[Day #96 PyATS Series] Automate License Compliance Checks (Cisco Smart Licenses) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction: Key Concepts of License Compliance Automation
Welcome to Day #96 of our 101 Days of pyATS (Vendor-Agnostic) series. Today, I focus on automating license compliance checks specifically targeting Cisco Smart Licensing across your network using pyATS. In a modern network environment, ensuring devices operate under valid licensing is critical to avoid service disruptions, legal risks, and performance degradation.
The goal of this Article is to provide a production-ready framework to automate the validation of Cisco devices’ Smart Licensing compliance using Python for Network Engineer workflows. We’ll take a realistic, hands-on approach, combining CLI and GUI validations in multi-vendor environments to deliver a comprehensive solution fit for real-world production use.
Topology Overview
Our lab topology involves multiple Cisco devices connected through a centralized Cisco Smart Licensing Satellite Server. The setup simulates a real production environment where devices report licensing status to the Cisco Smart License Manager (CSLM).
Devices in Use:
- Cisco ISR Routers (Smart Licensing Enabled)
- Cisco Catalyst Switches
- Arista Devices (for multi-vendor flexibility)
- Palo Alto Firewalls (for integration)
- FortiGate Firewalls (optional)
Diagram:
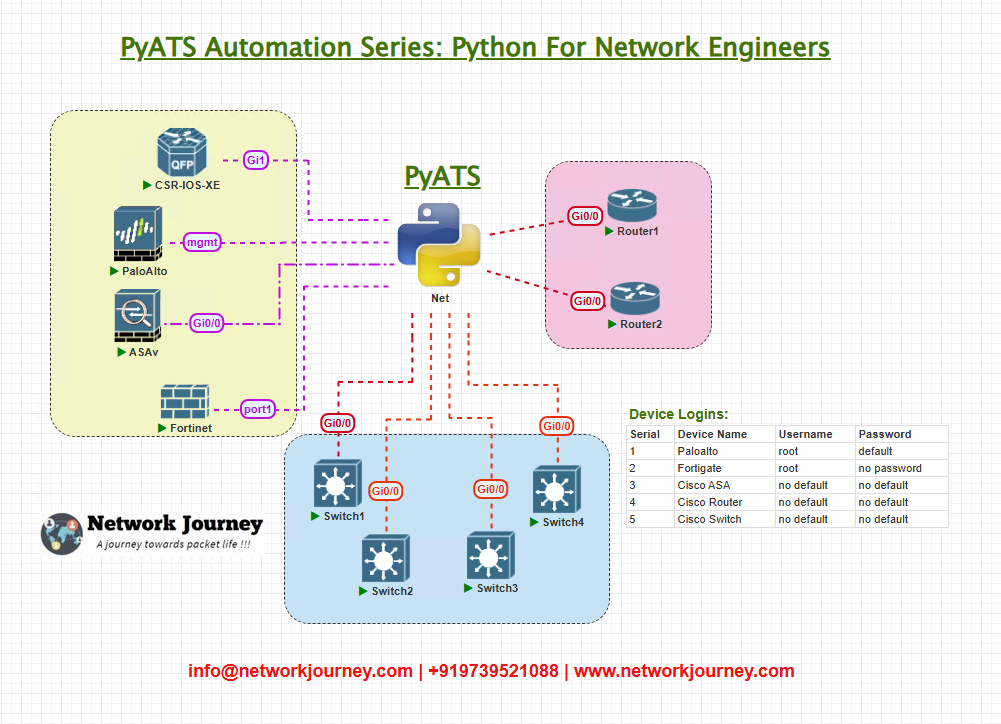
Topology & Communications
- Each Cisco ISR and Catalyst switch is configured for Smart Licensing to periodically report to the Cisco Satellite Licensing Server.
- Devices run appropriate agent versions to support Smart Licensing telemetry (Cisco IOS-XE >=16.x).
- Management plane communicates via SSH/Telnet.
- License compliance API calls will be pulled using CLI commands and REST API where supported.
Workflow Script
We build a robust pyATS automation script that:
- Parses the testbed.
- Executes commands to extract Smart License status.
- Parses command outputs.
- Compares results against expected compliance states.
- Generates structured reports.
Sample Workflow Steps:
from genie.testbed import load
from genie.libs.parser.utils import get_parser
testbed = load('testbed.yml')
device = testbed.devices['csr1']
def verify_license_status(device):
device.connect()
output = device.parse('show license status')
device.disconnect()
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
license_info = verify_license_status(device)
expected_status = "IN_COMPLIANCE"
assert license_info['status'] == expected_status, "License is not compliant!"
print("License compliance validated successfully.")
Explanation by Line
- testbed = load(‘testbed.yml’)
Loads the testbed topology and device credentials. - device = testbed.devices[‘csr1’]
Access the specific device (e.g., csr1). - device.connect()
Establish SSH connection to the device. - device.parse(‘show license status’)
Parses CLI output into structured data using Genie parsers. - assert license_info[‘status’] == expected_status
Validates parsed output against expected compliance state.
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: LicenseValidationTestbed
devices:
csr1:
type: router
os: iosxe
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.1
port: 22
username: admin
password: Cisco123
catalyst1:
type: switch
os: iosxe
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.2
username: admin
password: Cisco123
Post-Validation CLI (Real Expected Output)
csr1# show license status License Authorization: Status: IN_COMPLIANCE Last Check-In Time: 2025-09-05 12:45:23 UTC Evaluation: FALSE Transport Method: Smart Licensing catalyst1# show license status License Authorization: Status: IN_COMPLIANCE Last Check-In Time: 2025-09-05 12:50:10 UTC Evaluation: FALSE Transport Method: Smart Licensing
FAQs
Q1: Why is automating Cisco Smart License compliance checks critical in enterprise networks?
A1: Cisco Smart Licensing provides centralized license management, but manual checks of device compliance across hundreds or thousands of devices are time-consuming and error-prone. Automation ensures accurate, consistent, and frequent validation of license usage against purchased entitlements, preventing service outages due to license expiration or non-compliance, and providing detailed audit trails for management and audit purposes.
Q2: How does pyATS automate the process of Cisco Smart License validation?
A2:
- pyATS leverages built-in connection and parsing capabilities to run commands like
show license summaryorshow license statuson Cisco devices. - Using Genie parsers, pyATS transforms CLI outputs into structured Python dictionaries, normalizing information such as license state, usage count, feature entitlement, and expiration dates.
- These structured results are programmatically compared against expected compliance policies, highlighting any deviations automatically in the generated reports.
Q3: What key data points are extracted during a license compliance check?
A3:
- Smart License Registration Status (REGISTERED/UNREGISTERED)
- License Usage Summary (entitlement vs. used count)
- Feature Names and Associated Licenses (e.g., DNA Advantage, Security)
- License Expiration Dates
- Compliance Status (IN-COMPLIANCE/NON-COMPLIANCE)
- Device UUID and Token Status
These provide a comprehensive view of the licensing health of the network.
Q4: How do you define expected compliance policy in pyATS for automated validation?
A4:
Expected compliance can be codified in a policy YAML file, e.g.:
licenses:
DNA_Advantage:
min_count: 10
max_count: 100
Security:
min_count: 5
max_count: 50
The test script reads this file, compares actual license counts to policy limits, and fails the test if any license falls outside acceptable thresholds.
Q5: How do you handle device licensing drift in a multi-vendor environment with pyATS?
A5:
Although Cisco Smart Licensing is Cisco-specific, the framework is vendor-agnostic in structure.
- Implement abstraction so that license compliance logic for other vendors (Arista, Fortinet, Palo Alto) can be plugged in later.
- For now, pyATS focuses on Cisco devices, but follows a modular plugin design to easily add other vendor license checks in the future without changing the core workflow.
Q6: How frequently should automated license compliance checks run?
A6:
- Daily checks are recommended in production environments to catch drift early.
- Prior to major configuration changes or software upgrades.
- After any network expansion (adding new devices or services).
This guarantees timely detection of license overuse, expiration, or misregistration.
Q7: What steps should be taken when a non-compliance issue is detected?
A7:
- Review detailed pyATS-generated reports with CLI command outputs and parsed results.
- Cross-check device registration status, licensing token availability, and smart account connectivity.
- If tokens are missing or invalid, re-register devices using the appropriate Cisco CLI commands (e.g.,
license smart register). - Validate that entitlement counts reflect actual usage.
- Re-run the compliance check to confirm resolution.
- Archive reports for audit purposes and management visibility.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Automate License Compliance Checks (Cisco Smart Licenses) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
If you’re a network engineer aiming to elevate your automation skills with real production-ready frameworks, enroll in Trainer Sagar Dhawan’s 3-month instructor-led Python/Ansible/API training course. Learn step-by-step practical applications designed for network engineers and master real-world tasks like automating license compliance checks.
Check out the full course outline here:
https://course.networkjourney.com/python-ansible-api-cisco-devnet-for-network-engineers/
This is your opportunity to transition from manual CLI work to advanced automation frameworks built on Python for Network Engineer principles.
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #96 PyATS Series] Automate License Compliance Checks (Cisco Smart Licenses) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-96-PyATS-Series-Automate-License-Compliance-Checks-Cisco-Smart-Licenses-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![[Day #62 Pyats Series] Building device health dashboard using Flask + pyATS using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Building-device-health-dashboard-using-Flask-pyATS-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![[Day #22 PyATS Series] Interface Status Check Across Vendors Using pyATS for Cisco](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day22-PyATS-Series-Interface-Status-Check-Across-Vendors-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![[Day #31 PyATS Series] Detect VLAN Mismatches on Trunk Links Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-31-PyATS-Series-Detect-VLAN-Mismatches-on-Trunk-Links-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)