Real-World Use Case of Conditional Routing in Enterprise Networks [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
Can I send traffic based on user type or maybe only during a specific time?” That’s when Conditional Routing enters the game — it’s like having a smart traffic police that directs cars based on who is driving and what the current road conditions are. In this post, I’ll break down Conditional Routing like I would in one of our live sessions. Real-life use cases, practical labs, and some cool CLI to bring it all together. So grab your chai or coffee, and let’s make Conditional Routing crystal clear.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief
Conditional Routing is a method of forwarding packets based on specific conditions — like source IP, destination IP, packet size, application type, or even time of day. It’s not a protocol itself, but rather a technique implemented using policy-based routing (PBR), route-maps, and match conditions.
Why Do We Use Conditional Routing?
- Traditional routing works on destination-based logic — the shortest or best metric wins.
- Conditional Routing gives you flexibility to override that logic.
- Think of it as routing with a brain. For example:
- Route VOIP traffic via low-latency MPLS.
- Send backup traffic only after business hours.
- Direct traffic from the finance department through a firewall inspection path.
How Does It Work?
You configure a set of conditions using access-lists or route-maps. These conditions are matched and then tied to specific actions like setting a next-hop or a specific interface. The router checks these rules before making a routing decision.
Conditional routing uses:
- Route-maps: Define conditions and actions.
- Access-lists: Match traffic.
- Policy-based routing (PBR): Apply route-maps to interfaces.
- When is it Needed?
- Dual ISP environments.
- Routing specific departments via dedicated links.
- Load balancing based on custom logic.
- Failover with intelligence.
- Application-aware routing for performance or cost optimization.
Conditional Routing Summary
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Based on | Source IP, Destination IP, Application, Interface, Time of Day, etc. |
| Implements | Route-map + ACL + PBR |
| Works at | Control Plane level |
| Overrides | Traditional destination-based routing |
| Common Protocol Used | None — it uses native IOS features |
| Integrated with | MPLS, QoS, IP SLA, VRF, etc. |
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Flexible and dynamic routing decisions | Requires careful planning |
| Supports business-driven traffic steering | Troubleshooting can be harder than static routing |
| Application or department-specific control | Limited hardware support on legacy devices |
| Can enhance security posture | Can increase CPU utilization on high-speed links |
Essential CLI Commands
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
show route-map | Displays route-map configuration |
show ip policy | Verifies PBR applied on interface |
show access-lists | Shows ACLs used in policy |
debug ip policy | Real-time packet routing decisions (use with caution) |
show ip route | Verifies final routing decisions |
| `show run | section route-map` |
show ip sla statistics | Monitor traffic patterns with IP SLA (if used) |
Real-World Use Case
| Scenario | Conditional Logic | Routing Decision |
|---|---|---|
| VOIP prioritization | Match UDP ports 16384-32767 | Route via low-latency MPLS link |
| Backup traffic after hours | Match IP + time-range | Route via backup Internet link |
| Internet vs Intranet split | Match destination subnet | Intranet via leased line, Internet via broadband |
| Guest Wi-Fi via firewall | Match VLAN or subnet | Route through firewall inspection interface |
| Cloud application prioritization | Match app IPs (O365, Zoom, etc.) | Route via primary ISP with SLA |
SMALL EVE-NG LAB
LAB TOPOLOGY
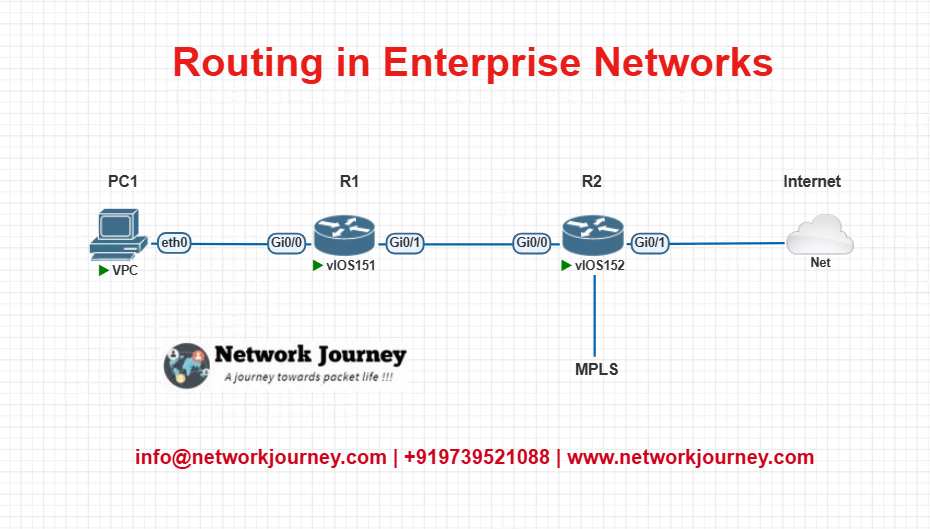
Objective
Route traffic from PC1:
- Web traffic (TCP port 80) via R2 → Internet.
- All other traffic via MPLS link.
LAB CONFIGURATION (CLI)
1. Access-list to Match Web Traffic
ip access-list extended WEB_TRAFFIC
permit tcp any any eq 80
2. Route-map for Conditional Routing
route-map CONDITIONAL_ROUTE permit 10
match ip address WEB_TRAFFIC
set ip next-hop 192.168.1.2 ! IP of R2
3. Apply Route-map to Interface
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip policy route-map CONDITIONAL_ROUTE
4. Static Route for Default
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.2 ! MPLS next-hop
5. Verification
show ip policy
show route-map
debug ip policy
Troubleshooting Tips
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Route-map not taking effect | Interface not configured with policy | Check ip policy route-map on the correct interface |
| Wrong traffic being rerouted | Incorrect ACL matching | Revisit access-list and test with show access-lists |
| No change in routing behavior | Static/default route takes precedence | Ensure route-map is first hit in the policy |
| CPU spikes | Heavy PBR on high-speed interfaces | Use carefully or offload to hardware |
| Only partial traffic rerouted | ACLs too specific | Generalize ACL without compromising requirements |
Most Common FAQs
1. What is conditional routing in enterprise networks?
Answer:
Conditional routing is the practice of forwarding traffic based on specific conditions like reachability, route availability, source, or destination criteria — instead of following the default route decision.
It enables flexible path selection, based on:
- Network availability
- Application requirements
- Failover mechanisms
- Policy-based decisions
In simple terms, it’s “If X is true, then route via Y”.
2. When should conditional routing be used in enterprise environments?
Answer:
Use conditional routing when:
- You want to failover between WAN links based on reachability.
- Certain applications (e.g., VoIP) need to use specific ISP links.
- You must route branch traffic differently based on time-of-day, interface status, or reachability of services.
- You need redundancy with intelligence — not just blindly load-balancing.
3. What technologies support conditional routing in Cisco IOS?
Answer:
Common technologies that enable conditional routing include:
| Technology | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Policy-Based Routing (PBR) | Route based on source, destination, or protocol. |
| Tracking + IP SLA | Monitor next-hop and trigger route change. |
| Object Tracking | Conditional static routing based on interface or IP status. |
| Route-maps | Advanced conditional logic for redistribution or route filtering. |
4. What is a real-world example of conditional routing using IP SLA + tracking?
Answer:
Scenario: An enterprise has two internet links (ISP1 and ISP2). You want to prefer ISP1 but failover to ISP2 only if ISP1’s next-hop becomes unreachable.
Solution:
- Configure IP SLA to ping ISP1’s gateway.
- Track the reachability.
- Use static routes with tracking:
ip sla 1
icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source-interface GigabitEthernet0/0
frequency 5
ip sla schedule 1 life forever start-time now
track 1 ip sla 1 reachability
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.0.2.1 track 1
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 198.51.100.1 200
Now, the default route conditionally fails over based on reachability.
5. How does Policy-Based Routing (PBR) enable conditional routing?
Answer:
PBR overrides routing decisions based on matched conditions like:
- Source IP
- Destination IP
- DSCP, ACL, protocol
Example:
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any
route-map PBR-VOICE permit 10
match ip address 101
set ip next-hop 10.0.0.1
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip policy route-map PBR-VOICE
Here, traffic from 192.168.10.0/24 is routed via a specific next-hop, regardless of the main routing table.
6. Can conditional routing help in application-aware routing (AppQoS)?
Answer:
Yes. Conditional routing can be integrated with:
- NBAR (Network-Based Application Recognition)
- QoS policies
- PBR based on DSCP or ports
For example, route VoIP traffic over MPLS, and bulk data over broadband using match conditions and set ip next-hop.
This ensures traffic engineering based on application needs, not just IP address.
7. How is conditional static routing different from dynamic routing?
Answer:
| Feature | Conditional Static Routing | Dynamic Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Uses | Backup paths, specific failover cases | Full network topology learning |
| Needs configuration | Manual + IP SLA or tracking | Uses OSPF/EIGRP/BGP protocols |
| Failover reaction time | Fast with SLA | Slower (convergence delay) |
| Control | High (predictable) | Medium |
Conditional static routes give greater control in edge routing or ISP failover scenarios.
8. What’s the best way to test conditional routing in a lab?
Answer:
Use EVE-NG or GNS3 with:
- Two routers representing ISP1 and ISP2.
- IP SLA to test reachability.
- Route tracking to manipulate static routes.
- Optional: PBR on LAN-facing interfaces to simulate app-aware routing.
Use debug ip routing and show ip route to verify changes dynamically.
9. What are some CLI commands to verify conditional routing status?
Answer:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
show ip sla statistics | IP SLA success/failure |
show track | Track object status |
show ip route | Current routing decisions |
show route-map | Match/set logic in route-maps |
show ip policy / debug ip policy | For PBR debugging and verification |
These help confirm if conditional logic is triggering correctly.
10. What are common mistakes to avoid in conditional routing?
Answer:
- Forgetting to tie tracking to the static route.
- Using
set interfaceinstead ofset ip next-hopin PBR (can fail if ARP fails). - Not testing both failure and recovery scenarios.
- Applying PBR on the wrong interface (PBR is inbound only).
- Not adding a default or backup route for fallback.
Always test thoroughly in a lab before going live.
YouTube Video: Conditional Routing Explained with Lab
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: Real-World Use Case of Conditional Routing in Enterprise Networks Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Real-World Use Case of Conditional Routing in Enterprise Networks is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Real-World Use Case of Conditional Routing in Enterprise Networks [ CCNP ENTERPRISE ]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Real-World-Use-Case-of-Conditional-Routing-in-Enterprise-Networks-CCNP-ENTERPRISE-.png)
![[DAY#9 PyATS Series] Parsing show ip interface brief across vendors using pyATS [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/DAY9-PyATS-Series-Parsing-show-ip-interface-brief-across-vendors-using-pyATS-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![Mastering Ping and Traceroute: Advanced Options Every Network Engineer Should Know [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Mastering-Ping-and-Traceroute_Advanced-Options-Every-Network-Engineer-Should-Know_networkjourney.png)
![Overlay Technologies for CCNP Enterprise: The Complete 2025 Guide with Labs, CLI & Exam Relevance [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Overlay-Technologies-for-CCNP-Enterprise_networkjourney.png)