[Day #101 PyATS Series] Graduation Project: Build and Share Your pyATS Multi-Vendor Validation Suite on GitHub Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction: Key Concepts
Welcome to Day #101 of the 101 Days of pyATS (Vendor-Agnostic) series! Today marks the culmination of our journey: building a production-ready, multi-vendor pyATS validation suite and publishing it on GitHub.
For a Python for Network Engineer, this final project is your opportunity to:
- Integrate all prior skills: CLI/GUI validation, multi-vendor testing, audit reports, plugin-based frameworks.
- Create a modular, reusable, version-controlled testing suite.
- Showcase your work to management, peers, and the wider networking community.
- Learn best practices for open-source network automation projects.
By the end of this Article, you will have a GitHub-ready suite demonstrating end-to-end automation mastery.
Topology Overview
For the graduation project, our lab topology simulates a multi-vendor enterprise network:
- Core Layer: Cisco ISR routers
- Distribution Layer: Cisco Catalyst & Arista switches
- Edge Layer: Palo Alto & FortiGate firewalls
- Access Layer: Hosts and virtual clients
- Automation Server: pyATS testing framework, Jenkins/GitHub Actions integration
Simplified Topology Diagram:
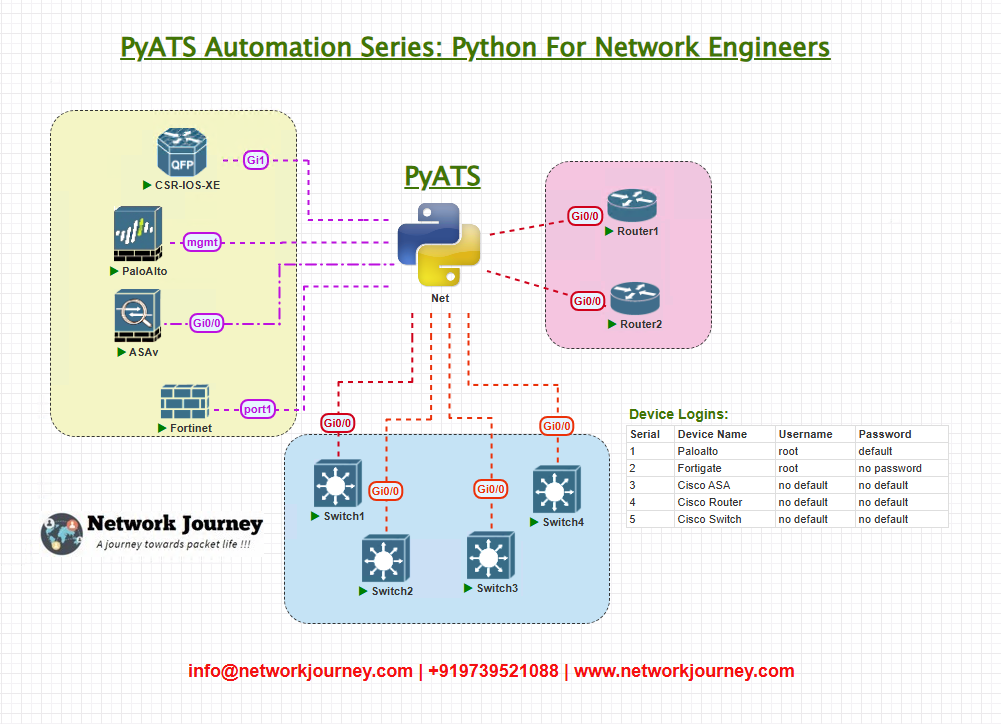
This ensures you can validate routing, interface status, service reachability, security policies, and compliance checks across multiple vendors.
Topology & Communications
- Device Communication Protocols: SSH, REST API, NETCONF
- Automation Architecture:
- Core: pyATS test execution engine
- Plugins: Modular checks for interfaces, routing, firewalls, services, and licenses
- Reporting: JSON → HTML/PDF, GitHub README updates
- CI/CD Integration: GitHub Actions for scheduled tests and report generation
- Parallel Execution: Using pyATS
pcallfor multi-device validation - Data Aggregation: CLI outputs via Genie parsers, API snapshots for GUI-based devices
Workflow Script
The graduation project workflow includes:
- Load
testbed.ymlfor device definitions. - Execute multi-vendor validation plugins (interfaces, BGP, firewall rules, services, compliance).
- Aggregate results into structured JSON.
- Generate HTML/PDF reports.
- Automatically update GitHub repository with results and documentation.
- Optionally, trigger GitHub Actions workflow for scheduled tests.
Core Script: graduation_suite.py
import os
import json
from datetime import datetime
from pyats.async_ import pcall
from genie.testbed import load
from jinja2 import Environment, FileSystemLoader
from weasyprint import HTML
from git import Repo
# Load testbed
testbed = load('testbed.yml')
# Discover plugins
PLUGIN_DIR = 'plugins'
plugins = [f.replace('.py','') for f in os.listdir(PLUGIN_DIR) if f.endswith('.py')]
def run_plugin(device_name, plugin_name):
device = testbed.devices[device_name]
device.connect()
plugin_module = __import__(f'plugins.{plugin_name}', fromlist=['run'])
result = plugin_module.run(device)
device.disconnect()
return {device_name: result}
# Execute plugins across all devices
all_results = {}
for plugin in plugins:
results = pcall(run_plugin, *[(dev.name, plugin) for dev in testbed.devices.values()])
all_results[plugin] = results
# Save JSON results
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
json_file = f'audit_results_{timestamp}.json'
with open(json_file, 'w') as f:
json.dump(all_results, f, indent=2)
# Generate HTML report
env = Environment(loader=FileSystemLoader('templates'))
template = env.get_template('audit_report.html')
html_out = template.render(results=all_results, timestamp=timestamp)
html_file = f'audit_report_{timestamp}.html'
with open(html_file, 'w') as f:
f.write(html_out)
# Convert to PDF
HTML(html_file).write_pdf(f'audit_report_{timestamp}.pdf')
# GitHub integration: Commit and push results
repo = Repo('.')
repo.git.add([json_file, html_file, f'audit_report_{timestamp}.pdf'])
repo.index.commit(f'Add audit reports {timestamp}')
origin = repo.remote(name='origin')
origin.push()
print("Reports generated and pushed to GitHub!")
Explanation by Line
pcall(run_plugin, ...): Executes plugins on multiple devices simultaneously.- JSON Output: Provides structured, machine-readable data for reporting.
- Jinja2 Templates: Converts JSON into management-friendly HTML reports.
- WeasyPrint HTML → PDF: Produces professional-grade PDFs for sharing.
- GitPython Integration: Automatically commits reports to GitHub for version-controlled audit tracking.
- Plugin Modularity: Each plugin is independent, supporting multi-vendor environments.
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: GraduationProjectLab
devices:
core1:
type: router
os: iosxe
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.10.10.1
username: admin
password: Cisco123
dist1:
type: switch
os: iosxe
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.10.20.1
username: admin
password: Cisco123
arista1:
type: switch
os: eos
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.10.30.1
username: admin
password: Arista123
palo1:
type: firewall
os: panos
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.10.40.1
username: admin
password: Palo123
forti1:
type: firewall
os: fortios
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.10.50.1
username: admin
password: Forti123
Post-Validation CLI (Expected Outputs)
Interface Status Validation
core1> show interfaces Interface Status Admin Speed Duplex Gi0/0 up up 1000 full Gi0/1 down down 1000 full
Firewall Policy Validation
palo1> show security policies Policy Source Destination Action P1 ANY ANY permit P2 ANY ANY deny
GitHub Integration Confirmation
$ git status On branch main Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'. Changes to be committed: new file: audit_report_20250906_103045.html new file: audit_report_20250906_103045.pdf new file: audit_results_20250906_103045.json
FAQs
Q1: What is the goal of this graduation project?
A1: The goal is to create a fully functional, production-ready pyATS validation suite that:
- Validates multi-vendor network devices (Cisco, Arista, Palo Alto, Fortigate, etc.)
- Automates health checks, configuration compliance, and service validation
- Can be version-controlled and shared on GitHub
This project demonstrates your ability to build, test, and maintain reusable automation frameworks.
Q2: Why is using GitHub important for a pyATS validation suite?
A2: GitHub enables:
- Version control for scripts, test cases, and templates
- Collaboration with peers or mentors
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines (e.g., GitHub Actions) for automated testing
- Portfolio visibility, showcasing your network automation skills to recruiters or management
Q3: How do you ensure multi-vendor compatibility in the suite?
A3: Key strategies include:
- Using vendor-agnostic abstractions in test scripts
- Leveraging pyATS Genie parsers for normalized CLI outputs
- Implementing conditional logic for vendor-specific commands
- Maintaining a common result model for reports and dashboards
This allows a single framework to validate diverse network environments seamlessly.
Q4: How can you structure your pyATS validation suite for scalability?
A4: Recommended structure:
- testbed.yml – defines all devices, credentials, and connections
- testcases/ – contains modular test scripts (interface checks, routing, ACLs)
- plugins/ – reusable functions or vendor-specific extensions
- reports/ – automated HTML, PDF, or Markdown outputs
- CI/CD integration – for automated validation on every commit
This structure ensures reusability, maintainability, and expandability.
Q5: How do you handle configuration drift or failed validations?
A5: pyATS supports:
- Capturing before/after snapshots for configurations
- Highlighting drift from golden templates
- Logging failed test results with detailed CLI output
- Generating visual dashboards for easy root-cause analysis
This ensures rapid remediation and compliance tracking across multi-vendor environments.
Q6: How can the suite be used in professional environments?
A6: Applications include:
- Pre-production validation of new devices or software upgrades
- Continuous monitoring of multi-vendor networks
- Audit and compliance reporting
- Hands-on portfolio demonstration for automation engineers
It provides real-world value beyond academic exercises.
Q7: How do you integrate CI/CD pipelines for the GitHub-hosted suite?
A7: By using GitHub Actions or similar CI tools:
- Test scripts run automatically on push or pull requests
- Results and reports are archived or emailed
- Alerts or dashboards notify teams of failed tests or compliance issues
This enables continuous validation and versioned network audits.
Q8: What are the long-term benefits of completing this project?
A8: Benefits include:
- Mastery of pyATS and multi-vendor automation frameworks
- Hands-on experience with CI/CD integration and GitHub versioning
- Creation of a reusable and scalable network testing toolkit
- Demonstrated capability for production-grade network automation
- Portfolio evidence for career advancement as a Python for Network Engineer
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Graduation Project: Build and Share Your pyATS Multi-Vendor Validation Suite on GitHub Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
Take your Python for Network Engineer skills to the next level by mastering multi-vendor automation frameworks and GitOps workflows.
Join Trainer Sagar Dhawan’s 3-month instructor-led program to learn:
- Advanced pyATS testing frameworks
- Multi-vendor automation (Cisco/Arista/Palo Alto/FortiGate)
- CI/CD and GitHub integration
- Professional reporting dashboards
- Realistic, production-grade labs
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #101 PyATS Series] Graduation Project: Build and Share Your pyATS Multi-Vendor Validation Suite on GitHub Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-101-PyATS-Series-Graduation-Project-Build-and-Share-Your-pyATS-Multi-Vendor-Validation-Suite-on-GitHub-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![[Day #52 PyATS Series] Writing pyATS Plugins for Vendor-Specific Features using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-52-PyATS-Series-Writing-pyATS-Plugins-for-Vendor-Specific-Features-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)

![[Day #11 PyATS Series] Parsing MAC Address Tables (Cisco/Arista/Palo Alto/Fortigate) using pyATS – Python for Network Engineer](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/DAY11-PyATS-Series-Parsing-MAC-address-tables-Cisco-Arista-Paloalto-Fortigate.png)