[Day 50] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Wireless Profiling & Endpoint Classification
Table of Contents
Introduction
Wireless profiling in Cisco ISE fingerprints devices (OS, vendor, type) and classifies them so your authorization rules can apply the right VLAN/dACL/SGT automatically.
Today you’ll enable profiler probes, wire them to a 9800-CL WLC, build custom profiling policies, and finally enforce access based on the detected profile—for example: Apple iOS → BYOD VLAN; Android → Internet-only; IP-Cameras → IoT dACL.
Problem Statement
On wireless networks, you often don’t know what is connecting: phones, laptops, scanners, cameras. Without device identity, you can’t:
- Enforce least privilege (IoT vs. user phones vs. laptops).
- Auto-segment devices based on OS/type.
- Audit and troubleshoot effectively (wrong OS → wrong supplicant).
You need a repeatable, low-touch mechanism to discover and classify endpoints as they attach to Wi-Fi and then map them to the correct access.
Solution Overview (What you will build)
- Turn on ISE Profiler Service and probes (RADIUS, DHCP, HTTP, SNMP traps, NMAP optional).
- Feed attributes to ISE from the WLC (RADIUS accounting, session updates).
- Create custom Profiling Policies and Logical Profiles (e.g., Apple-iOS, Android-Device, IoT-Camera).
- Reference Endpoint Profile in Authorization Policy to push VLAN/dACL/SGT.
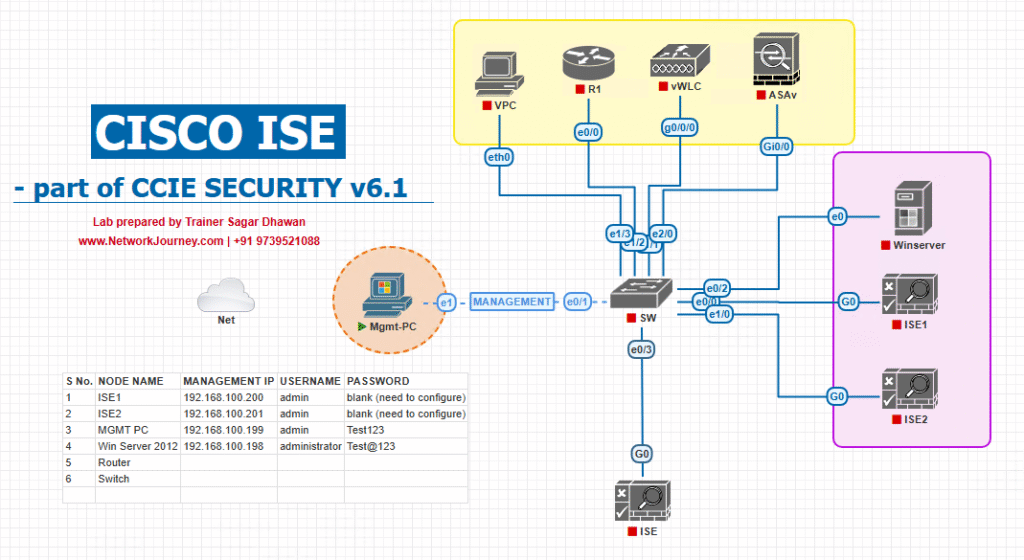
Sample Lab Topology
Platform
- VMware/EVE-NG
- Cisco ISE 3.x (single node lab: PAN/PSN)
- Cisco WLC 9800-CL (or AireOS 8.10+ equivalents)
- Catalyst L2 switch (virtual OK)
- Windows Server (optional: DHCP/DNS/AD for completeness)
- Endpoints: iPhone/iPad, Android, Windows 11 laptop, an IP camera (simulated or real)
Topology Layout:
Step-by-Step GUI Configuration Guide (with validation)
PREREQS (once)
- Time/DNS aligned on ISE/WLC/clients.
- WLC added in ISE: Administration > Network Resources > Network Devices (RADIUS secret set).
- On WLAN, RADIUS Accounting enabled (interim updates recommended).
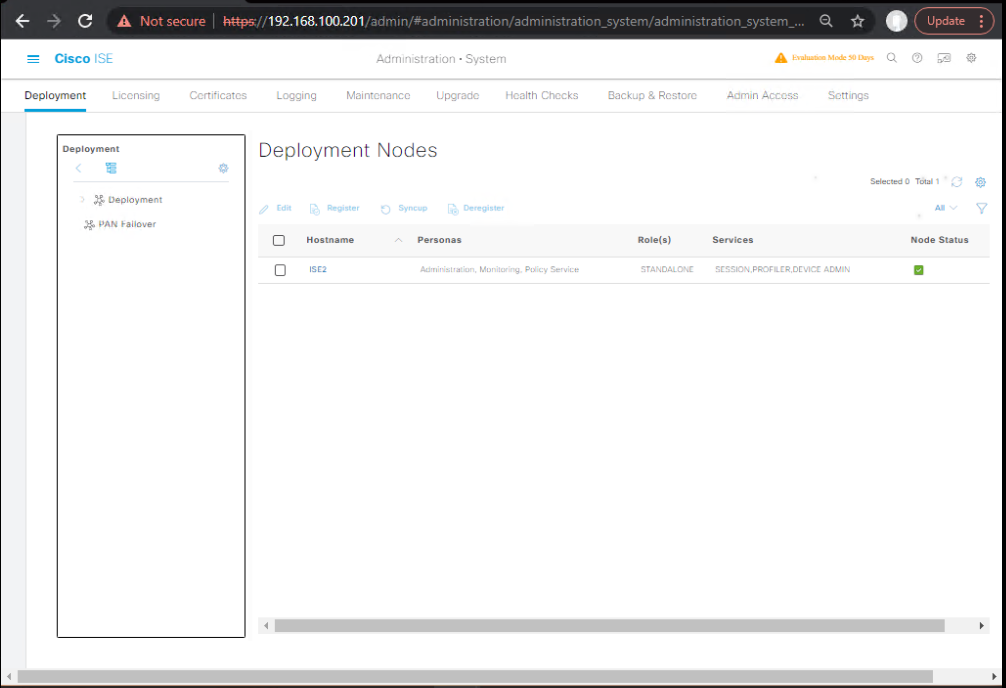
A) ISE — Enable Profiler Service & Probes
- Enable Profiler Service on PSN
- Administration > System > Deployment > (select PSN) > Edit
- Check Enable Profiling Service
- Under Profiler Configuration, enable probes:
- RADIUS, DHCP, HTTP, SNMP Trap (NMAP optional)
- Save & allow services to restart
[Screenshot: ISE Deployment – Profiler Service]
- DHCP Probe (optional but recommended)
- Administration > System > Settings > Profiler > DHCP
- Enable, and if using SPAN/RSPAN to ISE, configure DHCP SPAN receiver interface accordingly.
[Screenshot: ISE DHCP Probe]
- Feed Service (keep profiles current)
- Administration > System > Settings > Profiler > Feed Service
- Enable updates (use Smart Account if required)
[Screenshot: ISE Profiler Feed Service]
Validate (GUI)
- Work Centers > Profiler > Endpoint Classification shows built-in policies.
- Operations > Reports > Profiler appears in reports list.
B) WLC 9800-CL — Ensure RADIUS Accounting for Profiling
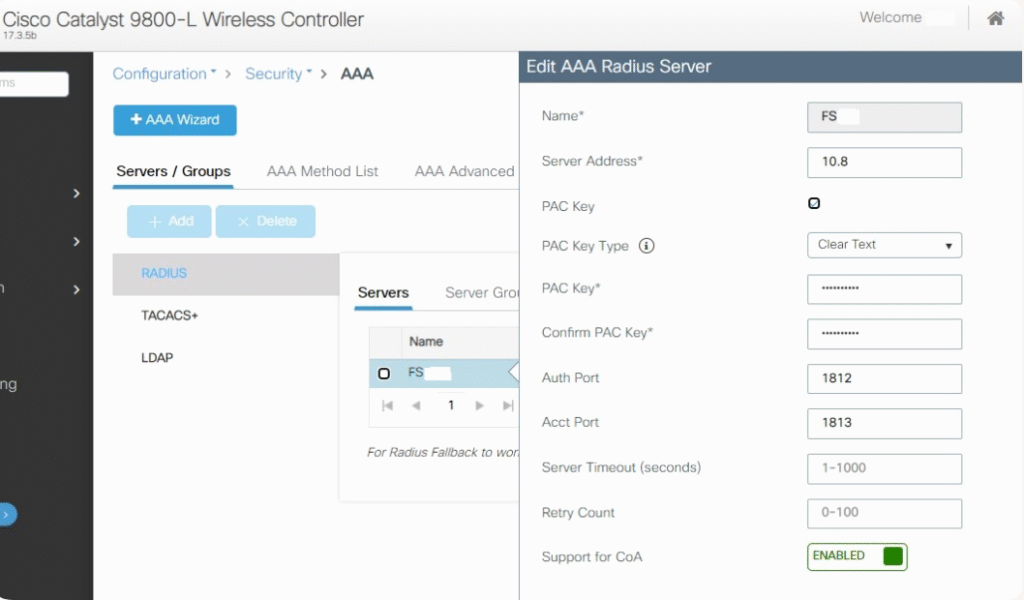
- RADIUS Servers
- Configuration > Security > AAA > Servers > RADIUS → Add ISE (auth+acct)
- [Screenshot: WLC RADIUS Servers]
- WLAN (CORP-WLAN)
- Configuration > Tags & Profiles > WLANs → Edit CORP-WLAN
- Security > AAA: Set RADIUS Authentication = ISE; RADIUS Accounting = ISE
- Accounting: Enable Interim Update (e.g., 5 min)
- Policy Profile: AAA Override = Enabled
- [Screenshot: WLC WLAN AAA]
Validate (CLI)
show wlan summary show wireless client mac <client-mac> show aaa servers show logging | inc AAA|RADIUS|acct
C) ISE — Create Endpoint Identity Groups (optional, for visibility)
- Administration > Identity Management > Groups > Endpoint Identity Groups > Add
IoT-CamerasMobile-AppleMobile-Android- [Screenshot: ISE Endpoint Groups]
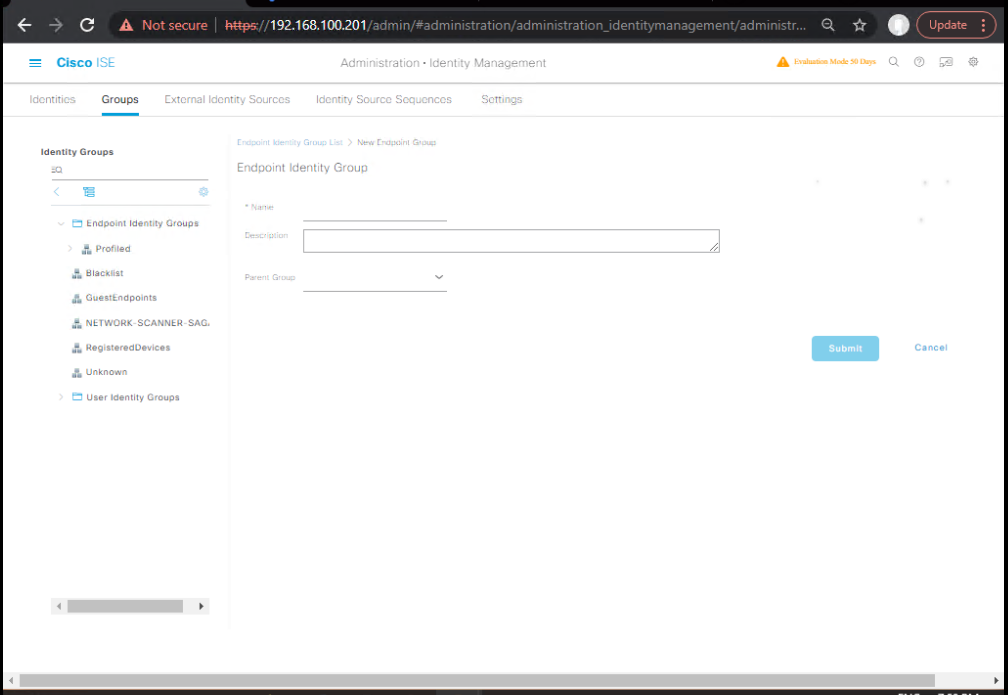
(We’ll primarily use Endpoint Profile in policy; groups help reporting and optional overrides.)
D) ISE — Build Custom Profiling Conditions & Policies
Target: classify Apple iOS, Android, and IoT Camera.
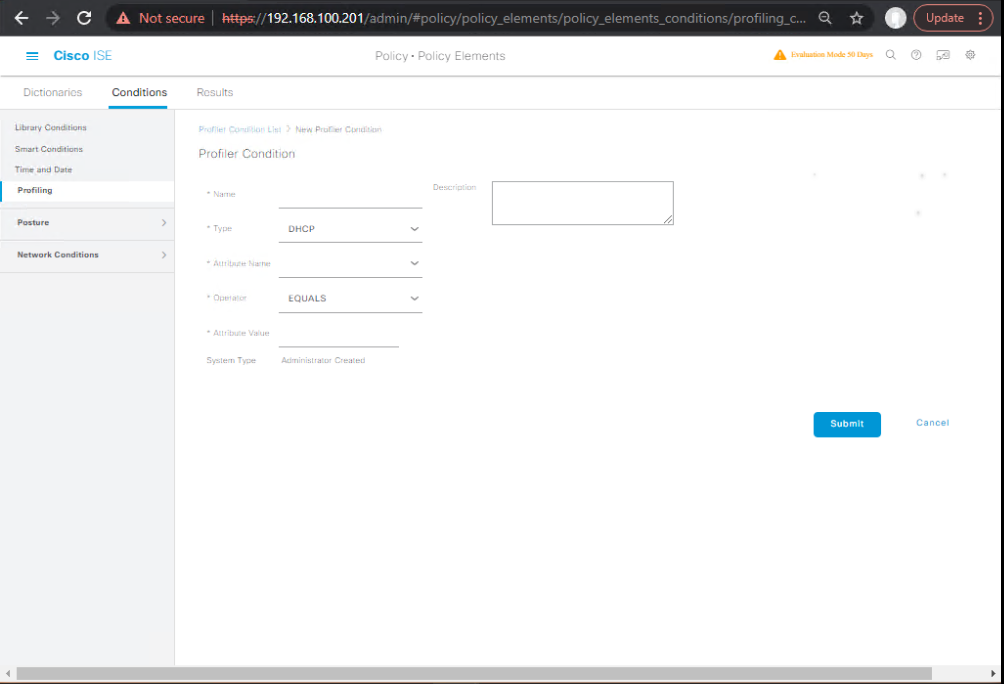
- Create Reusable Conditions
- Policy > Policy Elements > Conditions > Profiling > Create
- Cond-iOS-UA:
HTTP User-Agent CONTAINS "iPhone" OR "iPad" - Cond-iOS-DHCP:
DHCP Vendor Class CONTAINS "apple" - Cond-Android-DHCP:
DHCP Vendor Class CONTAINS "android" - Cond-Android-UA:
HTTP User-Agent CONTAINS "Android" - Cond-IoT-OUI:
MAC OUI IN {your camera vendor OUIs} - Cond-IoT-DHCP:
DHCP Option55 CONTAINS "12","28"(example camera fingerprints)
[Screenshot: ISE Profiling Conditions]
- Cond-iOS-UA:
- Policy > Policy Elements > Conditions > Profiling > Create
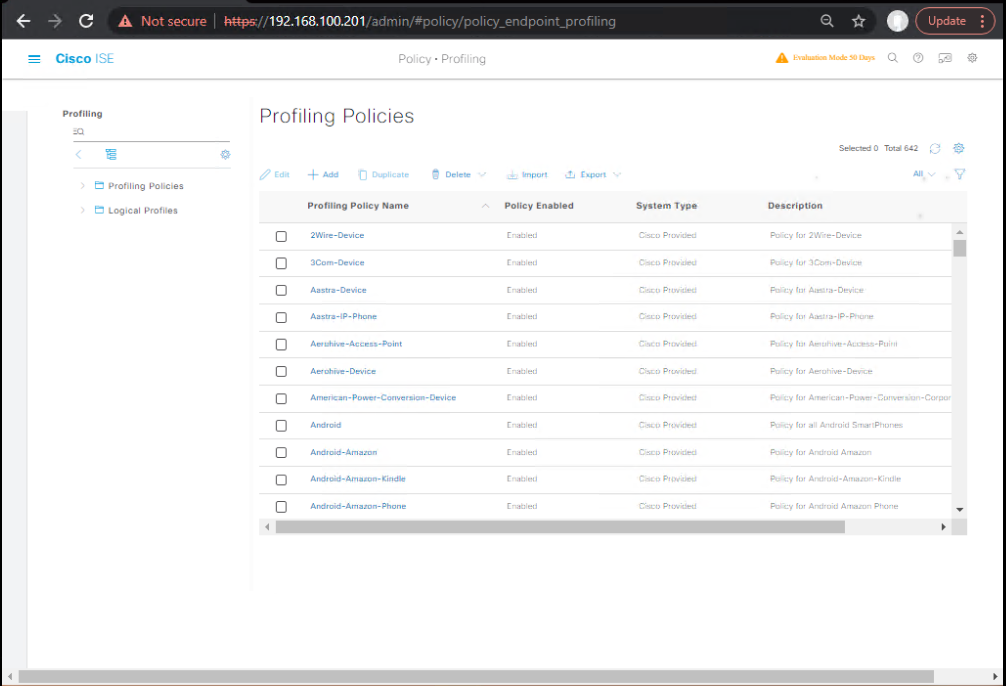
- Create Profiling Policies
- Policy > Profiling
- Policy: Apple-iOS-Custom
- If
(Cond-iOS-UA OR Cond-iOS-DHCP)→ Profile = Apple-iOS
- If
- Policy: Android-Device-Custom
- If
(Cond-Android-UA OR Cond-Android-DHCP)→ Profile = Android-Device
- If
- Policy: IoT-Camera-Custom
- If
(Cond-IoT-OUI AND/OR Cond-IoT-DHCP)→ Profile = Camera-Device (or create new custom profile)
[Screenshot: ISE Profiling Policies]
- If
- Policy: Apple-iOS-Custom
- Policy > Profiling
- Logical Profiles (optional aggregation)
- Work Centers > Profiler > Logical Profiles > Add
- Name:
Mobile-Devices - Members:
Apple-iOS,Android-Device
[Screenshot: Logical Profile]
- Name:
- Work Centers > Profiler > Logical Profiles > Add
Validate (GUI)
- Context Visibility > Endpoints
- Connect test devices → ensure Profile becomes
Apple-iOS/Android-Device/Camera-Device - Attributes tab should list DHCP, HTTP, RADIUS sources used
[Screenshot: Endpoint Attributes]
- Connect test devices → ensure Profile becomes
E) ISE — Authorization Policy Based on Profile
- Results: Authorization Profiles
- Policy > Policy Elements > Results > Authorization > Authorization Profiles > Add
ALLOW-MOBILE- VLAN:
BYOD-VLANor dACL:BYOD_CORP_LIMITED
- VLAN:
ALLOW-IOT-CAMERA- dACL:
IOT_CAMERA_OUTBOUND_ONLY(DNS/DHCP/NTP + RTSP to NVR)
- dACL:
QUAR-UNKNOWN- dACL:
RESTRICT_ALL_EXCEPT_DNS_DHCP
[Screenshot: AuthZ Profiles]
- dACL:
- Policy > Policy Elements > Results > Authorization > Authorization Profiles > Add
- Policy Sets
- Policy > Policy Sets > Wireless-Corp
- Authorization Policy (top-down):
- IF
EndpointProfile = Apple-iOS OR Android-Device→ ALLOW-MOBILE - IF
EndpointProfile = Camera-Device→ ALLOW-IOT-CAMERA - ELSE → QUAR-UNKNOWN
[Screenshot: ISE Policy Set Screen]
- IF
Validate (GUI)
- Operations > RADIUS > Live Logs
- Check Authorization Result shows the expected profile-based rule.
- Context Visibility > Endpoints
- Verify Profile and Authorization match.
Validate (WLC CLI)
show wireless client mac <client-mac> detail ! Confirm WLAN, VLAN, Policy Profile, Session ACL/dACL applied debug aaa all debug wireless mac <client-mac> events undebug all
F) (Optional) ISE — NMAP Active Scanning for Unknown Devices
- Administration > System > Settings > Profiler > NMAP Scan
- Enable and define Scan Ranges (guest/BYOD subnets)
- Choose Scan Template (basic port list)
- [Screenshot: NMAP Settings]
Validate
- Operations > Reports > Profiler → Nmap scan results tie-break ambiguous profiles.
G) Troubleshooting & Quick RCA
- No profile assigned / stays Unknown
- Check RADIUS accounting enabled on WLAN and received by ISE.
- Ensure DHCP probe sees requests (SPAN/RSPAN in place if used).
- Verify Feed Service and built-in rules synced.
- Wrong profile
- Open Endpoint > Attributes to see which probe won; adjust policy order or add AND conditions.
- Policy not enforcing
- Verify AuthZ rule hit in Live Logs; on WLC confirm AAA Override and ACL/VLAN pushed.
FAQs (Wireless Profiling & Endpoint Classification)
1) How does Cisco ISE actually identify a wireless device’s type?
ISE combines multiple probes (RADIUS, DHCP, HTTP, SNMP, NMAP) to collect attributes like MAC OUI, DHCP Option 55, HTTP User-Agent, and RADIUS Calling Station ID. These attributes are matched against profiling policies in a top-down order to assign a profile (e.g., Apple-iOS, Android-Device, Printer).
2) Is RADIUS accounting enough for wireless profiling, or do I need DHCP SPAN?
RADIUS accounting is often enough to get MAC OUI, SSID, AP name, and sometimes device OS, but DHCP probe data significantly improves accuracy. DHCP SPAN is recommended if you want faster classification without waiting for HTTP or NMAP triggers.
3) Can profiling be used on both MAB and 802.1X SSIDs?
Yes. Profiling works regardless of the authentication method. The Endpoint Profile is determined after the first RADIUS authentication and accounting exchange, then updated as more probes collect data.
4) What happens if a device matches multiple profiles?
ISE evaluates profiling policies in order. The first matching policy wins, so you should put your most specific rules above generic ones to avoid false positives.
5) Why does some profiling happen instantly, but others take minutes?
It depends on when probes collect their data:
- RADIUS → instant (at connect)
- DHCP → at IP request (usually instant on connect)
- HTTP → after first web access attempt
- NMAP → after scan is triggered (can be minutes later)
6) How can I enforce VLAN or ACL based on profile?
In the Authorization Policy, match the EndpointProfile condition and return a VLAN assignment or downloadable ACL in an Authorization Profile. Ensure the WLC has AAA Override enabled so it accepts ISE’s result.
7) Can I manually change a wrong profile?
Yes. In Context Visibility > Endpoints, edit the endpoint and set a Static Profile Assignment. However, this bypasses dynamic profiling—so fix policy conditions if the mismatch happens often.
8) How do I verify what probe data was used for a device’s profile?
In Context Visibility > Endpoints, select the device → Attributes tab. You’ll see each attribute and which probe provided it (RADIUS, DHCP, HTTP, etc.). This is critical for troubleshooting misclassifications.
9) Is the ISE Feed Service mandatory for profiling?
No, but it’s strongly recommended. Feed Service updates Cisco’s database of vendor OUIs, DHCP signatures, and profiling policies, which improves classification accuracy without manual updates.
10) How can I export a list of all devices by profile type?
Go to Context Visibility > Endpoints, filter by Profile = <desired profile> or Profile != Unknown, then click Export (CSV). This is useful for inventory reports, audits, or migration planning.
YouTube Link
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to my YouTube channel Network Journey and join my instructor-led classes for hands-on, real-world ISE experience
Closing Notes
You now have profiling → classification → enforcement on wireless: ISE learns who/what the device is, and your policy auto-segments it with the right VLAN/dACL/SGT. Keep probes on, accounting reliable, and review Live Logs + Endpoint Attributes for fast RCA.
Upgrade Your Skills – Start Today
Turn this profiling lab into a production-ready, interview-winning blueprint with expert coaching.
Join 4-Month, Instructor-Led CCIE Security & Cisco ISE Mastery:
- Live NAC/BYOD/Profiling/SGT/pxGrid deep dives
- Full EVE-NG topologies + graded lab workbooks & solution keys
- Real-world WLC 9800 + ISE Profiler designs (RADIUS/DHCP/HTTP/NMAP)
- Lifetime recordings, career mentorship, mock interviews
Free Lead Magnet for enrollees: Wireless Profiling Pack
- Ready-to-use profiling conditions, AuthZ rule templates, dACL snippets, and a Troubleshooting Playbook (ISE + WLC CLI).
Secure your seat & syllabus: https://course.networkjourney.com/ccie-security/
(Enroll now—get the Pack + orientation labs to accelerate your deployment)
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088


![[Day 40] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: End-to-End Wired Authentication Lab Validation](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-40-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-End-to-End-Wired-Authentication-Lab-Validation.png)
