OSPF LSA Types Explained: Complete Guide with CLI, EVE-NG Lab & Real-World Use Cases [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
Today we’re going to tackle one of the most crucial yet often misunderstood parts of OSPF—LSA Types. When I train CCNA and CCNP candidates, many get confused with when and where to use Type 1 vs Type 3 or what the heck Type 7 LSAs really do in a stub area.
So, I created this blog to simplify things. Whether you’re prepping for certifications or dealing with real production networks, this post will give you clarity on OSPF LSAs, complete with CLI commands, a real-world lab, and troubleshooting tips. Let’s go!
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief – What are OSPF LSAs?
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a link-state routing protocol that uses Link State Advertisements (LSAs) to exchange routing and topology information.
LSAs are building blocks of OSPF—they tell routers about:
- Links and neighbors
- External routes
- Network topology
Each LSA Type serves a unique purpose and is confined to specific areas based on OSPF design.
Key LSA Types (0–7)
- Type 1 (Router LSA) – Advertises a router’s interfaces and cost, stays within the area.
- Type 2 (Network LSA) – Generated by the DR, represents a multi-access segment like Ethernet.
- Type 3 (Summary LSA) – Sent by ABRs to advertise routes between areas.
- Type 4 (ASBR Summary LSA) – Tells other areas about the ASBR’s location.
- Type 5 (External LSA) – Advertises routes redistributed from other protocols like BGP or EIGRP.
- Type 6 – Multicast (Not commonly used)
- Type 7 (NSSA External LSA) – Used in NSSA areas instead of Type 5s.
Types 1–2 are intra-area, 3–4 are inter-area, and 5/7 are external routes.
Summary – OSPF LSA Types, Scope & Use Cases
| LSA Type | Name | Generated By | Scope | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Router LSA | All routers | Area-local | Describes router interfaces and costs |
| 2 | Network LSA | DR only | Area-local | Lists routers in a broadcast segment |
| 3 | Summary LSA | ABR | Area to area | Advertises routes between areas |
| 4 | ASBR Summary LSA | ABR | Area to area | Points to ASBR location |
| 5 | External LSA | ASBR | Entire OSPF domain | Redistributed routes from outside OSPF |
| 6 | Multicast LSA | (Not used) | N/A | Specialized – not widely implemented |
| 7 | NSSA External LSA | ASBR in NSSA | NSSA area only | External routes in NSSA instead of Type 5 |
Essential CLI Commands (Show, Debug, Verify)
| Task | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| View OSPF LSA database | show ip ospf database | Shows all LSA types in the database |
| View Type 1 LSAs | show ip ospf database router | Lists router LSAs |
| View Type 2 LSAs | show ip ospf database network | Lists network LSAs |
| View inter-area summary LSAs | show ip ospf database summary | Lists Type 3/4 LSAs |
| View external routes (Type 5) | show ip ospf database external | Lists redistributed routes |
| View Type 7 LSAs in NSSA | show ip ospf database nssa-external | NSSA-specific LSAs |
| Debug LSA updates | debug ip ospf lsa-generation | Watch LSA generation |
Real-World Use Cases
| Scenario | LSA Types Involved | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Basic OSPF single area | Type 1, 2 | Internal routers and multi-access segments |
| ABR between Area 0 and Area 1 | Type 1, 2, 3 | Routes summarized from one area to another |
| Redistributing BGP into OSPF | Type 5, Type 4 | Injecting external routes via ASBR |
| NSSA with external routes | Type 7 (converted to 5) | Type 7 LSAs used to avoid full Type 5 flooding |
| DR/BDR election and segment updates | Type 2 | Generated by DR to list segment participants |
EVE-NG Lab – OSPF LSA Types Demonstration
Lab Objective:
- Configure OSPF with multiple areas and observe LSA types exchanged between routers.
- Simulate NSSA and external route redistribution.
Topology Diagram
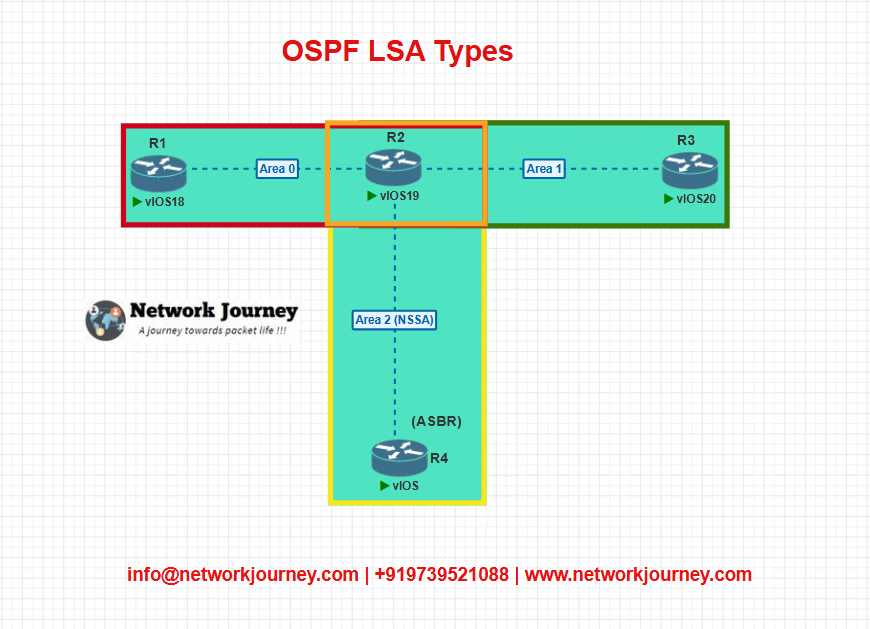
Configuration Snippets
R1 (Backbone Router):
router ospf 1 network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R2 (ABR):
router ospf 1 network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 1 network 10.2.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
R3 (Area 1):
router ospf 1 network 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
R4 (NSSA + Redistribution):
router ospf 1 network 10.2.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 2 nssa redistribute static subnets
After configuration, use
show ip ospf databaseto observe Type 1, 3, 5, and 7 LSAs.
Troubleshooting Tips
| Problem | Likely Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Missing external route | ASBR not generating Type 5/7 | Check redistribute and route map configs |
| Type 3 LSA not received | ABR not configured correctly | Verify ABR interface area membership |
| Incomplete topology | Router not forming neighbor | Check OSPF network and hello timers |
| No Type 7 in NSSA | Area not defined as NSSA | Use area 2 nssa on both ends |
| LSAs stuck in database | Database not aging | Use clear ip ospf process to refresh |
FAQ – OSPF LSA Types
1. What is an LSA in OSPF and why is it important?
Answer:
LSA stands for Link-State Advertisement. It’s the core data structure used in OSPF to share routing and topology information between routers. LSAs are flooded within areas, forming the Link-State Database (LSDB). Routers then run the Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm on this LSDB to calculate optimal paths. Without LSAs, OSPF cannot function.
2. How many LSA types exist in OSPF, and are all of them used commonly?
Answer:
There are 11 types of LSAs in OSPFv2. However, in most enterprise networks, you’ll frequently encounter:
- Type 1 – Router LSA
- Type 2 – Network LSA
- Type 3 – Summary LSA
- Type 4 – ASBR Summary LSA
- Type 5 – External LSA
- Type 7 – NSSA External LSA
Types 6, 8, 9, 10, and 11 are rarely used and mostly appear in special scenarios like multicast OSPF or Opaque LSAs for TE extensions.
3. What is a Type 1 LSA (Router LSA)?
Answer:
A Type 1 LSA is generated by every OSPF router for each area it belongs to. It contains:
- The router’s connected interfaces.
- IP addresses.
- Link types and cost.
These LSAs are flooded within the area and used by other routers to build a map of that area’s topology.
4. What is a Type 2 LSA (Network LSA)?
Answer:
A Type 2 LSA is generated by the Designated Router (DR) on broadcast and non-broadcast multi-access (NBMA) networks. It:
- Represents the multi-access network as a pseudo-node.
- Lists all routers connected to that network.
It simplifies SPF calculations by reducing the number of neighbor relationships each router has to manage.
5. What is a Type 3 LSA (Summary LSA), and how does it work across areas?
Answer:
A Type 3 LSA is generated by ABRs to advertise inter-area routes. It:
- Summarizes routes from one area and injects them into another.
- Does not carry topology details — only reachability info.
This helps OSPF scale by minimizing LSDB sizes in large, multi-area networks.
6. What is a Type 4 LSA (ASBR Summary LSA)?
Answer:
Type 4 LSAs are also generated by ABRs, but they advertise the reachability of an ASBR. This is essential because:
- When an ASBR injects external routes (via Type 5 or 7 LSAs), routers in other areas need to know how to reach the ASBR.
- Type 4 LSAs provide this path information.
7. What is a Type 5 LSA (External LSA)?
Answer:
A Type 5 LSA is generated by an ASBR to advertise external routes from other protocols (like BGP, static, EIGRP, etc.). It:
- Is flooded throughout the OSPF domain (except stub areas).
- Carries two types of external metrics: E1 (cumulative cost) and E2 (default, external cost only).
Use Type 5 LSAs when you need OSPF to carry non-OSPF routes.
8. What is a Type 7 LSA and where is it used?
Answer:
A Type 7 LSA is generated by an ASBR inside an NSSA area (Not-So-Stubby Area). Since Type 5 LSAs aren’t allowed in NSSA, Type 7 is used instead and:
- Is converted to Type 5 by the ABR when leaving the NSSA.
- Allows route redistribution while preserving the stub nature of the area.
Type 7 LSAs provide flexibility in hybrid designs.
9. How can I view LSA information using CLI on Cisco routers?
Answer:
Use the following commands:
- View all LSAs: bashCopyEdit
show ip ospf database - View specific types: bashCopyEdit
show ip ospf database router show ip ospf database network show ip ospf database summary show ip ospf database external
These commands are crucial for troubleshooting and understanding OSPF behavior in labs or production.
10. Can you summarize LSA types, their sources, and scopes in a table?
Answer:
| LSA Type | Name | Generated By | Scope | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Router LSA | All OSPF Routers | Within the same area | Advertises router links |
| Type 2 | Network LSA | DR | Within the same area | Advertises multi-access networks |
| Type 3 | Summary LSA | ABR | Inter-area | Advertises inter-area networks |
| Type 4 | ASBR Summary LSA | ABR | Inter-area | Advertises ASBR location |
| Type 5 | External LSA | ASBR | Throughout the OSPF domain | Advertises external routes |
| Type 7 | NSSA External LSA | ASBR in NSSA | NSSA area only | External routes in NSSA (converted) |
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: OSPF LSA Types Explained: Complete Guide with CLI, EVE-NG Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement OSPF LSA Types is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![OSPF LSA Types Explained: Complete Guide with CLI, EVE-NG Lab & Real-World Use Cases. [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/OSPF-LSA-Types-Explained_Complete-Guide-with-CLI-EVE-NG-Lab-Real-World-Use-Cases_networkjourney.png)
![Python Script to Pull Interface Status – Your First Step into Network Automation [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Python-Script-to-Pull-Interface-Status-–-Your-First-Step-into-Network-Automation-1.png)
![Cloud Networking Made Simple: Dive into IaaS, PaaS & SaaS [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Cloud-Networking-Made-Simple_-Dive-into-IaaS_-PaaS_SaaS_networkjourney.png)
![Wireshark Filter Mastery: Pro-Level Tips for Layer 2 & Layer 3 Packet Analysis [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Wireshark-Filter-Mastery_Pro-Level-Tips-for-Layer-2_Layer-3-Packet-Analysis_networkjourney.png)