[Day #34 PyATS Series] DHCP Snooping & Binding Table Verification Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Snooping is an essential security feature in enterprise networks. It acts as a firewall between untrusted hosts and trusted DHCP servers to protect against rogue DHCP attacks. Verifying the DHCP snooping configuration and ensuring the binding table’s integrity across multiple switches is crucial for maintaining a secure and reliable network.
In today’s post, part of the 101 Days of pyATS (Vendor-Agnostic) series, Trainer Sagar Dhawan demonstrates how to automate DHCP snooping and binding table verification using pyATS. Designed for Python for Network Engineer learners, this tutorial covers:
- Checking if DHCP snooping is enabled on all required VLANs
- Validating trusted/untrusted interfaces
- Parsing and verifying DHCP binding tables
- Generating automated reports for consistent auditing
By the end of this article, you will have a production-ready script for ensuring DHCP security consistency across your Cisco network devices.
Topology Overview
In this lab topology:
- SW1, SW2, and SW3 are Layer 2 access switches
- DHCP snooping is configured on VLANs 10, 20
- DHCP server resides on a trusted uplink interface
- The goal is to verify snooping configurations and binding table entries on all switches.
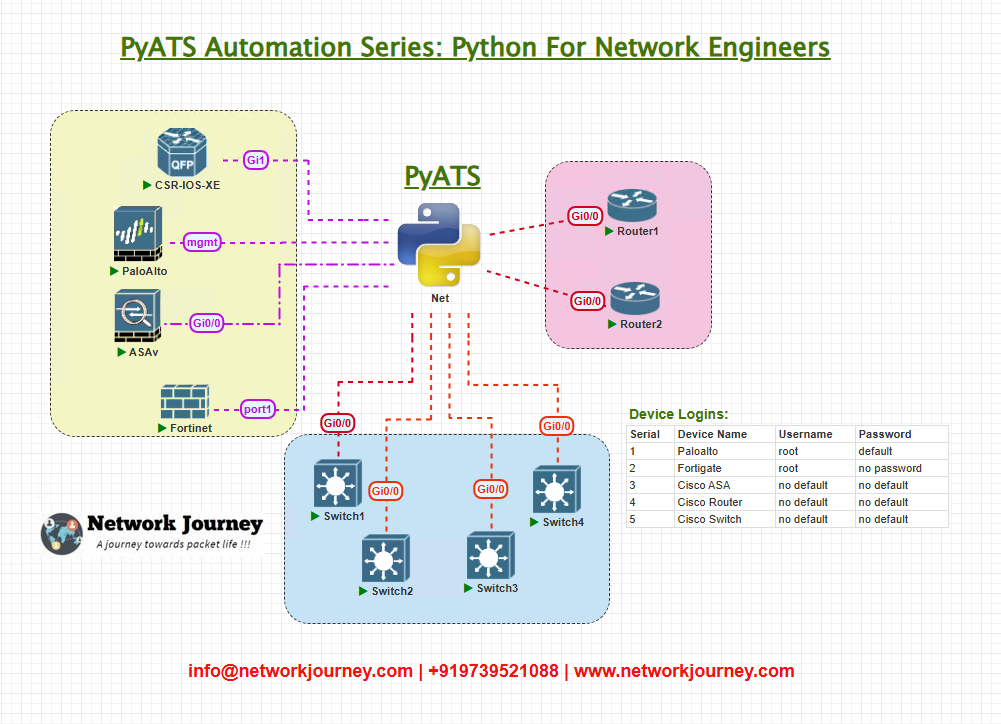
Topology & Communications
- Protocols: DHCP Snooping with Layer 2 switching
- Verification:
show ip dhcp snoopingandshow ip dhcp snooping binding - Connection: CLI-based SSH sessions handled via pyATS testbed
- Steps:
- Connect to each switch
- Verify DHCP snooping status per VLAN
- Check trusted ports and validate DHCP bindings
- Generate JSON report highlighting discrepancies
Workflow Script
from genie.testbed import load
import json
def check_dhcp_snooping(device):
device.connect(log_stdout=False)
snooping = device.parse('show ip dhcp snooping')
binding = device.parse('show ip dhcp snooping binding')
device.disconnect()
return {
'snooping': snooping,
'binding': binding
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
testbed = load('testbed.yml')
devices = testbed.devices
report = {}
for name, device in devices.items():
print(f"Checking DHCP snooping on {name}...")
report[name] = check_dhcp_snooping(device)
with open('dhcp_snooping_report.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(report, f, indent=4)
print(json.dumps(report, indent=4))
Explanation by Line
- check_dhcp_snooping: Parses snooping status and binding table from each switch
- Main loop: Iterates over all switches to collect data
- Output: JSON file containing snooping and binding info for reporting and audits
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: dhcp_snooping_test
devices:
SW1:
os: iosxe
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.101.21
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: cisco123
SW2:
os: iosxe
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.101.22
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: cisco123
SW3:
os: iosxe
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.101.23
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: cisco123
Post-validation CLI Screenshots (Expected Output)
SW1:
SW1# show ip dhcp snooping Switch DHCP snooping is enabled DHCP snooping is configured on following VLANs: 10,20 Trusted Interfaces: Gi0/1
Binding Table:
SW1# show ip dhcp snooping binding MacAddress IpAddress Lease(sec) Type VLAN Interface 00:11:22:33:44:55 192.168.10.10 800 dhcp-snooping 10 Gi0/2
Script Output:
{
"SW1": { ... },
"SW2": { ... },
"SW3": { ... }
}
FAQs
1. Does the script validate DHCP snooping status across VLANs?
Yes. It parses snooping configuration to verify that DHCP snooping is enabled on all expected VLANs, highlighting any missing configurations.
2. Can it detect if a port is incorrectly configured as trusted or untrusted?
Yes. The script checks trusted/untrusted interface status, helping you spot misconfigured ports that may allow rogue DHCP servers.
3. Does it verify active DHCP bindings?
Yes. The script collects binding table entries, allowing you to validate that legitimate DHCP leases exist and detect anomalies like duplicate IPs or MAC addresses.
4. Will the solution work with different Cisco platforms?
Yes. The script is compatible with IOS and IOS-XE devices using Genie parsers supported by pyATS.
5. Can the script be integrated into CI/CD pipelines?
Absolutely. The JSON output can be consumed by DevOps workflows for automated, continuous DHCP snooping validation.
6. Is the solution scalable for large networks with many switches?
Yes. pyATS supports parallel device connections, enabling checks across dozens or hundreds of switches efficiently.
7. Does it validate DHCP snooping rate limits and Option-82 settings?
Not by default, but you can extend the script to parse and validate DHCP snooping rate limits and Option-82 configurations.
8. Is it safe to run this validation script in production?
Yes. It uses read-only show commands, ensuring no impact on production network configurations.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: DHCP snooping & binding table verification using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
Automating DHCP snooping and binding verification enhances network security and reduces manual auditing. Trainer Sagar Dhawan offers a 3-month instructor-led training covering Python, Ansible, APIs, and Cisco DevNet for Network Engineers, equipping you with skills to automate real-world networking scenarios.
Join Our Training and elevate your career with expert-led Python for Network Engineer training.
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #34 PyATS Series] DHCP Snooping & Binding Table Verification Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-34-PyATS-Series-DHCP-Snooping-Binding-Table-Verification-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![[Day #41 PyATS Series] Validate Routing Table Entries Across Cisco/Arista/Palo Alto/Fortigate Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-41-PyATS-Series-Validate-Routing-Table-Entries-Across-Cisco-AristaPalo-AltoFortigate-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![Ticket#10 - NAT Overload Failure: Why Users Couldn't Access the Internet – A Real Fix [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/nj-blog-post-Ticket-10.jpg)
![[Day #28 Pyats Series] SNMP configuration consistency check using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/SNMP-configuration-consistency-check-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)