[DAY#6 PyATS Series] Using pyATS CLI tools: pyats learn, pyats parse using PyATS [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction: Your First Step into CLI Magic with pyATS
Today’s blog is all about unlocking the CLI power of pyATS, specifically:
pyats learn– Automatically discover your device statepyats parse– Convert CLI outputs into JSON for automation logic
These tools are a goldmine for Python for Network Engineer workflows, especially when working across vendors like Cisco, Arista, Palo Alto, and FortiGate.
By the end of this article, you’ll be able to:
- Connect to multi-vendor devices using testbed
- Learn and parse device states
- Integrate CLI parsing into your automation pipelines
Let’s jump in.
Topology Overview
Here’s the setup we’re working with:
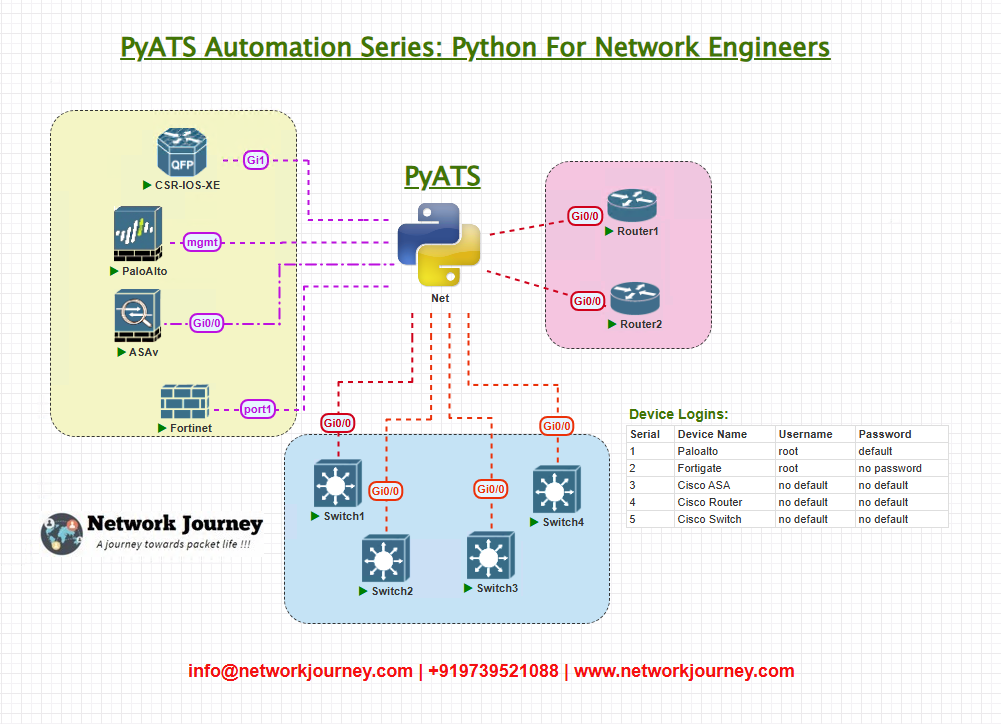
Each device is reachable over SSH via its management IP address. The pyATS runner machine initiates all interactions using Unicon and the pyats CLI.
Why Vendor‑Agnostic Testing Matters
Networks today aren’t purely Cisco anymore. Most enterprise and cloud architectures include Arista for DC switching, FortiGate or Palo Alto for firewalls, and Cisco for routing/access.
Here’s how vendor-agnostic automation tools like pyATS change the game:
| Problem | With pyATS CLI Tools |
|---|---|
| Inconsistent device outputs | Structured JSON from parse |
| Time-consuming manual validation | Auto-learn config/state using learn |
| Separate scripts per vendor | Unified CLI abstraction layer |
| Difficulty in comparing configs | Use diff with learn snapshots |
| Risk of human error | Repeatable CLI workflows |
Using pyats learn and pyats parse, you get programmable CLI intelligence—something legacy tools can’t offer.
Topology & Communications
Make sure your devices meet these basic requirements before proceeding:
| Device | Vendor | IP Address | SSH Access | Required OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Cisco IOS | 10.0.0.11 | Yes | IOSv |
| SW1 | Arista EOS | 10.0.0.12 | Yes | vEOS |
| PA1 | Palo Alto | 10.0.0.13 | Yes | PAN-OS (CLI enabled) |
| FG1 | FortiGate | 10.0.0.14 | Yes | FortiOS |
Ensure:
- SSH/CLI is enabled
- Admin credentials are set
- pyATS can reach all hosts from your runner
Workflow: pyATS CLI Commands in Action
Step 1: Test Connectivity
pyats validate testbed testbed.yml
Step 2: Learn Device State
pyats learn interface --testbed-file testbed.yml --devices R1
This will collect all interface data from R1 and store it under ./snapshots.
Step 3: Parse CLI Output
pyats parse "show version" --testbed-file testbed.yml --devices R1
This parses the raw CLI output and returns a structured JSON object.
Explanation by Line
Here’s what’s happening behind the scenes for each command:
1. pyats validate testbed
- Ensures your YAML is syntactically correct.
- Checks device reachability and credentials.
2. pyats learn <feature>
- Runs predefined parsers for a given feature (like
interface,routing, etc.) - Saves results in a JSON file
- Works across supported vendors (limited features for Palo/Forti)
3. pyats parse "<command>"
- Runs the specified command on the target device
- Uses Genie parsers to structure output
- Helps in extracting key-value data from legacy CLI
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: MultiVendorLab
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: password123
devices:
R1:
os: ios
type: router
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.0.0.11
SW1:
os: eos
type: switch
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.0.0.12
PA1:
os: panos
type: firewall
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.0.0.13
FG1:
os: fortinet
type: firewall
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.0.0.14
Multi‑Vendor CLI Screenshots
Cisco (show version parsed)
{
"version": {
"version_short": "15.6",
"platform": "IOSv",
"hostname": "R1"
}
}
Arista (show interfaces)
{
"Ethernet1": {
"oper_status": "up",
"mtu": 1500
}
}
Palo Alto / FortiGate
# No built-in parsers for most CLI, but connection via pyATS is working # Can use custom parsers or external JSON logic
For Palo and Forti, you can still automate CLI collection and parse manually or with custom Python functions.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between learn and parse in pyATS?
Answer:
learndiscovers full feature states using multiple commands (like all interfaces).parseruns a single command and parses its output to JSON.
2. Can I use parse with FortiGate or Palo Alto?
Answer:
Native Genie parsers are limited. You’ll likely need custom parsing logic using regex or TextFSM for unsupported vendors.
3. How to diff two snapshots using pyATS?
Answer:
pyats diff snapshots/R1/initial snapshots/R1/modified
This helps track config or state drift between two time points.
4. Is this usable in CI/CD pipelines?
Answer:
Yes! All pyats CLI tools are CLI-native and can be integrated into Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab pipelines.
5. How does pyATS handle login issues or SSH timeout?
Answer:
It raises Unicon exceptions, which are caught in CLI logs. Always validate testbed and use proper os, type, and ip.
6. What features are supported under learn?
Answer:
Common ones: interface, routing, platform, ospf, bgp, lldp, etc. Vendor support varies—best with Cisco and Arista.
7. Can I export parsed output to a file?
Answer:
Yes:
pyats parse "show version" --testbed-file testbed.yml --devices R1 > output.json
8. Is Genie still required separately?
Answer:
Genie is integrated into pyATS 23+. You don’t need separate installs unless using legacy APIs.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Using pyATS CLI Tools: pyats learn, pyats parse – Vendor-Agnostic for Cisco, Arista, Palo Alto, FortiGate Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training Program
If you’re enjoying these hands-on CLI workflows, it’s time to take it to the next level.
Trainer Sagar Dhawan is conducting a 3-Month Instructor-Led Program tailored for network engineers:
- Python for Network Engineer automation
- Ansible + REST APIs
- Cisco DevNet Blueprints
- pyATS – from beginner to production
Click below to view course outline and enroll:
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Course Outline:
https://course.networkjourney.com/python-ansible-api-cisco-devnet-for-network-engineers/
Whether you’re a beginner or working professional, this program will help you build a solid automation portfolio.
Join our community. Future-proof your career.
![[DAY#6 PyATS Series] Using pyATS CLI tools: pyats learn, pyats parse using PyATS [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/DAY6-PyATS-Series-Using-pyATS-CLI-tools-pyats-learn-pyats-parse-using-PyATS-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![[Day#3 PyATS Series] Installing pyATS & Genie (core, NX-OS, IOS-XR plugins) using pyATS for Cisco](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day3-PyATS-Series-Installing-pyATS-Genie-core-NX-OS-IOS-XR-plugins-using-pyATS-for-Cisco_networkjouney.png)
![[Day #17 Pyats Series] Creating a device inventory report (hostname, model, OS) using pyATS for Cisco](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Creating-a-device-inventory-report-hostname-model-OS-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![[Day 16] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Understanding 802.1X Authentication Flow](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-16-–-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Understanding-802.1X-Authentication-Flow.png)