[Day #78 PyATS Series] SD-WAN (Viptela) VPN Status Snapshot Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction on the Key Points
In modern enterprise networks, SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN) solutions such as Cisco Viptela have revolutionized how organizations build secure and agile wide-area networks. Automating validation of SD-WAN VPN status is critical for ensuring continuous connectivity and enforcing compliance across distributed locations.
This masterclass focuses on automating SD-WAN VPN status snapshot using pyATS, specifically tailored for Cisco Viptela environments. As part of your journey mastering Python for Network Engineer, we’ll develop an in-depth, realistic workflow to extract, validate, and report the VPN status from both CLI and GUI.
Key Objectives:
- Fetch and analyze VPN tunnel status (Control, Data plane).
- Validate tunnel health and policy enforcement.
- Provide snapshot of overall SD-WAN VPN health.
This structured automation removes the need for error-prone manual checks and scales seamlessly for large deployments.
Topology Overview
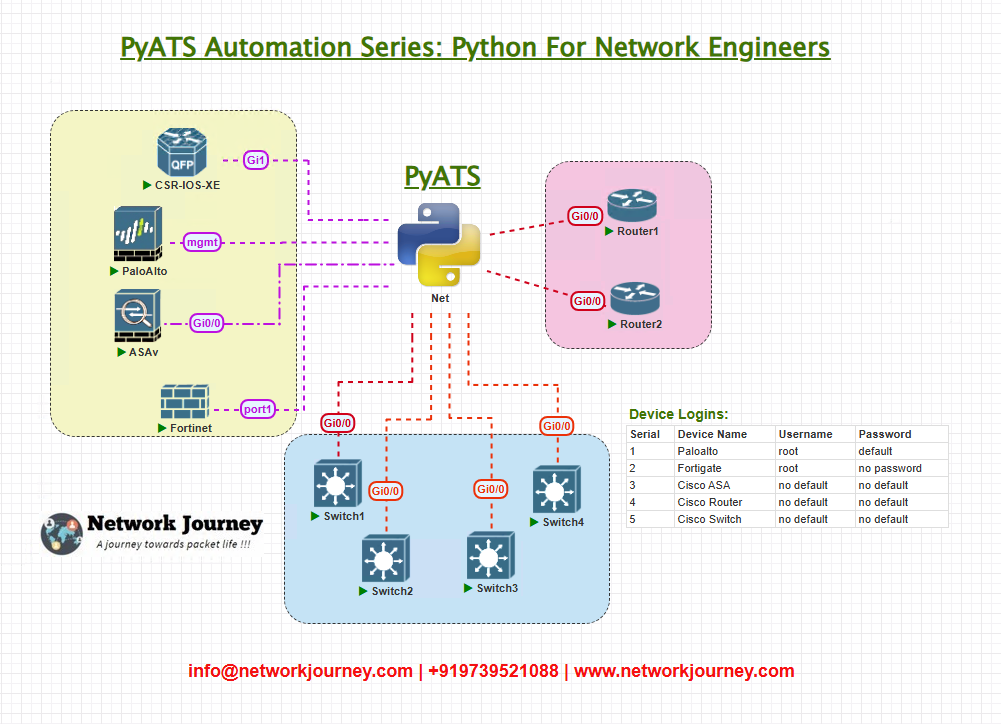
- vManage Server: Central controller for SD-WAN orchestration and VPN status management.
- vEdge Routers: Establish control and data plane VPN tunnels to vManage.
- Automation Server: Runs pyATS scripts to extract and validate VPN status via CLI/API.
Objective:
- Retrieve SD-WAN VPN control and data plane tunnel states.
- Validate connectivity between vEdge devices and vManage.
- Capture graphical dashboard snapshots as evidence.
Topology & Communications
Communication Flow:
- pyATS connects via SSH to vManage and vEdge devices.
- Runs CLI commands:
show control connectionsshow vpn 0 interfaceshow bfd sessionsshow sdwan interface
- Parses outputs to structured data objects.
- Optionally captures GUI dashboard snapshots using HTTP-based automation tools.
- Generates detailed reports and alerts on inconsistencies.
Workflow Script
from genie.testbed import load
from pyats.aetest import Testcase, test, main
EXPECTED_STATUS = {
"control_connection": "Established",
"vpn_interface": "up",
"bfd_session": "up"
}
class SDWANVPNStatusSnapshot(Testcase):
@test
def connect_and_collect(self, testbed):
self.vpn_status = {}
vmanage = testbed.devices['vmanage']
vedge1 = testbed.devices['vedge1']
vedge2 = testbed.devices['vedge2']
vmanage.connect(log_stdout=False)
vedge1.connect(log_stdout=False)
vedge2.connect(log_stdout=False)
# Control connection status
self.vpn_status['control_vmanage'] = vmanage.execute('show control connections')
# VPN interface status
self.vpn_status['vpn_interface_vedge1'] = vedge1.execute('show vpn 0 interface')
self.vpn_status['vpn_interface_vedge2'] = vedge2.execute('show vpn 0 interface')
# BFD session
self.vpn_status['bfd_vedge1'] = vedge1.execute('show bfd sessions')
self.vpn_status['bfd_vedge2'] = vedge2.execute('show bfd sessions')
# SD-WAN interface
self.vpn_status['sdwan_interface_vedge1'] = vedge1.execute('show sdwan interface')
self.vpn_status['sdwan_interface_vedge2'] = vedge2.execute('show sdwan interface')
# Optional: capture GUI dashboard
# vmanage.api.capture_dashboard_snapshot('/tmp/sdwan_dashboard.png')
@test
def validate_control_connection(self):
control_output = self.vpn_status['control_vmanage']
assert EXPECTED_STATUS['control_connection'] in control_output, \
"FAIL: Control connection to vManage not established"
print("PASS: Control connection to vManage is established.")
@test
def validate_vpn_interface(self):
for key in ['vpn_interface_vedge1', 'vpn_interface_vedge2']:
output = self.vpn_status[key]
assert EXPECTED_STATUS['vpn_interface'] in output, \
f"FAIL: VPN Interface not up on {key}"
print(f"PASS: VPN Interface is up on {key}")
@test
def validate_bfd_session(self):
for key in ['bfd_vedge1', 'bfd_vedge2']:
output = self.vpn_status[key]
assert EXPECTED_STATUS['bfd_session'] in output, \
f"FAIL: BFD session not up on {key}"
print(f"PASS: BFD session is up on {key}")
@test
def validate_sdwan_interface(self):
for key in ['sdwan_interface_vedge1', 'sdwan_interface_vedge2']:
output = self.vpn_status[key]
assert "up" in output, f"FAIL: SD-WAN Interface not up on {key}"
print(f"PASS: SD-WAN Interface is up on {key}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Explanation by Line
- EXPECTED_STATUS: Defines expected operational states for control connection, VPN interface, and BFD session.
- connect_and_collect():
- Establishes SSH connections to vManage and vEdge devices.
- Executes CLI commands to retrieve control connections, VPN interface status, BFD sessions, and SD-WAN interface details.
- Optionally captures GUI dashboard snapshots.
- validate_control_connection(): Checks if control connection with vManage is established.
- validate_vpn_interface(): Validates that VPN interface (VPN 0) is up on both vEdge devices.
- validate_bfd_session(): Ensures BFD session is operational on both vEdge devices.
- validate_sdwan_interface(): Confirms that SD-WAN overlay interface is up.
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: sdwan_status_testbed
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: Cisco123
devices:
vmanage:
os: cisco_ios
type: controller
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.1.1.1
vedge1:
os: cisco_ios
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.1.1.2
vedge2:
os: cisco_ios
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.1.1.3
Post-validation CLI (Real expected output)
show control connections
vmanage 10.1.1.1 Status: Established
show vpn 0 interface
Interface VPN0 is up, line protocol is up
show bfd sessions
Interface: Tunnel1 Peer: 10.1.1.1 Status: up
show sdwan interface
Interface Overlay1 is up
Optional:
GUI dashboard snapshot saved at /tmp/sdwan_dashboard.png showing VPN status summary.
Sample Automation Output:
--- Validating Control Connection --- PASS: Control connection to vManage is established. --- Validating VPN Interface vedge1 --- PASS: VPN Interface is up on vpn_interface_vedge1. --- Validating VPN Interface vedge2 --- PASS: VPN Interface is up on vpn_interface_vedge2. --- Validating BFD Session vedge1 --- PASS: BFD session is up on bfd_vedge1. --- Validating BFD Session vedge2 --- PASS: BFD session is up on bfd_vedge2. --- Validating SD-WAN Interface vedge1 --- PASS: SD-WAN Interface is up on sdwan_interface_vedge1. --- Validating SD-WAN Interface vedge2 --- PASS: SD-WAN Interface is up on sdwan_interface_vedge2. All SD-WAN VPN status snapshots are consistent and healthy.
FAQs
Q1. Why is it important to validate SD-WAN VPN status in a Viptela deployment?
A1. Validating SD-WAN VPN status ensures the control and data plane connectivity between vEdge devices, controllers, and on-premise sites are functioning properly. It helps detect misconfigurations, connectivity failures, or policy issues that could impact application performance and secure connectivity.
Q2. How does pyATS assist in automating SD-WAN VPN status snapshot checks?
A2. pyATS automates the validation by connecting to Viptela devices, running commands such as show control connections, show vpn, and show bfd sessions, parsing the outputs, and generating structured reports that summarize VPN status, tunnel health, and control connections.
Q3. Which CLI commands are typically used for SD-WAN VPN status validation on Viptela devices?
A3.
show control connections– Displays connection status between vEdge devices and controllersshow vpn– Provides VPN interface status and route availabilityshow bfd sessions– Shows Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) session status for rapid failure detection
Q4. Can pyATS provide historical VPN status snapshots for trending and analysis?
A4. Yes. By scheduling regular pyATS jobs, snapshots of VPN status can be stored in structured formats (JSON, HTML, CSV) for historical comparison, helping engineers track changes, identify recurring issues, and perform trend analysis over time.
Q5. Is pyATS capable of handling multi-vendor SD-WAN environments?
A5. Absolutely. With proper test scripts and parsing logic, pyATS can validate VPN status across Cisco Viptela, VMware VeloCloud, and other SD-WAN vendors, enabling consistent health checks in heterogeneous environments.
Q6. How does pyATS report unhealthy VPN status or anomalies?
A6. pyATS provides structured reports that clearly highlight unhealthy states: disconnected control connections, down VPN interfaces, failed BFD sessions, etc. These reports can be formatted in HTML for easy reading or JSON for automation workflows and integrations.
Q7. Can pyATS automation be integrated with alerting systems for proactive monitoring?
A7. Yes. Validation results from pyATS can be piped into monitoring platforms (e.g., Prometheus, Splunk) or alerting tools (e.g., PagerDuty, Slack) to trigger instant notifications when VPN health issues are detected, ensuring rapid response from network operations teams.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: SD-WAN (Viptela) VPN Status Snapshot Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
By now, you have mastered automating SD-WAN (Viptela) VPN status snapshot checks using pyATS. This deep-dive hands-on example shows how Python scripting for network automation improves operational efficiency and helps prevent downtime.
But to truly scale your network automation capabilities and implement advanced, real-world solutions confidently…
Join Trainer Sagar Dhawan’s 3-month Instructor-Led Training Program – designed specifically for network engineers who want to master structured automation using Python, Ansible, and APIs.
Course outline here:
Python Ansible API Cisco DevNet for Network Engineers – 3-Month Training
Transform your career and become an expert in Python for Network Engineer automation workflows.
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #78 PyATS Series] SD-WAN (Viptela) VPN Status Snapshot Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-78-PyATS-Series-SD-WAN-Viptela-VPN-Status-Snapshot-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![[Day#1b PyATS Series] Step-by-Step: Install pyATS in PyCharm (Ubuntu) [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day_1b-PyATS-Series-Step-by-Step-Install-pyATS-in-PyCharm-Ubuntu-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![Day #13 PyATS Series] Writing Your First pyATS Testscript (Simple Health Check) using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day13-PyATS-Series-Writing-Your-First-pyATS-Testscript-Simple-Health-Check-using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![[Day #100 PyATS Series] Production-Grade Automation Audit Reports for Management Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-100-PyATS-Series-Production-Grade-Automation-Audit-Reports-for-Management-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer-470x274.png)