2025 Guide: Overlay vs Underlay in SD-WAN – What’s Changed? [CCNP Enterprise]
If you’re anything like my students or clients, you’ve probably heard the words “overlay” and “underlay” thrown around constantly in the world of SD-WAN. But in 2025, how much do you really understand about how these layers work—and more importantly, how they’ve evolved?
Today, we’re diving deep into the core difference between overlay and underlay in SD-WAN, how Cisco and other vendors are redefining their roles, and what changes you need to keep in mind when designing or troubleshooting a next-gen WAN architecture.
Let’s make this easy, practical, and 100% aligned with what you’d expect from a CCNP Enterprise-level breakdown.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief: What Are Overlay & Underlay?
Underlay Network
The underlay is the physical network—your routers, switches, MPLS links, internet circuits, and fiber connections. It’s the actual transport path over which data is carried.
Think of it as the road infrastructure that carries vehicles.
- Examples: Internet, MPLS, LTE/4G/5G links
- Carries packets from site to site
- Usually managed by ISPs or service providers
Overlay Network
The overlay is the virtual network created on top of the underlay. It uses tunnels, such as IPsec, GRE, or VXLAN, to form logical paths between branch locations.
Imagine a dedicated, encrypted tunnel over the internet, like a subway system built under existing roads.
- Built using SD-WAN controllers
- Routes traffic based on policies (App-aware routing)
- Enables segmentation and security
Why Overlay/Underlay Separation Matters
In traditional WAN, these layers are tightly coupled. In SD-WAN, they are decoupled, giving you greater flexibility, control, and visibility. This separation is the reason we now enjoy application-aware routing, path failover, and end-to-end telemetry.
What’s Changed in 2025?
| Change Area | Traditional SD-WAN (Pre-2023) | Modern SD-WAN (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Transport Dependence | MPLS dominated | DIA, 5G, broadband now primary underlays |
| Control Plane | Controller-initiated tunnels | AI-enhanced path selection + auto-heal |
| Security | IPsec + basic firewall | SASE, ZTNA integrated in overlay |
| Telemetry | SNMP & NetFlow | Real-time visibility with ML-based alerts |
| Policy Deployment | Manual CLI-based | Centralized with intent-based GUI tools |
Summary: Overlay vs Underlay
| Feature | Underlay | Overlay |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Physical packet transport | Virtual path for logical traffic flow |
| Technology | MPLS, Internet, LTE | IPsec, GRE, VXLAN |
| Control Plane | Static/dynamic routing | Controller-based routing policies |
| Visibility | Device-level | End-to-end application flow |
| Configuration Method | Manual (CLI or NMS) | Centralized via SD-WAN controller |
| Example Protocols | OSPF, BGP | OMP (Cisco SD-WAN), VXLAN |
Essential CLI Commands
| Purpose | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| View transport interfaces | show sdwan interface | Lists interfaces used in underlay |
| View BFD status | show sdwan bfd sessions | Monitors overlay tunnel health |
| Display OMP routes | show omp routes | Shows overlay reachability |
| Check control connections | show control connections | Validates overlay connectivity |
| Troubleshoot underlay path loss | ping <next-hop IP> | Underlay path reachability check |
| Debug tunnel flaps | debug tunnel-events | See tunnel stability issues |
Real-World Use Case: Multisite SD-WAN Deployment
| Site | Underlay | Overlay Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| HQ | Dual DIA + MPLS | Full-mesh overlay with segmentation |
| Branch A | Broadband + 5G backup | Tunnel to HQ + App policy for VoIP |
| Branch B | Internet only | Tunnel to data center via controller |
| Cloud Hub | Direct connect + VPN | Overlay extension using IPsec tunnels |
EVE-NG LAB: Overlay and Underlay Demo
LAB TOPOLOGY
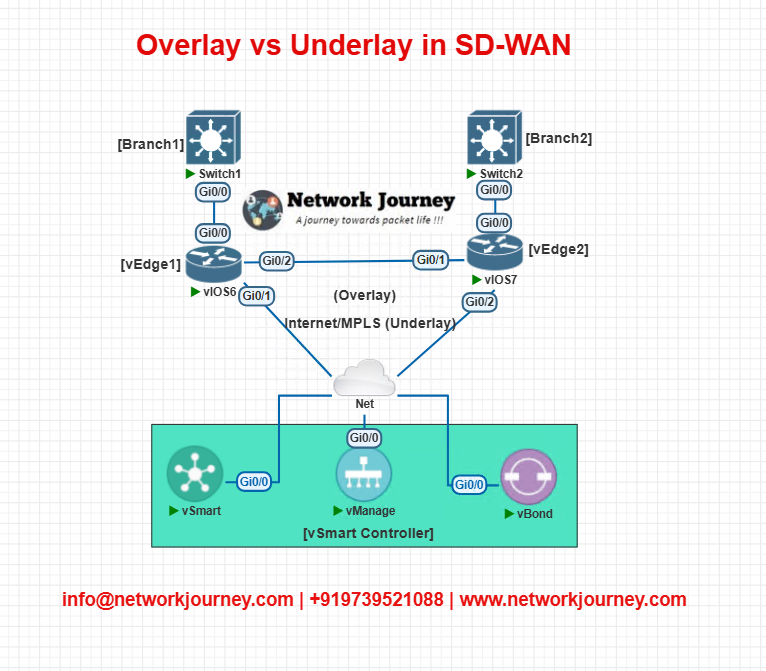
LAB CLI CONFIGURATION
vEdge1 Underlay Interface
interface ge0/0 ip address 192.0.2.10/30 tunnel-interface encapsulation ipsec color biz-internet
Overlay BFD Configuration
bfd-template 100ms multiplier 7 interval 100
vSmart Policy Snippet
vpn-list DATA
vpn 10
traffic-policy VOIP-QoS
sequence 10
match application voip
action
accept
set
preference 100
restrict
Troubleshooting Tips
| Problem | Likely Cause | Suggested Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Tunnel down | No control connection | Check show control connections |
| App routing not working | Missing policy on vSmart | Review centralized policy config |
| Underlay unreachable | ISP down or interface error | Check ping, show interfaces |
| Packet loss on tunnel | BFD instability | Tune BFD template settings |
| Overlay route missing | OMP route not advertised | Verify OMP routes on vEdge and vSmart |
FAQs About Overlay vs Underlay in SD-WAN
1. What is the Underlay Network in SD-WAN?
Answer:
The underlay refers to the physical or transport network — such as MPLS, broadband internet, or LTE — that carries the actual data packets. It’s the real path between sites, responsible for basic IP connectivity.
In SD-WAN, the underlay is usually abstracted, but it still plays a critical role in determining performance, loss, latency, and jitter.
2. What is the Overlay Network in SD-WAN?
Answer:
The overlay is the logical or virtual network built on top of the underlay. It uses tunnels (typically IPsec or GRE) to securely transport data between SD-WAN edge devices.
The overlay enables centralized policies, segmentation, encryption, and application-aware routing — making it the intelligent layer of the SD-WAN architecture.
3. How Do Overlay and Underlay Work Together in SD-WAN?
Answer:
The overlay uses the underlay as a transport medium. Think of the underlay as the road and the overlay as your GPS system guiding the traffic.
The SD-WAN controller constantly monitors underlay performance and dynamically selects the best path for each application using the overlay logic. This allows real-time failover and application-based path selection.
4. What’s New in Overlay/Underlay Design for SD-WAN in 2025?
Answer:
In 2025, several enhancements are trending:
- Cloud-native underlays (like AWS/Azure fabric extensions) are being integrated.
- AI-driven path selection improves application performance.
- Overlay security is now often integrated with Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA).
- Enhanced telemetry and real-time analytics provide better insight into both layers.
5. Can You Give a Simple Analogy to Understand Overlay vs Underlay?
Answer:
Sure!
Imagine the underlay as the physical road system — highways, streets, lanes.
The overlay is your GPS with traffic-aware routing, live directions, and preferred paths.
The GPS (overlay) doesn’t own the road (underlay), but it optimizes how you travel across it based on real-time conditions.
6. Is It Possible to Have Multiple Underlays in a Single SD-WAN Deployment?
Answer:
Absolutely. SD-WAN is designed to aggregate multiple transport types (MPLS, Internet, LTE, 5G).
This gives businesses:
- Redundancy
- Cost optimization (use MPLS for critical apps, broadband for best-effort traffic)
- Seamless failover and load balancing
Each underlay can be used intelligently by the overlay based on defined SLAs and policy.
7. How Does SD-WAN Ensure Application-Aware Routing Over the Overlay?
Answer:
SD-WAN uses application recognition engines (like DPI) and metrics from the underlay (delay, loss, jitter) to make decisions in real time.
Policies are defined based on:
- Application type (e.g., Zoom, SAP)
- User groups or branch locations
- Path health
The overlay dynamically routes the traffic over the best available underlay link based on those conditions.
8. What Happens If an Underlay Link Fails? Does the Overlay Automatically Adjust?
Answer:
Yes. One of the major strengths of SD-WAN is dynamic path selection.
If an underlay link fails or degrades beyond threshold, the overlay:
- Immediately reroutes traffic via another healthy underlay path.
- Maintains tunnel continuity (if possible) to avoid session drops.
- Ensures seamless failover using protocols like BFD or IP SLA.
This ensures high availability and better user experience.
9. Are Routing Protocols Still Used in Overlay and Underlay Networks?
Answer:
Yes — but with a modern twist.
- Underlay might use traditional routing protocols (like OSPF, BGP) for basic connectivity.
- Overlay may use control-plane protocols like OMP (Overlay Management Protocol) in Cisco SD-WAN or BGP in other vendors to exchange reachability information.
This separation allows scalable and flexible route control between branches, data centers, and cloud.
10. How Should a CCNP Engineer Approach Overlay vs Underlay in Real Deployments?
Answer:
As a CCNP Enterprise engineer, think in layers:
Always monitor both layers — issues in underlay can still disrupt the overlay!
Design the underlay for redundancy, quality, and secure physical transport.
Build intelligent overlays with policy-based routing, segmentation, and SLA assurance.
Use centralized controllers (like vSmart in Cisco SD-WAN) for overlay orchestration.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: Overlay vs Underlay in SD-WAN – What’s Changed? Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Overlay vs Underlay in SD-WAN – What’s Changed? is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![2025 Guide: Overlay vs Underlay in SD-WAN – What’s Changed?[CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Overlay-vs-Underlay-in-SD-WAN_networkjourney-1.png)
![[Day 31] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Wired Posture Assessment Overview](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-31-–-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Wired-Posture-Assessment-Overview-1.png)

![[Day 41] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Wireless 802.1X Authentication Overview](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-41-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Wireless-802.1X-Authentication-Overview.png)