[Day #36 Pyats Series] Port-channel consistency validation across platforms using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction on the Key Points
In modern enterprise networks, port-channels (also known as EtherChannels, LAGs, or bundles) are essential for link aggregation, redundancy, and high-throughput architecture between switches, routers, and firewalls. However, one of the most common root causes of inconsistent port-channel states is configuration mismatch across member interfaces or devices.
Today’s focus in the “101 Days of pyATS (Vendor-Agnostic)” series is how to automate port-channel consistency checks across Cisco platforms using pyATS and Genie parsers.
With the power of Python for Network Engineers, you can validate the operational and configured state of each member interface, check protocol (PAgP/LACP) health, and ensure uniform settings across all devices in just a few seconds.
Whether you are working with physical infrastructure or cloud labs like EVE-NG, this automation provides a scalable way to enforce port-channel health before outages occur.
Topology Overview
For this validation scenario, we’re using two Cisco IOS-XE routers (or switches) configured with a port-channel between them.
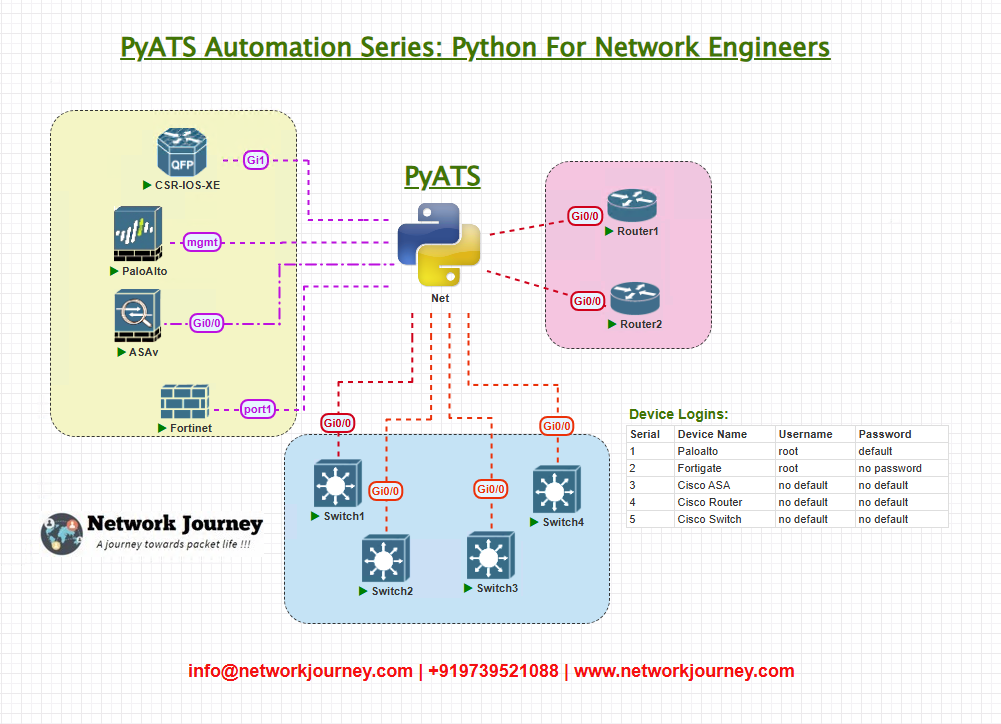
Key Parameters:
- Protocol: LACP
- Interfaces: Gi0/1 and Gi0/2 on both devices
- Bundle Name: Port-Channel1
- Goal: Validate consistency of port-channel config and operational status
Topology & Communications
We will:
- Connect to R1 and R2 using
pyATS - Parse
show etherchannel summaryandshow interfacescommands - Compare protocol states, bundle IDs, and active members
- Highlight any inconsistencies (e.g., mismatched LACP mode, incorrect port states)
Workflow Script
Below is the complete pyATS script to validate port-channel consistency between R1 and R2:
#!/usr/bin/env python
from genie.testbed import load
import pprint
# Load testbed file
testbed = load('testbed.yml')
r1 = testbed.devices['R1']
r2 = testbed.devices['R2']
# Connect to devices
r1.connect(log_stdout=False)
r2.connect(log_stdout=False)
# Parse etherchannel summary
r1_summary = r1.parse('show etherchannel summary')
r2_summary = r2.parse('show etherchannel summary')
# Helper function to extract active interfaces
def get_po_members(summary):
members = []
for po in summary['interfaces']:
members.extend(summary['interfaces'][po]['ports'])
return sorted(members)
# Extract and compare
r1_members = get_po_members(r1_summary)
r2_members = get_po_members(r2_summary)
print("\n=== R1 Port-Channel Members ===")
pprint.pprint(r1_members)
print("\n=== R2 Port-Channel Members ===")
pprint.pprint(r2_members)
# Validation logic
if r1_members == r2_members:
print("\n Port-channel member consistency PASS between R1 and R2.")
else:
print("\n Port-channel member inconsistency DETECTED.")
Explanation by Line
load('testbed.yml'): Loads device connectivity info.device.connect(): Establishes SSH connection using pyATS.parse('show etherchannel summary'): Parses structured output using Genie.get_po_members(): Extracts member interfaces for each port-channel group.- The comparison checks that both ends have the same members.
You can extend this script to check LACP flags, port states, bundle mode, and interface config using additional parsers like show running-config interface.
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: PO_Validation
credentials:
default:
username: cisco
password: cisco
devices:
R1:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.100.1
R2:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.100.2
Make sure SSH is enabled and reachable on both devices.
Post-validation CLI Screenshots (Real expected output)
Sample: show etherchannel summary on R1
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports ------+-------------+----------+--------------------------------------------- 1 Po1(SU) LACP Gi0/1(P) Gi0/2(P)
Parsed Output (Genie format)
{
'interfaces': {
'Port-channel1': {
'ports': ['GigabitEthernet0/1', 'GigabitEthernet0/2'],
'protocol': 'lacp',
'flags': 'SU',
}
}
}
Expected Outcome
Both R1 and R2 should return the same ports in their respective Port-Channel groups. If there’s a mismatch — say Gi0/2 is missing or down — the script will highlight it instantly.
FAQs
1] What is Port-Channel consistency, and why is it critical to validate across platforms?
Port-Channel consistency ensures that all member interfaces of a port-channel (LAG) have identical configuration parameters—such as speed, duplex, MTU, VLAN membership, trunking mode, LACP settings, and more.
If mismatches occur, the port-channel might:
- Remain down (Protocol mismatch)
- Be partially functional (Some links excluded)
- Trigger err-disabled state (e.g., EtherChannel misconfig)
Cross-vendor validation (Cisco, Arista, Juniper) becomes essential in hybrid DC environments, especially with MLAG or multi-chassis EtherChannel setups.
2] Which pyATS Genie parsers are used to validate port-channel consistency?
Depending on the platform, you can use:
Cisco IOS/IOS-XE:
show etherchannel summaryshow interfaces <int> switchportshow interfaces <int>
NX-OS:
show port-channel summaryshow port-channel compatibility-parameters
Arista EOS:
show port-channel
All of the above can be parsed using device.parse() in pyATS. Example:
device.parse("show etherchannel summary")
Once parsed, you can loop through each interface and validate key parameters like admin status, speed, MTU, and mode.
3] What are the most common parameters to validate for consistency in port-channels?
Some key parameters to check for consistency across member interfaces:
- Speed and Duplex
- MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit)
- Trunk/Access mode
- Native VLAN (if trunk)
- Allowed VLANs
- LACP mode (active/passive/on)
- Interface status (up/down/err-disabled)
A mismatch in any of these can break aggregation, especially across platforms with different defaults.
4] How can I identify mismatched port-channel members using parsed data in pyATS?
Here’s a basic logic in Python:
portchannel = device.parse("show etherchannel summary")
members = portchannel['interfaces']['Port-channel1']['members']
inconsistencies = []
for member in members:
intf_data = device.parse(f"show interfaces {member}")
mtu = intf_data['interfaces'][member]['mtu']
speed = intf_data['interfaces'][member]['bandwidth']
# Compare against baseline
if mtu != 1500 or speed != 1000000000:
inconsistencies.append(member)
This returns interfaces with mismatched parameters.
5] How can I perform port-channel validation across vendors (e.g., Cisco ↔ Arista)?
Since CLI syntax differs, use Genie parsers specific to the OS and normalize data at the logic level. For example:
- Cisco:
device.os = "iosxe"
- Arista:
device.os = "eos"
After parsing both outputs, map parameters (e.g., mtu, speed, vlans) to a common schema, then compare like:
if cisco_member['mtu'] != arista_member['mtu']:
print("MTU mismatch found between Cisco and Arista")
This is true vendor-agnostic validation, ideal for hybrid data centers.
6] What issues can arise from inconsistent LACP modes across platforms?
LACP mode inconsistency (active ↔ passive, or on ↔ active) can result in:
- No aggregation: If both ends are passive
- Unidirectional links: Only one side transmits
- Err-disabled state: Detected as misconfig
Using pyATS:
if cisco_lacp_mode != arista_lacp_mode:
print("LACP mode mismatch")
Cross-validation is key here, especially during migrations or brownfield onboarding.
7] Can I automate pre-check and post-check validation of port-channels using pyATS?
Yes! Use a workflow like this:
- Pre-check: Capture parsed
show etherchannelandshow interfaceoutputs. - Change: Apply config (e.g., add new member).
- Post-check: Parse again and compare using
Diff.
Sample:
from genie.utils.diff import Diff diff = Diff(pre_output, post_output) diff.findDiff() print(diff)
This validates consistency and confirms if the change succeeded.
8] How to troubleshoot a port-channel that’s up, but only one link is forwarding?
Possible causes:
- MTU mismatch
- VLAN mismatch (in trunk mode)
- LACP unidirectional failure
- STP blocking one member
Use pyATS to check each member interface:
parsed = device.parse("show interfaces")
for intf, details in parsed['interfaces'].items():
if 'Port-channel' in details.get('members', []):
print(f"{intf} → status: {details['oper_status']} | MTU: {details['mtu']}")
You can then alert on any inactive or blocked links.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Port-channel consistency validation across platforms using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
If you’re eager to build real-world network automation use cases like this, Trainer Sagar Dhawan is conducting a 3-Month Instructor-Led Training that covers everything from beginner Python scripts to advanced multi-vendor pyATS workflows.
Real-world automation with Python for Network Engineers
Vendor-agnostic approach (Cisco, Arista, Palo Alto, FortiGate)
Ansible + API + NETCONF/RESTCONF
pyATS & Genie hands-on labs
Lifetime access to portal and community support
Ready to start automating?
View Course Outline & Join Now
Whether you’re starting out or already DevNet certified, our course will transform your manual CLI skills into scalable automation pipelines. Master Python for Network Engineer workflows and future-proof your career.
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #36 Pyats Series] Port-channel consistency validation across platforms using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Port-channel-consistency-validation-across-platforms-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![[Day #47 PyATS Series] Logging & Debug Outputs Parsing Automation Using pyATS for Cisco](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-47-PyATS-Series-Logging-Debug-Outputs-Parsing-Automation-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![Ansible Playbook for VLAN Configuration – Automate Smarter, Not Harder! [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Ansible-Playbook-for-VLAN-Configuration-–-Automate-Smarter-Not-Harder-1.png)
![[Day #55 Pyats Series] Using Cisco/Arista/Paloalto/Fortigate with pyATS using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Using-CiscoAristaPaloaltoFortigate-with-pyATS-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)