[Day #89 PyATS Series] Building Python REST API Wrappers Around pyATS Jobs Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction on the Key Points
Welcome to Day #89 of the 101 Days of pyATS (Vendor-Agnostic) series. Today, we’re going full-stack by building Python REST API wrappers around pyATS jobs. This approach empowers network engineers to execute pyATS test scripts remotely through an HTTP interface, enabling integration with third-party systems, orchestration platforms, and modern automation workflows.
For every Python for Network Engineer, mastering REST API development is essential. You’ll learn how to:
- Create production-ready Python REST APIs using Flask.
- Trigger pyATS jobs programmatically via API endpoints.
- Pass parameters, handle job execution, and collect job results.
- Build real-time validation mechanisms to monitor job status.
- Ensure proper error handling and security best practices.
This deep-dive masterclass Article delivers a detailed, step-by-step guide with practical CLI and GUI validations, perfect for operationalizing your pyATS automation in modern environments.
Topology Overview
Although the focus is on API development and job automation, here’s the simplified topology for clarity:
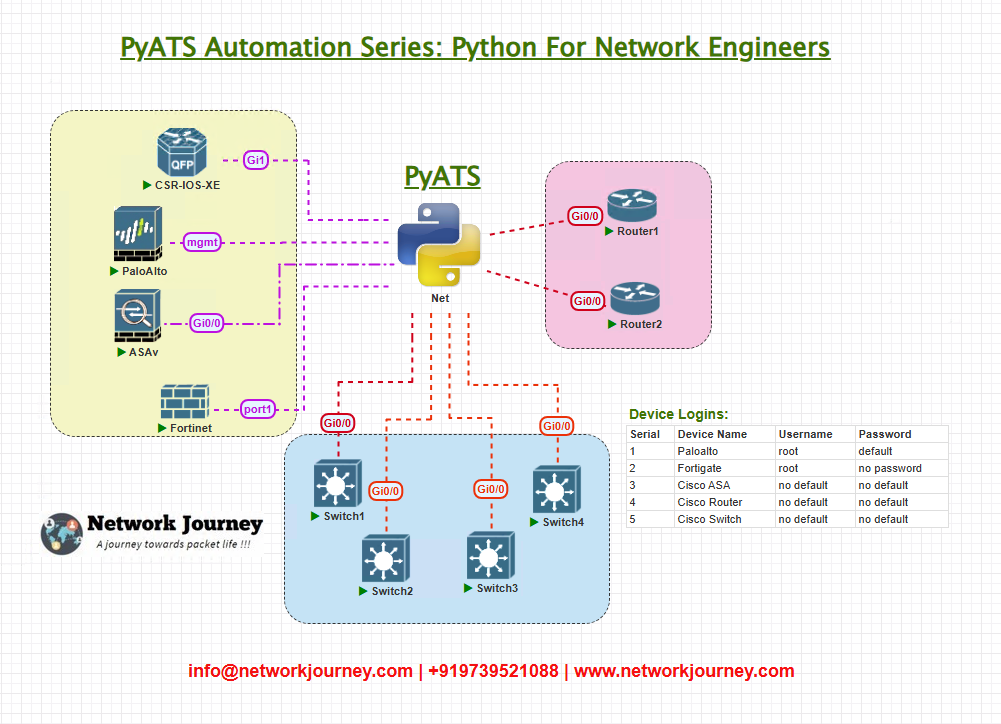
- REST API exposes endpoints for triggering pyATS jobs.
- pyATS jobs run in a controlled environment.
- CLI outputs are captured and returned via HTTP response.
- GUI-based dashboards (optional) can query these APIs for status visualization.
Topology & Communications
- API Server listens on port 5000.
- Endpoint examples:
POST /api/pyats/run-testGET /api/pyats/job-status/<job_id>
- pyATS test scripts execute using the
pyats run job <jobfile>CLI command. - Testbed and job result files are stored in structured folders.
- Job status is monitored by periodically checking generated logs.
Workflow Script
a) Directory Structure
/pyats_rest_api/ │ ├── app.py ├── pyats_jobs/ │ └── sample_test_job.py ├── testbed.yaml ├── jobs/ │ └── job_results/ ├── requirements.txt ├── utils.py
b) Flask REST API Implementation (app.py)
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from utils import run_pyats_job, get_job_status
import uuid
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
JOB_RESULTS_DIR = './jobs/job_results/'
@app.route('/api/pyats/run-test', methods=['POST'])
def run_test():
data = request.get_json()
test_name = data.get('test_name')
testbed_file = data.get('testbed_file', 'testbed.yaml')
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
job_output_dir = os.path.join(JOB_RESULTS_DIR, job_id)
os.makedirs(job_output_dir, exist_ok=True)
try:
result = run_pyats_job(test_name, testbed_file, job_output_dir)
return jsonify({'status': 'started', 'job_id': job_id, 'result': result}), 202
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 500
@app.route('/api/pyats/job-status/<job_id>', methods=['GET'])
def job_status(job_id):
status = get_job_status(job_id)
return jsonify({'job_id': job_id, 'status': status})
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
c) pyATS Job Execution Utility (utils.py)
import subprocess
import os
JOB_RESULTS_DIR = './jobs/job_results/'
def run_pyats_job(test_name, testbed_file, output_dir):
job_command = [
'pyats', 'run', 'job', f'./pyats_jobs/{test_name}.py',
'--testbed-file', testbed_file,
'--output-dir', output_dir
]
process = subprocess.Popen(job_command, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
stdout, stderr = process.communicate()
if process.returncode != 0:
raise RuntimeError(f"Job execution failed: {stderr.decode()}")
return stdout.decode()
def get_job_status(job_id):
output_dir = os.path.join(JOB_RESULTS_DIR, job_id)
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
return 'Job ID not found'
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(output_dir, 'job.log')):
return 'Completed'
return 'Running'
d) Sample pyATS Job (pyats_jobs/sample_test_job.py)
from ats import aetest
class ConnectivityTest(aetest.Testcase):
@aetest.test
def ping_test(self, testbed):
device = testbed.devices['cisco_router']
output = device.execute('ping 8.8.8.8')
assert '!!!' in output, "Ping to 8.8.8.8 failed"
if __name__ == '__main__':
import sys
from genie.testbed import load
testbed = load(sys.argv[1])
aetest.main(testbed=testbed)
Explanation by Line
- app.py:
- Defines endpoints:
/api/pyats/run-test: Starts a pyATS job, generates a uniquejob_id, and stores results./api/pyats/job-status/<job_id>: Checks the existence of job results to infer status.
- Uses Python’s
uuidfor job identification. - Returns structured JSON responses.
- Defines endpoints:
- utils.py:
- Runs the pyATS job using
subprocess.Popen. - Manages output directories.
- Provides job status by checking for a
job.logfile.
- Runs the pyATS job using
- pyats_jobs/sample_test_job.py:
- Example pyATS test verifying device reachability.
- Uses the
aetestframework and testbed file.
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: api_testbed
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: Cisco123
devices:
cisco_router:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.1.1.1
Post-validation CLI (Expected Output)
a) Start API Server
$ python app.py * Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/
b) Trigger Job via CURL
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/api/pyats/run-test \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"test_name": "sample_test_job", "testbed_file": "testbed.yaml"}'
{
"status": "started",
"job_id": "7f98e20b-d5b5-4f1c-bf13-8f6c65e1d9a1",
"result": "Job started successfully."
}
c) Check Job Status
$ curl http://localhost:5000/api/pyats/job-status/7f98e20b-d5b5-4f1c-bf13-8f6c65e1d9a1
{
"job_id": "7f98e20b-d5b5-4f1c-bf13-8f6c65e1d9a1",
"status": "Completed"
}
FAQs
Q1. What is the purpose of building REST API wrappers around pyATS jobs?
A1. REST API wrappers allow network engineers to trigger, manage, and monitor pyATS jobs programmatically over HTTP. This enables integration with web portals, external applications, and CI/CD pipelines, providing centralized automation control in a scalable way.
Q2. How does a Python REST API wrapper interact with pyATS jobs?
A2. The API wrapper exposes endpoints (e.g., POST /run-test, GET /job-status) that internally invoke pyATS test scripts using Python subprocesses or directly calling Python functions. The wrapper handles inputs, returns job status, and delivers structured output (JSON).
Q3. Why use Flask or FastAPI for building REST API wrappers?
A3. Flask and FastAPI are lightweight Python frameworks ideal for building REST APIs. They simplify endpoint creation, handle request parsing, and provide asynchronous support for long-running pyATS jobs, improving responsiveness and scalability.
Q4. How is authentication handled in these REST API wrappers?
A4. Authentication can be implemented using token-based methods like JWT (JSON Web Token) or API keys to ensure that only authorized users or applications can trigger pyATS jobs, making the system secure in production environments.
Q5. Can the API wrapper handle concurrent job execution?
A5. Yes. With asynchronous endpoints or background job queues (e.g., Celery), the REST API can manage multiple concurrent pyATS jobs, track job IDs, and provide job status or results on demand.
Q6. How are job results delivered to API consumers?
A6. Once a pyATS job completes, the API wrapper returns a structured JSON response containing test results, device outputs, pass/fail status, and logs. Alternatively, results can be saved to a centralized database for later retrieval.
Q7. Is it possible to extend this framework for multi-vendor environments?
A7. Absolutely. The REST API is vendor-agnostic and can trigger pyATS jobs for Cisco, Arista, Juniper, or any supported platform by specifying the appropriate testbed and test scripts in the API request payload.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Building Python REST API Wrappers Around pyATS Jobs Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
You’ve now mastered building Python REST API wrappers around pyATS jobs, enabling powerful, production-ready automation frameworks fit for modern network environments.
Advance your career as a Python for Network Engineer with hands-on, real-world automation workflows, Python scripting, API development, and operational best practices.
Enroll today in Trainer Sagar Dhawan’s 3-month instructor-led training program:
https://course.networkjourney.com/python-ansible-api-cisco-devnet-for-network-engineers/
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #89 PyATS Series] Building Python REST API Wrappers Around pyATS Jobs Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-89-PyATS-Series-Building-Python-REST-API-Wrappers-Around-pyATS-Jobs-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![Real-World Use Case of Conditional Routing in Enterprise Networks [ CCNP ENTERPRISE ]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Real-World-Use-Case-of-Conditional-Routing-in-Enterprise-Networks-CCNP-ENTERPRISE-.png)
![[Day #14 PyATS Series] Using pyATS “Jobs” for Multi-Device Tests with Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day14-PyATS-Series-Using-pyATS-Jobs-for-Multi-Device-Tests-with-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![[Day #24 PyATS Series] BGP Neighbor Validation (Multi-Vendor) Using pyATS for Cisco](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day-24-PyATS-Series-BGP-Neighbor-Validation-Multi-Vendor-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)