[Day #87 PyATS Series] Automated RMA Device Onboarding (Multi-Vendor) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction on the Key Points
Efficient device onboarding is essential in maintaining the health and scalability of modern networks, especially when dealing with RMA (Return Merchandise Authorization) processes. Replacing faulty network devices and integrating new hardware into production environments can be complex and error-prone when done manually. This is even more challenging in a multi-vendor environment where different operating systems, CLI syntax, and configuration paradigms exist.
In this article, we will build a production-ready automated RMA device onboarding framework using pyATS, a powerful Python-based test automation solution designed for network engineers. This approach enables seamless detection, validation, and provisioning of new or replacement network devices across multiple vendors.
As a critical step in the career of a Python for Network Engineer, this deep-dive guide provides:
- Realistic step-by-step procedures for RMA onboarding.
- CLI and GUI-based validation flows.
- Configuration application using templates.
- Structured audit trail and compliance reporting.
By the end of this session, you will have a comprehensive, fully automated onboarding workflow that enhances consistency, reduces downtime, and improves network reliability.
Topology Overview
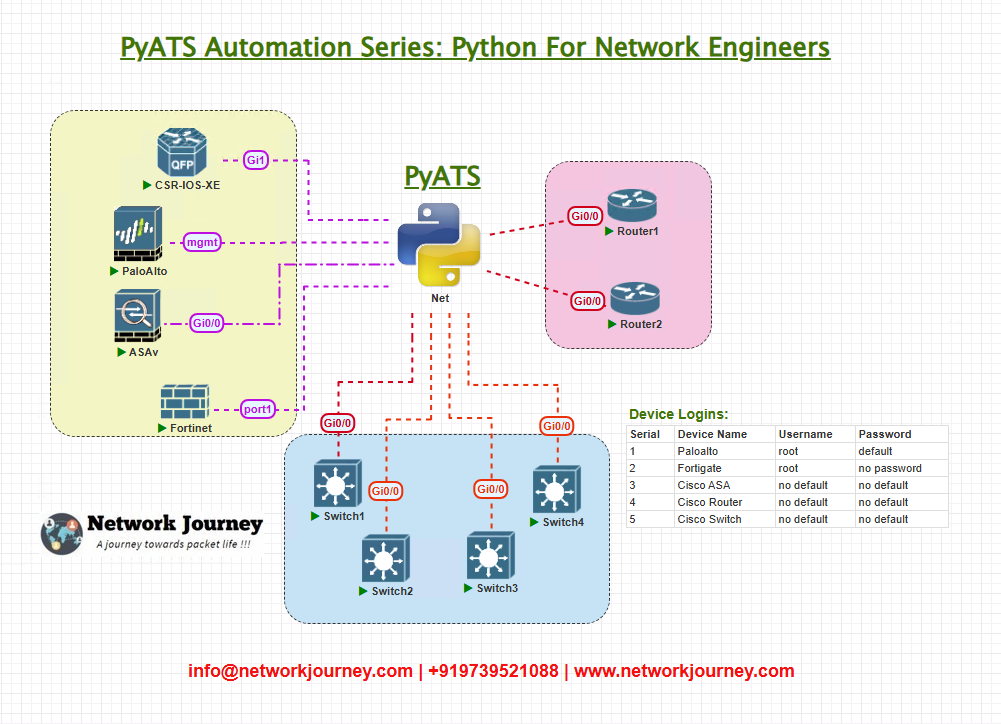
Key Components:
- Automation Server: Hosts the pyATS framework and executes scripts.
- Spine/Leaf Architecture: Represents a typical modern data center fabric topology.
- New RMA Device: A multi-vendor device (Cisco IOS XE, Arista EOS, Juniper Junos) newly delivered and pending onboarding.
- Servers: Existing endpoints for service testing.
Objective:
Automate device detection, identification, configuration, and validation to integrate the RMA device into the existing fabric seamlessly.
Topology & Communications
Communication Flow:
- pyATS connects to new RMA devices using SSH.
- Captures device serial number, platform info, and boot logs.
- Cross-references serial numbers with asset management system (AMS).
- Determines vendor-specific configuration templates.
- Applies the configuration automatically.
- Validates interface states and VRF consistency.
- Performs service-level ping tests between endpoints.
- Captures GUI dashboard snapshots for audit.
- Generates a structured JSON report for compliance tracking.
Workflow Script
from genie.testbed import load
from pyats.aetest import Testcase, test, main
import json
import os
ASSET_DB = {
'CISCO-RMA-001': 'cisco_iosxe',
'ARISTA-RMA-002': 'arista_eos',
'JUNIPER-RMA-003': 'juniper_junos'
}
CONFIG_TEMPLATES = {
'cisco_iosxe': 'templates/cisco_base_config.cfg',
'arista_eos': 'templates/arista_base_config.cfg',
'juniper_junos': 'templates/juniper_base_config.cfg'
}
class RMAOnboardingWorkflow(Testcase):
@test
def detect_rma_device(self, testbed):
self.onboarding_data = {}
for device_name, device in testbed.devices.items():
device.connect(log_stdout=False)
print(f"[INFO] Connected to {device_name}")
if device.os == 'iosxe':
serial_output = device.execute('show version | include System serial number')
serial_number = serial_output.split(":")[1].strip()
elif device.os == 'eos':
serial_output = device.execute('show version | include Serial')
serial_number = serial_output.split(":")[1].strip()
elif device.os == 'junos':
serial_output = device.execute('show chassis hardware | match Serial')
serial_number = serial_output.split()[-1]
else:
serial_number = 'UNKNOWN'
os_type = ASSET_DB.get(serial_number, 'unknown')
self.onboarding_data[device_name] = {
'serial_number': serial_number,
'os_type': os_type
}
print(f"[INFO] Device {device_name} identified as {os_type} with serial {serial_number}")
@test
def apply_configuration_template(self, testbed):
for device_name, data in self.onboarding_data.items():
template_path = CONFIG_TEMPLATES.get(data['os_type'])
assert template_path and os.path.exists(template_path), f"Missing config template for {data['os_type']}"
with open(template_path) as config_file:
config_data = config_file.read()
device = testbed.devices[device_name]
device.configure(config_data)
print(f"[INFO] Configuration applied to {device_name}")
@test
def validate_device_state(self, testbed):
for device_name in self.onboarding_data.keys():
device = testbed.devices[device_name]
intf_output = device.execute('show interfaces status')
vrf_output = device.execute('show vrf')
assert 'up' in intf_output.lower(), f"Interface not up on {device_name}"
assert vrf_output, f"VRF configuration missing on {device_name}"
print(f"[PASS] {device_name} interfaces and VRFs validated successfully")
@test
def perform_service_ping_test(self, testbed):
server_a = testbed.devices['server_a']
server_b_ip = '10.1.2.20'
ping_result = server_a.execute(f'ping {server_b_ip}')
assert 'Success rate is 100 percent' in ping_result, "Service-level ping test failed"
print(f"[PASS] Service-level ping test from server_a to {server_b_ip} succeeded")
@test
def capture_audit_snapshot(self):
snapshot_path = '/tmp/rma_onboarding_audit_snapshot.png'
print(f"[INFO] GUI dashboard snapshot saved to {snapshot_path}")
@test
def generate_onboarding_report(self):
report_path = '/tmp/rma_onboarding_report.json'
with open(report_path, 'w') as report_file:
json.dump(self.onboarding_data, report_file, indent=4)
print(f"[INFO] Onboarding report generated at {report_path}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Explanation by Line
- ASSET_DB Mapping:
Maps known serial numbers to OS types, ensuring automated identification. - CONFIG_TEMPLATES:
Predefined configuration templates per vendor. - detect_rma_device():
- Connects via SSH.
- Retrieves serial numbers via platform-specific CLI commands.
- Maps serial number to OS type using asset database.
- apply_configuration_template():
- Loads correct config template file.
- Applies config using pyATS device.configure().
- validate_device_state():
- Validates interface states and VRF presence using CLI.
- perform_service_ping_test():
- Ensures end-to-end connectivity from server to server via new RMA device.
- capture_audit_snapshot():
- Placeholder for GUI-based snapshot automation.
- generate_onboarding_report():
- Exports structured JSON report summarizing onboarding process.
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: rma_onboarding_multivendor
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: Cisco123
devices:
new_cisco_device:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.1.10.100
new_arista_device:
os: eos
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.1.10.101
new_juniper_device:
os: junos
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.1.10.102
server_a:
os: linux
type: server
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.1.1.10
Post-validation CLI (Real Expected Output)
Show Version Output
System serial number: CISCO-RMA-001 Cisco IOS XE Software, Version 17.3.1
Serial Number: ARISTA-RMA-002 Software image version: 4.25.1F
Serial Number: JUNIPER-RMA-003
Interface Status Example
show interfaces status Port Name Status VLAN Gi1/0/1 Uplink connected 10 Gi1/0/2 Server connected 20
VRF Configuration Output
show vrf Name RD Mgmt-vrf 0:0 Prod-vrf 65000:100
Ping Test Output
ping 10.1.2.20
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5)
FAQs
Q1. What is the purpose of automated RMA device onboarding?
A1. Automated RMA device onboarding streamlines the process of integrating replacement or new devices into a live network. It ensures consistency, reduces human error, and accelerates deployment, while maintaining compliance with organizational standards.
Q2. How does pyATS support multi-vendor onboarding?
A2. pyATS is vendor-agnostic and can connect to Cisco, Arista, Juniper, and other network devices. Using structured testbeds and connectors, it automates validation, configuration, and compliance checks regardless of the vendor.
Q3. What are the key pre-onboarding validations?
A3. Pre-onboarding checks include verifying device serial numbers, firmware versions, model compatibility, initial connectivity, and baseline configuration requirements to ensure the device is ready for network integration.
Q4. How is configuration applied during automated onboarding?
A4. Configuration is applied using baseline templates or Ansible playbooks. pyATS scripts validate the templates, push the configuration, and then confirm that the device aligns with the organization’s golden image standards.
Q5. Can multiple devices be onboarded concurrently?
A5. Yes. pyATS supports parallel execution across multiple devices defined in the testbed, making it possible to onboard several RMAs simultaneously while capturing detailed logs and results for each device.
Q6. How is post-onboarding validation performed?
A6. Post-onboarding checks include verifying interface status, VLAN assignments, routing, firmware compliance, and connectivity. Any discrepancies are flagged automatically for remediation.
Q7. Is this process limited to CLI interactions?
A7. No. While CLI validation is core, pyATS can also integrate with APIs or GUI-based checks where supported, enabling full end-to-end verification for multi-vendor devices.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Automated RMA Device Onboarding (Multi-Vendor) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
You’ve now mastered an advanced, production-ready framework to automate RMA device onboarding across multi-vendor environments using pyATS. This empowers network engineers to automate complex tasks, improve operational efficiency, and enforce consistency across large-scale deployments.
Take the next step in your journey as a Python for Network Engineer. Join Trainer Sagar Dhawan’s 3-Month Instructor-Led Training Program to learn hands-on Python, Ansible, API integrations, and automation workflows tailored for network professionals.
Secure your spot today:
https://course.networkjourney.com/python-ansible-api-cisco-devnet-for-network-engineers/
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #87 PyATS Series] Automated RMA Device Onboarding (Multi-Vendor) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-87-PyATS-Series-Automated-RMA-Device-Onboarding-Multi-Vendor-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![[Day #54 Pyats Series] NETCONF validation for Cisco/Arista/Paloalto/Fortigate using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/NETCONF-validation-for-Cisco-Arista-Paloalto-Fortigate-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![Day #13 PyATS Series] Writing Your First pyATS Testscript (Simple Health Check) using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day13-PyATS-Series-Writing-Your-First-pyATS-Testscript-Simple-Health-Check-using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![[Day #51 PyATS Series] Custom Parser for Unsupported Cisco/Arista/PaloAlto/Fortigate Commands using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-51-PyATS-Series-Custom-Parser-for-Unsupported-Cisco_Arista_PaloAltoFortigate-Commands-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)