoring.
7. How scalable is this approach for large switching environments?
pyATS supports parallel connections, allowing you to run the validation on dozens or hundreds of switches efficiently in a large-scale environment.
8. Can this script be adapted for non-Cisco devices?
Yes. With custom parsers or multi-vendor Genie support, this approach can be extended to Arista, Palo Alto, Fortinet, and other network vendors.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Checking STP Root Bridge Across Cisco Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
Automating STP root bridge validation is crucial for maintaining loop-free, resilient networks. Trainer Sagar Dhawan offers a 3-month instructor-led program on Python, Ansible, APIs, and Cisco DevNet for Network Engineers. Learn advanced network automation and testing techniques with hands-on labs.
Join Our Training to become proficient in Python for Network Engineer and lead the future of network automation.
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #30 PyATS Series] Checking STP Root Bridge Across Cisco Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-30-PyATS-Series-Checking-STP-Root-Bridge-Across-Cisco-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)

![[Day #24 PyATS Series] BGP Neighbor Validation (Multi-Vendor) Using pyATS for Cisco](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day-24-PyATS-Series-BGP-Neighbor-Validation-Multi-Vendor-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)