Ticket#4 – BGP Route Not Installing in RIB – Path Attributes and Fix [CCNP Enterprise]
Table of Contents
Problem Summary
A network engineer noticed that a BGP route was visible in the BGP table (show ip bgp) but not getting installed in the routing table (RIB) on a core router connected to multiple ISPs.
Traffic toward the advertised prefix was getting dropped. Despite the BGP session being established, the preferred route was not visible in show ip route.
Symptoms Observed
- BGP route seen in
show ip bgp - Route not present in
show ip route - BGP session was ESTABLISHED
- No explicit route filtering configured
- Ping/traceroute toward destination IP failed
- Redistribution into IGP was not taking place
Root Cause Analysis
When a BGP route appears in the BGP table but is missing from the RIB, it’s usually due to one of the following:
Most Common Causes:
- Higher Administrative Distance route exists (like static or connected)
- Invalid NEXT_HOP
- Route is not the best BGP path
- Route is marked as inaccessible
- Route is suppressed by RIB constraints
The Fix
Let’s walk through step-by-step diagnostics and the final fix applied.
Step 1: Verify BGP Route Exists
show ip bgp <prefix>
Step 2: Check If Installed in Routing Table
show ip route <prefix>
If not present, continue…
Step 3: Verify Administrative Distance Conflict
show ip route <prefix>
Look for a connected/static/OSPF/EIGRP route overriding BGP
Step 4: Check Next-Hop Reachability
show ip bgp <prefix>
show ip route <next-hop>
If next-hop unreachable → BGP won’t install it in RIB
Step 5: Force Next-Hop Self (if needed for eBGP)
router bgp 65000
neighbor x.x.x.x next-hop-self
Step 6: Check for RIB Filtering / Suppression
- BGP route-map might deny installation
- Check for maximum-paths, inbound filters, or route suppression
EVE-NG Lab Topology
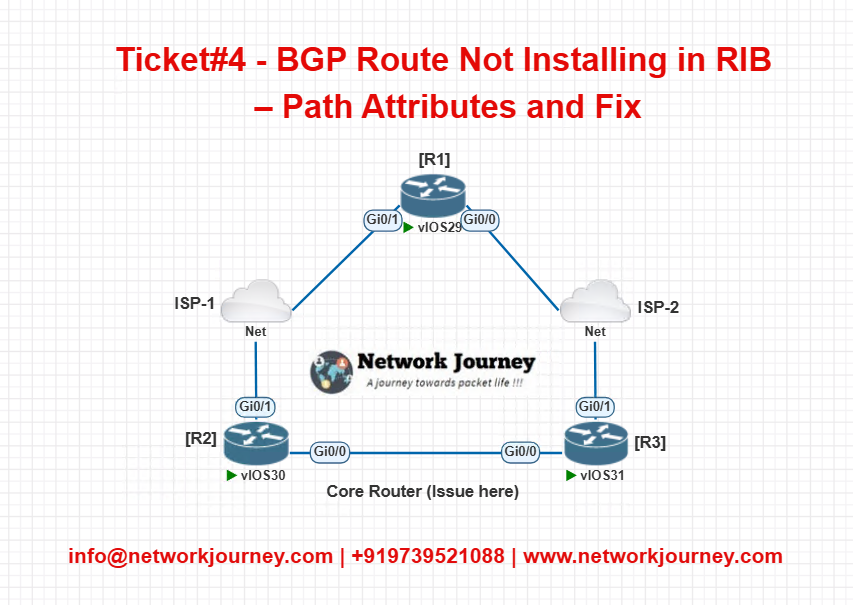
Lab Setup:
| Device | Role | AS | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | ISP-1 | 65001 | Advertises 100.1.1.0/24 |
| R2 | Core | 65000 | Receives route, not in RIB |
| R3 | ISP-2 | 65002 | Competing route via R3 |
Verification Commands
| Purpose | Command | Expected Output |
|---|---|---|
| See if BGP learned route | show ip bgp <prefix> | Entry present with valid attributes |
| See if route in RIB | show ip route <prefix> | Should show BGP or missing if not in RIB |
| Check next-hop reachability | ping <next-hop> / show ip route | Should be reachable |
| See which route is best | show ip bgp (look for >) | Only best route installs to RIB |
| See AD precedence | show ip route | Lower AD route may override BGP |
Key Takeaways
- BGP routes in BGP table ≠ Installed in RIB
- Always check next-hop reachability
- Best path selection matters for RIB install
- Competing static or IGP routes can suppress BGP
- Administrative Distance of BGP = 20 (eBGP), 200 (iBGP)
Best Practice / Design Tips
- Always configure
next-hop-selffor iBGP - Use
maximum-pathscarefully in load sharing - Redistribute BGP into IGP with proper route-maps
- Use loopback interfaces for peerings when possible
- Monitor route installation via syslog/snmp traps
FAQs
1. Why is my BGP route not in the routing table?
Answer:
Because either it’s not the best path, the next-hop is unreachable, or another route with lower AD is already installed.
2. What’s the administrative distance of BGP?
Answer:
eBGP: 20
iBGP: 200
3. What does > mean in the BGP table?
Answer:
It means the route is the best path and eligible to be installed in the RIB.
4. How can I check if a static route is overriding BGP?
Answer:
show ip route <prefix>
If static/connected/OSPF route is there, BGP won’t install.
5. Does next-hop need to be reachable for BGP route to be in RIB?
Answer:
Yes. If next-hop is unreachable, BGP will not install the route.
6. How to fix next-hop issues in iBGP?
Answer:
Use next-hop-self on the iBGP router:
router bgp 65000
neighbor 10.0.0.1 next-hop-self
7. Can BGP show a route that is not installed in RIB?
Answer:
Yes. It can be seen in show ip bgp but not in show ip route.
8. How to check which BGP route is best?
Answer:
Use:
show ip bgp <prefix>
The
>symbol indicates the best path.
9. What if two BGP routes are equal?
Answer:
You can enable load balancing using:
maximum-paths eibgp 2
10. Why does iBGP route not install even if it’s best?
Answer:
Because next-hop is not reachable or synchronization is enabled (older IOS versions).
11. Can I manually install a specific BGP route?
Answer:
No. Only best route chosen by BGP is installed automatically.
12. Does route filtering affect route installation?
Answer:
Yes. Route-maps or prefix-lists applied inbound may prevent the route from installing.
13. How to make sure BGP routes are redistributed into IGP?
Answer:
router ospf 1
redistribute bgp 65000 subnets route-map <map>
14. How to log BGP route installation issues?
Answer:
Enable:
debug ip routing
debug ip bgp
(Use with caution in production)
15. Can BGP advertise a route that is not in RIB?
Answer:
No. BGP will only advertise routes that exist in the RIB unless network <prefix> command is used with a matching route.
YouTube Link
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement BGP Route Not Installing in RIB – Path Attributes and Fix is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Ticket#4 - BGP Route Not Installing in RIB – Path Attributes and Fix [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/nj-blog-post-Ticket-4.jpg)
![LACP vs PAgP: Cisco EtherChannel Types Explained with CLI & EVE-NG Lab [2025]. [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/LACP-vs-PAgP_-Cisco-EtherChannel-Types-Explained-with-CLI_networkjourney.png)

![[Day 25] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Dynamic VLAN Assignment in Wired Networks](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-25-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Dynamic-VLAN-Assignment-in-Wired-Networks.png)