SNMPv2 vs SNMPv3: Secure and Scalable Network Monitoring [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
we’re diving into a classic comparison every network engineer must understand—SNMPv2 vs SNMPv3. If you’re preparing for CCNA, CCNP, or actively working with NMS (Network Management Systems), this topic is your foundation for monitoring, managing, and securing enterprise-grade networks.
In many real-world deployments, SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is used to monitor routers, switches, firewalls, and even servers. But as cyber threats have evolved, so have the protocols. That’s why understanding the evolution from SNMPv2 to SNMPv3 is essential—not just for configuration, but also for security, scalability, and compliance.
Let’s simplify the theory, see where each version fits, and configure them practically using CLI and EVE-NG simulation.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief: What is SNMP?
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is an application-layer protocol used for monitoring and managing network devices like routers, switches, firewalls, and servers. It operates using a manager-agent model where:
- SNMP Manager = NMS (e.g., SolarWinds, PRTG, Nagios)
- SNMP Agent = Cisco Router/Switch configured to expose data
- MIBs (Management Information Bases) = The database of readable device info
SNMPv2 Overview
SNMPv2c is widely used due to its simplicity. It supports:
- Bulk transfers (get-bulk)
- Improved error handling
- Community string-based authentication (clear-text)
While efficient, SNMPv2 lacks encryption, making it vulnerable in sensitive environments.
SNMPv3 Overview
SNMPv3 enhances SNMPv2 by introducing:
- User-based Authentication (MD5/SHA)
- Encryption (DES, AES)
- Access control
It’s secure, but more complex to configure, and requires user management and group policies.
Why This Matters?
In today’s security-first networking, SNMPv3 is the recommended version, especially in government, finance, and healthcare sectors. However, SNMPv2 is still widely used in closed or trusted networks where simplicity and performance matter.
Comparison: SNMPv2 vs SNMPv3
| Feature | SNMPv2c | SNMPv3 |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | Community string (plaintext) | Username/password (MD5/SHA) |
| Encryption | None | Yes (DES, AES) |
| Access Control | Limited | Advanced (Views, Groups) |
| Message Security | Unsecured | Authenticated & Encrypted |
| Scalability | Simple & Lightweight | Scalable with better control |
| Configuration Complexity | Simple | Complex |
| Suitable For | LAN, isolated environments | WAN, public networks, secure enterprises |
| Default Port | UDP 161 | UDP 161 (same, but different security) |
| Bulk Data Support | Yes | Yes |
| Standards | RFC 1901–1908 | RFC 3411–3418 |
Essential CLI Commands
Here’s a Cisco IOS-based reference table for SNMP configuration and verification:
| Task | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable SNMPv2 | snmp-server community public RO | Read-only access with community string |
| Enable SNMPv2 RW | snmp-server community private RW | Read-write access (less secure) |
| View SNMP configuration | `show run | include snmp` |
| SNMP debug | debug snmp packets | Monitor SNMP communication |
| Enable SNMPv3 User | snmp-server user admin SNMPGROUP v3 auth md5 cisco123 | Adds SNMPv3 user with authentication |
| SNMPv3 with encryption | snmp-server user admin SNMPGROUP v3 auth sha pass123 priv aes 128 key123 | Adds encrypted SNMPv3 user |
| Set SNMPv3 group | snmp-server group SNMPGROUP v3 priv | Creates SNMPv3 group with privacy |
| Disable SNMP | no snmp-server | Disables SNMP globally |
Real-World Use Case
| Scenario | SNMPv2c | SNMPv3 |
|---|---|---|
| Legacy enterprise LAN | Sufficient for basic monitoring | Overhead not needed |
| Government or banking sector | Not secure | Required for compliance (PCI, HIPAA, etc.) |
| ISP using centralized monitoring (NOC) | Simpler setup | More secure and scalable |
| Devices in remote locations over WAN | Data exposed | Secured over public transport |
| Integration with SIEM or analytics platforms | Supported but less secure | Better for compliance and audits |
EVE-NG Lab: SNMPv2 vs SNMPv3 Setup
Lab Topology
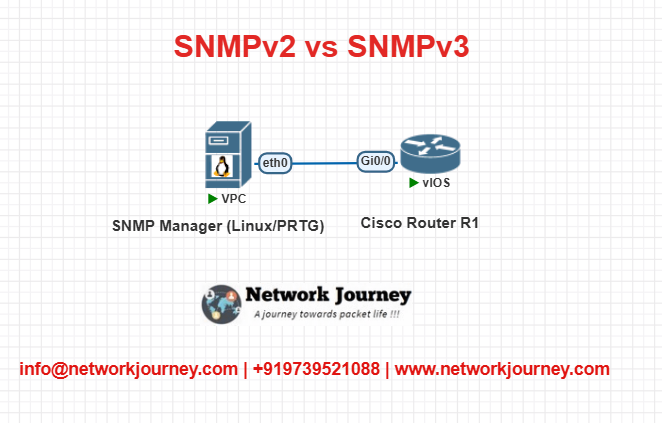
Objective:
Configure SNMPv2c and SNMPv3 on R1 and verify communication from SNMP Manager.
Configuring SNMPv2c on R1:
conf t hostname R1 snmp-server community public RO snmp-server community private RW snmp-server contact SagarDhawan snmp-server location EVE-LAB end
Configuring SNMPv3 on R1:
conf t snmp-server group SNMPGROUP v3 priv snmp-server user SNMPUSER SNMPGROUP v3 auth md5 authpass priv aes 128 privkey snmp-server location EVE-LAB snmp-server contact TrainerSagar end
Test from SNMP Manager:
- SNMPv2c:
snmpwalk -v2c -c public <router-IP> - SNMPv3:
snmpwalk -v3 -u SNMPUSER -A authpass -a MD5 -X privkey -x AES <router-IP>
Troubleshooting Tips
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| SNMPv3 fails to respond | Incorrect user/group setup | Verify show snmp user and passwords |
| SNMPv2c shows no data | Community string mismatch | Check exact string spelling (case-sensitive) |
| SNMP manager times out | Firewall or ACL blocks UDP port 161 | Permit SNMP traffic in ACL |
| SNMPwalk fails on v3 | Wrong auth/priv key type | Ensure MD5/SHA and DES/AES match configuration |
| Device not reachable via SNMP | SNMP not enabled on interface | Check SNMP enabled globally and on interface |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the primary difference between SNMPv2 and SNMPv3?
Answer:
The primary difference lies in security. SNMPv2c uses community strings for authentication, which are sent in cleartext, making it insecure. In contrast, SNMPv3 supports user-based authentication (with MD5 or SHA) and encryption (using DES or AES), making it suitable for enterprise environments where data confidentiality and integrity are crucial.
2. Can SNMPv2 and SNMPv3 be used simultaneously on a Cisco device?
Answer:
Yes. Cisco devices allow simultaneous configuration of both SNMPv2c and SNMPv3. This is especially useful during transitions or hybrid deployments. For example, legacy systems can continue using SNMPv2c while new systems securely connect via SNMPv3.
3. Is SNMPv3 compatible with existing SNMPv2-based monitoring tools?
Answer:
Not always. SNMPv3 introduces a different security model and message format, so the NMS (Network Management System) must support SNMPv3 explicitly. Tools like SolarWinds, PRTG, and Nagios support both, but configuration is separate from SNMPv2c profiles.
4. What authentication and encryption algorithms are used in SNMPv3?
Answer:
SNMPv3 supports:
- Authentication: MD5 or SHA
- Encryption (Privacy): DES, 3DES, or AES (128-bit)
These features offer data integrity, confidentiality, and authentication, making SNMPv3 suitable for secure environments like healthcare, banking, or government networks.
5. Which SNMP version should I use in a secure enterprise environment?
Answer:
Use SNMPv3 with authPriv mode in secure environments. It ensures:
- Authentication (to verify identity)
- Encryption (to protect data in transit)
- Access control (to limit data access)
SNMPv2c should only be used in isolated or low-risk LANs where security isn’t a major concern.
6. What are SNMP community strings in SNMPv2?
Answer:
Community strings are simple text passwords used in SNMPv2c to control access.
publicis typically for read-only access.privateis used for read-write access.
These strings are not encrypted, making them easy to sniff on the network. Hence, they are not recommended for untrusted or public environments.
7. How do I verify SNMPv3 configuration on a Cisco router or switch?
Answer:
Use the command:
show snmp user
It displays configured SNMPv3 users, authentication and encryption types. To verify if SNMP is working, use tools like snmpwalk or snmpget with appropriate SNMPv3 credentials and test access.
8. What port does SNMP use, and is it the same for all versions?
Answer:
Yes. SNMP uses:
- UDP port 161 for queries (get, set, walk)
- UDP port 162 for traps (unsolicited messages)
These ports are the same across SNMPv1, v2c, and v3, but ensure they are allowed through firewalls and ACLs in your network for proper communication.
9. Is SNMPv3 more resource-intensive than SNMPv2?
Answer:
Yes, slightly. Due to encryption and authentication overhead, SNMPv3 consumes more CPU and memory, especially when handling many requests. However, the performance difference is negligible on modern hardware and is worth the security trade-off.
10. What are best practices for implementing SNMPv3 in production?
Answer:
- Use authPriv (authentication + encryption) for all users
- Avoid using
noAuthNoPriv(unsecure) mode - Restrict access with ACLs
- Use unique usernames and passwords
- Monitor SNMP logs for suspicious activities
- Ensure all SNMPv3-configured devices and NMS are time-synced via NTP for authentication to work correctly
YouTube Link
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement SNMPv2 vs SNMPv3: Secure and Scalable Network Monitoring is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![SNMPv2 vs SNMPv3: Secure and Scalable Network Monitoring [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/SNMPv2-vs-SNMPv3-Secure-and-Scalable-Network-Monitoring_networkjourney.png)
![STP Root Bridge Election Explained: Priority, MAC & CLI Examples [2025]. [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/STP-Root-Bridge-Election-Explained_Priority_MAC_CLI-Examples_networkjourney.png)
![DIA vs Centralized Breakout: Which Internet Access Model Is Right for Your SD-WAN Network in 2025?. [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/DIA-vs-Centralized-Breakout-Which-Internet-Access-Model-Is-Right-for-Your-SD-WAN-Network-in-2025_networkjourney.png)
![Want to Stop Unauthorized Access? SSH and HTTPS Hardening Explained[CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/nj-blog-post-ssh-https.jpg)