Multicast in SD-WAN and Cloud Networks – Bringing One-to-Many to the Next Gen WAN [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
In this blog post, I’ll walk you through everything—from how multicast works (or breaks) in SD-WAN to cloud-native alternatives for multicast delivery, along with CLI examples, EVE-NG labs, and real-world use cases. Let’s dive into how the one-to-many paradigm is adapting to modern WAN architecture.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief – Multicast in the Era of SD-WAN and Cloud
Multicast allows efficient one-to-many delivery of data such as video streams, stock tickers, and software updates. In traditional on-prem networks, it leverages protocols like IGMP, PIM, and RPF to build delivery trees.
However, in SD-WAN, we deal with:
- Overlay tunnels
- Encrypted transport
- Dynamic routing topologies
- Vendor-driven forwarding planes
This causes challenges like:
- Lack of native multicast support in tunnels
- Difficulty performing RPF checks
- Cloud-native networks lacking Layer 2 multicast awareness
Moreover, cloud environments like AWS and Azure do not natively support multicast. Engineers must redesign multicast delivery using unicast replication, application-level multicast, or overlay-based solutions like Cisco SD-WAN’s vSmart-driven replication.
Multicast Deployment Models in Modern WAN
- SD-WAN with Native Multicast Support
Vendors like Cisco (Viptela), Fortinet, and Aruba support limited multicast over overlays using centralized controllers. - Multicast over GRE/IPSec
Legacy method using tunnels between routers. Not scalable. - Multicast to Unicast Conversion
Stream is replicated as unicast to each endpoint—simplifies transport but increases bandwidth. - Cloud Application Replication (Server-Side)
Apps like Zoom, YouTube Live, etc., use server farms to replicate streams, removing the need for true multicast.
Comparision – Traditional vs SD-WAN Multicast
| Aspect | Traditional WAN | SD-WAN/Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | IGMP, PIM, MSDP | Vendor-specific or app-based |
| Transport | IP natively supports multicast | Overlay tunnels need emulation |
| Delivery Tree | PIM-driven multicast trees | vSmart controller-based (e.g., Cisco SD-WAN) |
| Troubleshooting | RPF, show ip mroute | Control policy, centralized flow replication |
| Cloud Support | Limited | Native multicast unsupported in AWS, Azure |
| Scalability | High (on LAN) | Depends on replication design |
Pros and Cons
| Pros (SD-WAN/Cloud Multicast) | Cons |
|---|---|
| Centralized policy control | Not truly multicast over IP |
| Works across hybrid transport | Increased unicast replication overhead |
| Cloud-native scaling | Complex design and vendor lock-in |
| Integrates with app-layer delivery | May not meet real-time latency needs |
| Simplifies branch deployments | Requires deep understanding of platform |
Essential CLI Commands
| Platform | Purpose | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco SD-WAN (vEdge/vSmart) | View multicast routes | show omp multicast route |
| Cisco IOS | View PIM neighbors | show ip pim neighbor |
| Cisco IOS | Multicast routing table | show ip mroute |
| Cisco IOS | IGMP groups | show ip igmp groups |
| Fortinet SD-WAN | Multicast debug | diagnose debug application pim -1 |
| Viptela | See multicast control policies | show running-config policy |
| Viptela | View multicast client registration | show multicast clients |
| All | Verify replication | ping <multicast IP> or packet captures |
Real-World Use Case – IPTV Over SD-WAN in a Retail Chain
| Scenario | Details |
|---|---|
| Customer | Retail company with 50 branches |
| Requirement | Deliver centralized IPTV content to branches over SD-WAN |
| Challenge | No native multicast support over encrypted WAN |
| Solution | Cisco SD-WAN with vSmart multicast policy and unicast replication |
| Outcome | IPTV stream successfully delivered to all branches using optimized policies |
| Bonus | Enabled centralized control and easy branch provisioning |
EVE-NG Lab – Simulating Multicast over SD-WAN
Topology Diagram
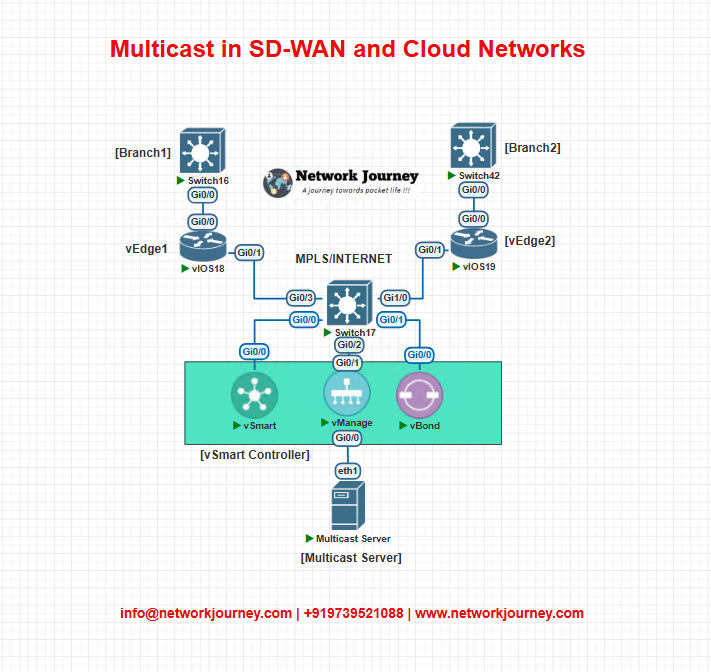
IP Schema
| Device | Interface | IP |
|---|---|---|
| vEdge1 | GE0/0 | 192.168.10.1/24 |
| vEdge2 | GE0/0 | 192.168.20.1/24 |
| Server | GE0/0 | 10.1.1.10 (Multicast Source) |
| Group IP | N/A | 239.1.1.1 |
CLI Configuration – Cisco SD-WAN vManage/vEdge
On vSmart (Policy)
policy
lists
prefix-list MULTICAST-GROUP
ip-prefix 239.1.1.1/32
...
centralized-control-policy MULTICAST-CONTROL
sequence 10
match
prefix-list MULTICAST-GROUP
action accept
On vEdge Devices
interface ge0/0
ip address 192.168.10.1/24
ip pim sparse-mode
ip igmp version 2
ip multicast-routing
ip pim rp-address 10.1.1.10
On Server (Linux)
ffmpeg -re -i video.mp4 -f mpegts udp://239.1.1.1:5000
Verification
vEdge# show ip igmp groups
vEdge# show omp multicast route
vSmart# show policy from-vsmart
Troubleshooting Tips
| Problem | Symptom | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No stream on branch | No IGMP join seen | Verify IGMP version and querier |
| High bandwidth | Unicast replication per branch | Enable efficient SD-WAN replication |
| RPF failures | Source not in routing table | Check underlay and OMP route propagation |
| Stream freezes | Packet loss | Use QoS and prioritize multicast DSCP |
| Unexpected flooding | IGMP snooping disabled | Enable on LAN switches if applicable |
FAQs – Multicast in SD-WAN and Cloud
1. Can multicast traffic be used across SD-WAN networks?
Answer:
Yes, but with careful design and vendor support. Traditional IP multicast relies on PIM and IGMP, which don’t natively work across SD-WAN overlays unless specifically supported.
Some SD-WAN solutions, like Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela), now support Multicast over the Overlay (OMP control plane)—allowing one-to-many distribution of multicast streams across vEdges/cEdges.
However, for platforms that don’t natively support multicast, you’ll need to tunnel, replicate unicast, or use multicast gateways.
2. How is multicast delivered across SD-WAN fabric?
Answer:
In Cisco SD-WAN, multicast is enabled by:
- Enabling multicast routing (PIM-SM) on vEdges/cEdges.
- Using the Overlay Management Protocol (OMP) to propagate multicast routing info.
- Forming Multicast Service Routes (MSRs) between edges.
The controller (vSmart) acts as the brain, learning group memberships and forming data-plane trees (like PIM). It’s more controlled than traditional multicast, fitting SD-WAN’s policy-centric model.
3. What are the use cases for multicast in SD-WAN and cloud networks?
Answer:
Common use cases include:
- Video conferencing and live corporate streaming across branches.
- Real-time market data in financial institutions.
- IoT updates or firmware pushes to multiple edge sites.
- Multicast-based applications in hybrid cloud, such as SCADA, digital signage, and telemetry.
Multicast saves bandwidth when the same content needs to reach multiple receivers — a crucial benefit in WAN optimization.
4. What are the challenges of enabling multicast in cloud environments like AWS, Azure, or GCP?
Answer:
Most public clouds don’t support native Layer 2 multicast. Multicast in cloud has these limitations:
- No IGMP or PIM natively.
- Virtual networks are isolated—requiring overlay tunneling or host-based replication.
- Requires third-party tools like GRE tunnels, VXLAN, or multicast gateways.
- Apps must be multicast-aware but cloud-friendly (e.g., SSM-style unicast streams).
Cloud providers prioritize scalability and stateless networking, which doesn’t always align with classic multicast models.
5. What alternatives exist if multicast isn’t supported in a cloud network?
Answer:
You can replicate multicast using:
- Unicast replication from a central server to each receiver.
- Application-layer multicast (e.g., WebRTC, RTMP/CDN-style distribution).
- Overlay multicast using GRE, VXLAN, or SD-WAN fabric.
- Deploy a Multicast Proxy VM in the cloud that handles IGMP joins and forwards streams to the application.
These methods mimic multicast functionality while adapting to cloud and overlay networking models.
6. How do I configure multicast in Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela)?
Answer:
Multicast configuration in Cisco SD-WAN involves:
- Enable PIM on VPN interfaces:
vpn 10
interface ge0/1
pim sparse-mode
- Define multicast group policies in centralized control policy:
omp
advertise multicast
- Enable IGMP and RP settings:
ip pim rp-address 1.1.1.1
ip igmp
- Use
show omp multicast,show ip pim rp,show ip mroutefor verification.
Cisco vManage also offers a GUI-based template workflow.
7. How does multicast differ between underlay vs overlay in SD-WAN?
Answer:
- Underlay multicast relies on traditional PIM/IGMP, needing every router in the path to support multicast.
- Overlay multicast (SD-WAN) uses tunnels and OMP to manage group memberships and forwarding trees.
Overlay multicast is application-aware, centrally controlled, and policy-enforced, offering better scalability and visibility in modern WAN architectures.
8. Is Source-Specific Multicast (SSM) supported in SD-WAN or cloud?
Answer:
Support for SSM (e.g., IGMPv3 + PIM-SSM) depends on the vendor and environment:
- Cisco SD-WAN supports basic PIM-SM and IGMPv2, and some advanced releases add partial SSM support.
- In cloud, true SSM is rare unless implemented at the app level using custom socket programming or through content delivery platforms.
If your app supports SSM, validate whether SD-WAN edges and firewalls honor the (S,G) flows without suppression.
9. How do I troubleshoot multicast issues in SD-WAN environments?
Answer:
Checklist to troubleshoot:
- Verify IGMP joins using
show ip igmp groups. - Confirm PIM neighbors with
show ip pim neighbor. - Check OMP multicast routes using
show omp multicast. - Validate policies pushing multicast groups (vSmart).
- Capture traffic with debugs or PCAP to confirm stream delivery.
- Look for replication delays or packet drops on tunnel interfaces.
Use vManage Logs, CLI show/debug, and edge counters for full visibility.
10. What’s the future of multicast in SD-WAN and cloud-native networks?
Answer:
Multicast is evolving, but not going away. Trends include:
- Transitioning to application-layer multicast for scalability.
- Hybrid architectures that use SD-WAN or cloud gateways to emulate multicast.
- Cloud-native multicast frameworks, possibly built on SRv6, EVPN, or multicast CDN services.
- Vendors increasingly building multicast-aware overlays, making deployment smoother across hybrid networks.
YouTube Video Link
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Multicast in SD-WAN and Cloud Networks – Bringing One-to-Many to the Next Gen WAN is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Multicast in SD-WAN and Cloud Networks – Bringing One-to-Many to the Next Gen WAN [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Multicast-in-SD-WAN-and-Cloud-Networks-–-Bringing-One-to-Many-to-the-Next-Gen-WAN.png)

![[Day 70] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Wireless NAC End-to-End Lab Validation](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-70-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Wireless-NAC-End-to-End-Lab-Validation.png)
![The Ultimate IPv6 Troubleshooting Guide: Tools, Tips, and Labs [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/nj-blog-post-ipv6-troubleshooting-guide.jpg)