Access Port vs Trunk Port Explained: Cisco CLI + EVE-NG Labs [2025] [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
If you’re diving into VLANs, there’s one thing you must get right—knowing when and how to use Access vs Trunk ports. I’ve seen learners assign a trunk port to a PC and wonder why nothing pings. Whether you’re preparing for your CCNA, labbing in EVE-NG, or deploying real-world switch configurations, this guide will make the differences crystal clear—with examples, CLI, labs, and troubleshooting tips. Let’s begin!
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief – Trunk Port vs Access Port
In VLAN-based networks, switch ports play two main roles:
- Access Port: Connects end devices (PCs, printers, IP phones) and belongs to a single VLAN. It sends and receives untagged traffic.
- Trunk Port: Connects switch to switch, switch to router, or to a hypervisor carrying multiple VLANs. It uses 802.1Q tagging to identify each VLAN’s traffic.
Think of Access ports as single-lane roads and Trunks as multi-lane highways carrying tagged traffic from several VLANs.
Cisco by default configures switch ports as Access. To configure a Trunk, you must set switchport mode trunk and allow VLANs if needed.
Both have their own use cases—Access ports for endpoint connections, Trunk ports for inter-switch links or router-on-a-stick designs.
Summary: Comparison of Trunk vs Access Ports
| Feature/Aspect | Access Port | Trunk Port |
|---|---|---|
| VLAN Assignment | One VLAN only | Multiple VLANs via tagging (802.1Q) |
| Use Case | PCs, printers, phones | Switch to switch, switch to router |
| Traffic Tagging | Untagged | Tagged using 802.1Q |
| Default Behavior | Belongs to VLAN 1 | Requires manual config |
| Native VLAN Support | Not required | Required for untagged frames |
| Security Risk | Lower | Higher (VLAN hopping if misconfigured) |
| Troubleshooting Complexity | Low | Higher – tagging and allowed VLAN issues |
Essential CLI Commands (Cisco IOS)
| Task | CLI Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Check current port mode | show interfaces <intf> switchport | Shows if port is access or trunk |
| Convert port to access | switchport mode access | Forces access mode |
| Assign VLAN to access port | switchport access vlan <vlan-id> | Binds access port to VLAN |
| Convert port to trunk | switchport mode trunk | Enables trunking on port |
| Set native VLAN on trunk | switchport trunk native vlan <vlan-id> | Specifies VLAN for untagged traffic |
| View trunk ports | show interfaces trunk | Displays trunk status and allowed VLANs |
| Check VLANs on switch | show vlan brief | Lists all VLANs and associated ports |
| Allow specific VLANs on trunk | switchport trunk allowed vlan <vlan-list> | Limits which VLANs are tagged on trunk |
| Debug VLAN tagging issues | debug sw-vlan packet | Troubleshoot trunk behavior (advanced) |
Real-World Use Cases
| Scenario | Port Type | Why It’s Used |
|---|---|---|
| Connecting a user PC to the network | Access Port | PC is in one VLAN only |
| Connecting switch to switch | Trunk Port | Multiple VLANs need to travel |
| Router-on-a-Stick (Inter-VLAN Routing) | Trunk Port | Router subinterfaces handle VLAN tags |
| IP phone + PC on same port (voice VLAN) | Access Port | Voice VLAN + data VLAN combination |
| Connecting Hypervisor/NIC with multiple VLANs | Trunk Port | VM traffic separation by VLAN |
EVE-NG Lab: Access & Trunk Port Demo
Lab Objective:
- PC1 (VLAN 10) and PC2 (VLAN 10) can ping each other via two switches using a trunk link.
- PC3 (VLAN 20) is isolated.
Topology:
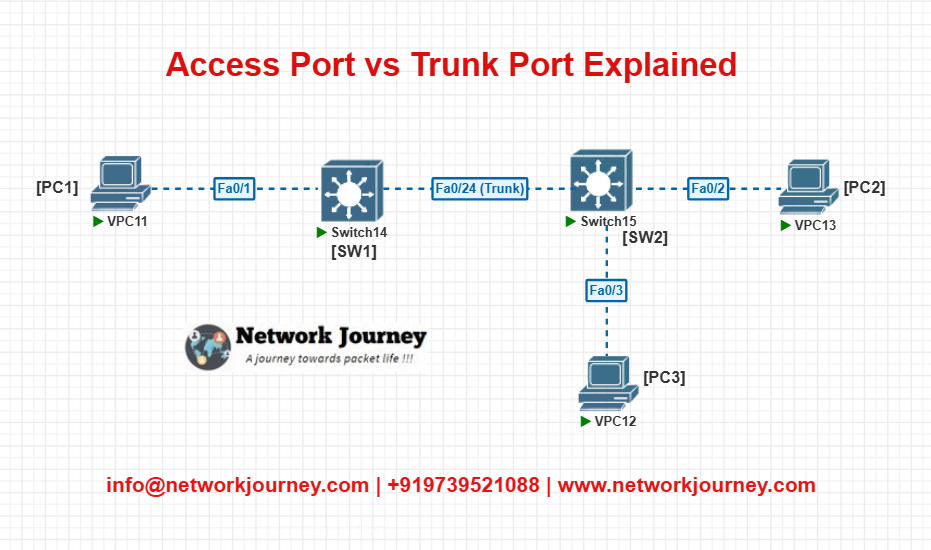
Config (SW1):
vlan 10 name SALES interface fa0/1 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 no shutdown interface fa0/24 switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20 no shutdown
Config (SW2):
vlan 10 name SALES vlan 20 name HR interface fa0/2 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 no shutdown interface fa0/3 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 20 no shutdown interface fa0/24 switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20 no shutdown
Verification
SW1# show interfaces trunk SW2# show vlan brief
- PC1 ↔ PC2 = Ping Success (Same VLAN across trunk)
- PC3 = Isolated in VLAN 20
Troubleshooting Tips
| Problem | Likely Cause | Fix or CLI Command |
|---|---|---|
| PC can’t reach other VLAN device | Wrong port mode | Check with show int switchport |
| Trunk link not working | Port not in trunk mode | switchport mode trunk |
| Traffic dropping between switches | VLAN not allowed on trunk | switchport trunk allowed vlan |
| Device not in correct VLAN | Misconfigured access VLAN | switchport access vlan <id> |
| CDP mismatch warning | Native VLAN mismatch | Match native VLANs on both ends |
FAQs: Trunk Port vs Access Port
1. What is the main difference between an access port and a trunk port?
Answer:
- Access Port: Carries traffic for only one VLAN. It’s used to connect end devices like PCs, printers, or IP phones.
- Trunk Port: Carries traffic for multiple VLANs using 802.1Q tagging. It’s typically used for switch-to-switch or switch-to-router links.
Access = single VLAN
Trunk = multiple VLANs
2. How do I configure an access port on a Cisco switch?
Answer:
interface fa0/1 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10
This sets the interface as an access port and assigns it to VLAN 10.
3. How do I configure a trunk port on a Cisco switch?
Answer:
interface gig0/1 switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20,30
This sets the port as a trunk and allows it to carry VLANs 10, 20, and 30.
You can also configure the native VLAN if needed:
switchport trunk native vlan 99
4. What is the native VLAN on a trunk port and why is it important?
Answer:
The native VLAN is the VLAN that is sent untagged on a trunk port. By default, it’s VLAN 1.
It must match on both ends of a trunk link, or you’ll receive native VLAN mismatch warnings and risk traffic being dropped or misrouted.
5. Can an access port receive tagged traffic?
Answer:
No. Access ports are designed to handle untagged Ethernet frames.
If tagged traffic (802.1Q) is received, it’s dropped unless the port supports voice VLANs or is misconfigured.
6. How do I verify if a port is in access or trunk mode?
Answer:
show interfaces switchport
or
show interfaces trunk
These commands display:
- Administrative/operational mode (access/trunk)
- VLAN assignments
- Allowed VLANs
- Native VLAN
7. What happens if both switches have mismatched port modes (access vs trunk)?
Answer:
If one side is configured as access and the other as trunk, it may cause:
- Link negotiation failure
- VLAN tagging issues
- Traffic might be dropped or misrouted
To avoid this, ensure that both ends of a link have matching modes or use Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) with caution.
8. Can I assign voice and data VLANs to the same access port?
Answer:
Yes. You can use a voice VLAN in addition to a data VLAN on an access port for IP phones:
interface fa0/2 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 switchport voice vlan 20
This allows the phone to tag voice traffic (VLAN 20), while the PC sends untagged traffic (VLAN 10).
9. How do trunk and access ports affect VLAN propagation in EVE-NG labs?
Answer:
In EVE-NG:
- Access ports connect end devices to a single VLAN.
- Trunk ports are used to link switches and route multiple VLANs across the lab.
Ensure correct VLAN tagging and trunking to simulate router-on-a-stick, inter-VLAN routing, or VTP scenarios properly.
10. How do I troubleshoot a trunk port that’s not carrying VLAN traffic?
Answer:
Use these steps:
- Check trunk status:
show interfaces trunk
- Confirm allowed VLANs:
show run interface gi0/1
- Check STP:
show spanning-tree vlan <id>
- Verify native VLAN matches on both sides:
show cdp neighbors detail
Most issues stem from allowed VLAN mismatch, STP blocking, or trunk misconfiguration.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: Access Port vs Trunk Port Explained: Cisco CLI + EVE-NG Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Access Port vs Trunk Port Explained: Cisco CLI + EVE-NG Labs is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Access Port vs Trunk Port Explained: Cisco CLI + EVE-NG Labs [2025]. [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Access-Port-vs-Trunk-Port-Explained_networkjourney.png)
![Ticket#3 - VLAN Mismatch: End Users Unable to Reach Gateway – A Real Cisco Fix [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/nj-blog-post-Ticket3.jpg)
![Native VLAN Mismatch Detection_The Hidden Threat to Your Network [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Native-VLAN-Mismatch-Detection_networkjourney.png)
![VLAN Creation_Troubleshooting_Complete Hands-On Guide with EVE-NG Lab_[CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/VLAN-Creation_Troubleshooting_Complete-Hands-On-Guide-with-EVE-NG-Lab_networkjourney.png)