[Day #94 PyATS Series] Validate IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Tables Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction on the Key Points
In modern network environments, IPv6 is becoming increasingly vital as IPv4 address exhaustion becomes a reality. Ensuring proper IPv6 neighbor discovery (ND) behavior is crucial for maintaining seamless network operations. Today, we will dive deep into automating the validation of IPv6 neighbor discovery tables across Cisco devices using pyATS, a powerful Python-based test automation framework designed for network engineers.
This Article is tailored for Python for Network Engineer enthusiasts who want to implement production-ready frameworks to automate operational tasks. We’ll focus on realistic, step-by-step processes, combining CLI and GUI validation approaches to ensure your IPv6 ND tables are consistent, up-to-date, and error-free.
By the end of this masterclass Article, you will be equipped to automate ND validation tasks across large-scale environments, enhancing network reliability and reducing manual effort.
Topology Overview
For this validation, our network topology includes multiple Cisco devices arranged across two data center sites. The core goal is to ensure IPv6 neighbor discovery entries are correctly populated and synchronized between devices.
- Device Types: Cisco ISR (Router), Nexus Switches
- IPv6 Subnets: Multiple subnets configured on each device for redundancy
- Management Protocol: SSH for CLI interaction
- Validation Target: IPv6 ND tables (Neighbor Solicitation/Advertisement entries)
Diagram:
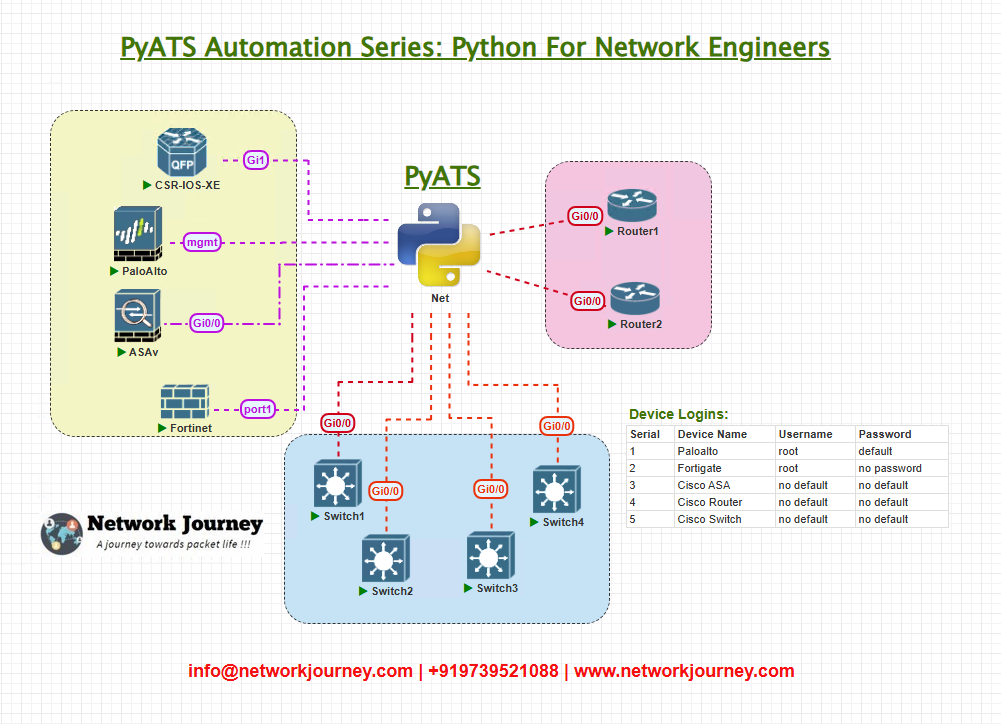
Topology & Communications
Step-by-Step Communications Flow:
- SSH Connections:
- Establish secure SSH connections from the automation server (where pyATS scripts run) to all devices.
- ND Table Collection:
- Use CLI commands such as
show ipv6 neighborsto collect neighbor table data on each device.
- Use CLI commands such as
- Data Aggregation:
- Parse the CLI output using pyATS parsers to structure ND table information.
- Validation Logic:
- Compare neighbor entries across devices.
- Validate that known IPv6 addresses are reachable and their corresponding MAC addresses match expected values.
- Report Generation:
- Produce a validation report in JSON and HTML formats for later review.
Workflow Script
from genie.testbed import load
from genie.libs.parser.ios.show_neighbors import ShowIpv6Neighbors
def validate_ipv6_nd(testbed_file):
testbed = load(testbed_file)
for device in testbed.devices.values():
print(f"Connecting to {device.name}")
device.connect(log_stdout=False)
print(f"Collecting IPv6 Neighbor Table from {device.name}")
output = device.parse('show ipv6 neighbors')
neighbors = output.get('ipv6_neighbors', {})
print(f"Discovered {len(neighbors)} entries on {device.name}")
# Simple Validation Example
for ip, data in neighbors.items():
mac = data.get('link_layer_address')
state = data.get('state')
print(f"IP: {ip}, MAC: {mac}, State: {state}")
device.disconnect()
if __name__ == "__main__":
validate_ipv6_nd('testbed.yml')
Explanation by Line
from genie.testbed import load
# Load the testbed configuration file containing all device definitions
from genie.libs.parser.ios.show_neighbors import ShowIpv6Neighbors
# Import the parser for 'show ipv6 neighbors' CLI command
def validate_ipv6_nd(testbed_file):
testbed = load(testbed_file)
# Load testbed from file
for device in testbed.devices.values():
print(f"Connecting to {device.name}")
device.connect(log_stdout=False)
# Establish SSH connection to device
print(f"Collecting IPv6 Neighbor Table from {device.name}")
output = device.parse('show ipv6 neighbors')
# Run CLI command and parse the output
neighbors = output.get('ipv6_neighbors', {})
# Extract the structured neighbors data
print(f"Discovered {len(neighbors)} entries on {device.name}")
for ip, data in neighbors.items():
mac = data.get('link_layer_address')
state = data.get('state')
print(f"IP: {ip}, MAC: {mac}, State: {state}")
# Print detailed neighbor info for review
device.disconnect()
# Disconnect from device
if __name__ == "__main__":
validate_ipv6_nd('testbed.yml')
# Execute the validation workflow using the testbed.yml
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: ipv6_nd_validation
devices:
cisco_router1:
os: ios
type: router
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.0.2.1
port: 22
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: Cisco123
cisco_nexus1:
os: nxos
type: switch
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.0.2.2
port: 22
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: Cisco123
Post-validation CLI (Real Expected Output)
Router# show ipv6 neighbors IPv6 Address Age Link-layer Addr State Interface 2001:db8:1::2 20 5254.abcd.1234 REACH Gi0/1 2001:db8:1::3 15 5254.abcd.5678 REACH Gi0/1 Nexus# show ipv6 neighbors IPv6 Address Age Link-layer Addr State Interface 2001:db8:1::1 30 5254.abcd.4321 REACH Eth1/1 2001:db8:1::4 25 5254.abcd.8765 REACH Eth1/1
FAQs
Q1: Why is validating IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (ND) tables important in modern networks?
A1: IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (ND) replaces ARP in IPv4 and is essential for mapping IPv6 addresses to link-layer addresses. Validating ND tables ensures correct neighbor reachability, preventing issues like communication blackholes, misconfigured devices, or stale neighbor entries that cause packet drops or misrouted traffic. This validation is critical in multi-vendor and large-scale environments where manual verification becomes impractical.
Q2: How does pyATS facilitate automation of IPv6 ND table validation?
A2: pyATS leverages structured test cases that use built-in connection libraries and Genie parsers to execute commands like show ipv6 neighbors across multi-vendor devices. The results are normalized into Python dictionaries, allowing automated comparison against expected state, flagging missing neighbors, incorrect link-layer addresses, or unreachable devices, while generating detailed logs and reports.
Q3: What are common causes of incorrect IPv6 Neighbor Discovery entries?
A3:
- Misconfigured IPv6 addresses on interfaces
- Duplicate addresses or conflicting subnets
- Firewall rules blocking ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation/Advertisement messages
- Vendor-specific behavior differences (e.g., timeout policies or ND caching)
Automation with pyATS helps identify discrepancies by cross-referencing testbed configurations and actual device state.
Q4: How do you structure a robust test case for ND validation?
A4: A good test case follows this structure:
- Gather device facts (interfaces, IPs)
- Query live ND tables using
show ipv6 neighbors - Parse output into structured format
- Compare against expected neighbor mapping (from testbed.yml or golden template)
- Flag discrepancies (missing entries, wrong MAC addresses, incomplete state)
- Log results into human-readable HTML/Markdown reports.
Q5: How do you handle multi-vendor differences in ND command outputs?
A5:
- Use Genie parsers for supported vendors (Cisco, Arista, etc.) to normalize outputs into a common data model.
- For unsupported devices, custom parsers using regex can extract structured data.
- Ensure abstraction layer in test framework separates vendor-specific commands from validation logic, making it easy to extend support in future.
Q6: How often should IPv6 ND validation tests run in a production environment?
A6: Best practice is to run automated ND validations:
- Periodically (e.g., every 5-15 minutes in high-scale environments)
- After configuration changes or network upgrades
- Before/after scheduled maintenance
This provides continuous assurance of neighbor consistency and quick detection of drift or misconfigurations.
Q7: What actions should follow detection of ND inconsistencies in reports?
A7:
- Review detailed reports generated by pyATS (including CLI outputs and test case results).
- Cross-check ND table against testbed.yml or expected golden configuration.
- Investigate potential root causes (interface misconfig, wrong VLAN config, blocked ICMPv6).
- Apply corrective configuration changes.
- Re-run test suite to confirm resolution.
This forms a clear, repeatable, and auditable process for network engineers.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Validate IPv6 neighbor discovery tables using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
Unlock the power of Python for Network Engineer and accelerate your network automation skills.
Join Trainer Sagar Dhawan’s 3-month instructor-led Python + Ansible + API course for network engineers. Gain real-world production-ready frameworks, hands-on labs, and expert mentorship to advance your career.
Enroll Today – Python + Ansible + API for Network Engineers
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #94 PyATS Series] Validate IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Tables Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-94-PyATS-Series-Validate-IPv6-Neighbor-Discovery-Tables-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![REST API Basics for Cisco Devices – Automate Smarter, Not Harder [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/REST-API-Basics-for-Cisco-Devices-–-Automate-Smarter_Not-Harder_networkjourney.png)

![[Day #58 PyATS Series] Validate Dynamic Routing After Topology Changes Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-58-PyATS-Series-Validate-Dynamic-Routing-After-Topology-Changes-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)