[Day 128] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Advanced BYOD Flow with Certificates
Table of Contents
Introduction
Picture this classroom demo: A user walks into the office, opens Wi-Fi settings, selects Corporate-BYOD, and — without IT touching the laptop — receives an identity certificate, configures the OS supplicant, and gets 802.1X/EAP-TLS access to the corporate network. No passwords, no wasteful help-desk resets, and authentication that ties a device identity (certificate) to posture and policy.
That is BYOD with certificates: the secure, scalable way to provide strong device identity using certificate-based authentication (EAP-TLS) and automated certificate enrollment (SCEP/EST or ISE internal CA). It replaces weak password flows with cryptographic identity, dramatically reducing lateral-movement risk, improving user experience, and enabling device posture + lifecycle control.
Today’s Article is hands-on: we’ll configure ISE to provision certificates (via SCEP/NDES or ISE’s EST/internal CA), create endpoint provisioning policies, enable EAP-TLS authentication flows, validate with CLI and GUI, capture packets, and build an operational troubleshooting playbook.
Problem Statement
Real challenges enterprises face with BYOD:
- Weak device identity (passwords on devices) → spoofing & credential theft.
- Manual certificate issuance → scaling and UX failure for thousands of devices.
- Fragmented MDM/NDES/CA integrations causing provisioning failures.
- Posture and lifecycle — how to revoke or re-issue device identity on compromise or employee exit.
Goal: Automate certificate issuance and onboarding so devices receive a trusted certificate automatically, use EAP-TLS for 802.1X, and ISE enforces posture/authorization based on the certificate and device posture.
Solution Overview (how Cisco ISE addresses the problem)
Cisco ISE supports multiple certificate enrollment approaches:
- SCEP (via Microsoft NDES) — widely used for automated device certificate issuance; ISE can be configured as a SCEP proxy to NDES so endpoints contact ISE and ISE talks to NDES/ADCS on behalf of clients. Cisco docs explain configuring SCEP RA profiles and the ISE SCEP proxy.
- EST (Enrollment over Secure Transport) / ISE internal CA — ISE provides EST and an internal CA service for certificate issuance, an alternative to external NDES. Use ISE CA/EST when you prefer an integrated PKI path.
- Certificate Provisioning Portal — ISE portal that lets users request device certs (or admins manually issue for devices like POS terminals). Useful for devices that can’t run full BYOD flows.
Once certificates are on devices, EAP-TLS becomes the authentication method. ISE maps certificate attributes (subject, SAN, device UUID) and posture results to Authorization Profiles (VLAN, dACL, SGT). For MDM integrations (Intune / Jamf), combine certificate issuance with device compliance checks and tie it to ISE policy. (Microsoft Learn, DCLessons)
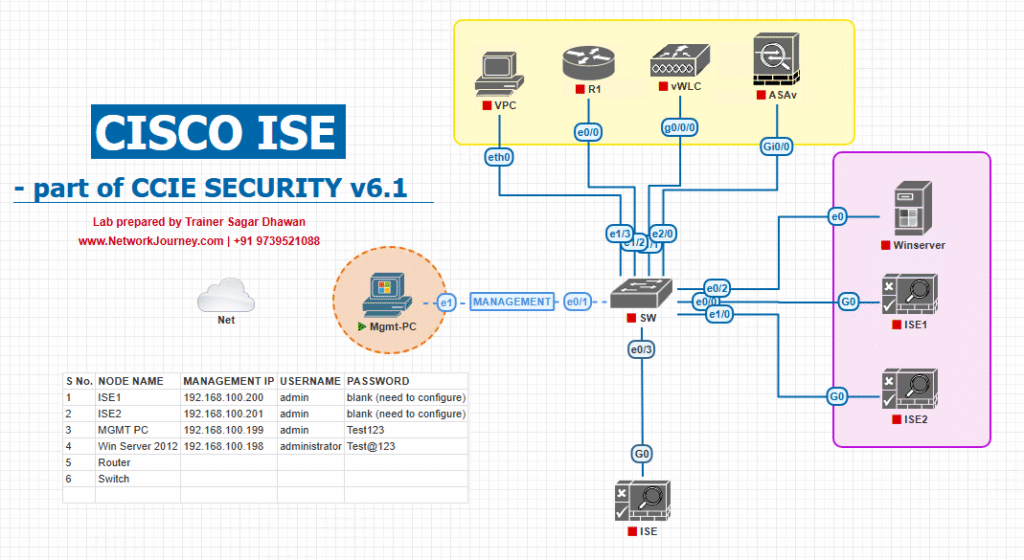
Sample Lab Topology
Platform: VMware or EVE-NG (both supported). Use snapshots for repeatability.
Components
- Cisco ISE (PAN + PSN; ISE 3.x recommended).
- Windows Server (ADCS + NDES) — AD Certificate Services + NDES role.
- Optional: MDM server (Microsoft Intune or other) — for MDM conditional checks.
- Catalyst Switch (9300) for wired 802.1X access.
- Catalyst 9800 WLC for wireless 802.1X (optional).
- Endpoints: Windows 10/11 laptop (scripting), iOS device (OTA), Android test device.
- Automation host: Ubuntu VM for curl/Postman, tcpdump, Wireshark.
IP Plan (example)
- ISE PAN: 10.10.10.10
- ISE PSN: 10.10.10.11
- AD/NDES server: 10.10.20.10
- Switch mgmt: 10.10.30.20
- Client subnet (BYOD VLAN): 172.16.110.0/24
Topology diagram:
Step-by-Step GUI Configuration Guide (with validation & CLI)
Pre-reqs checklist (before starting):
- ISE reachable from NADs and NDES server.
- Windows ADCS + NDES installed and reachable.
- Time (NTP) synchronized across ISE, NDES, NADs, endpoints.
- TLS certs for NDES IIS bindings if using HTTPS.
- Administrative credentials for ISE and ADCS.
Phase A — Prepare Certificate Infrastructure (ADCS + NDES)
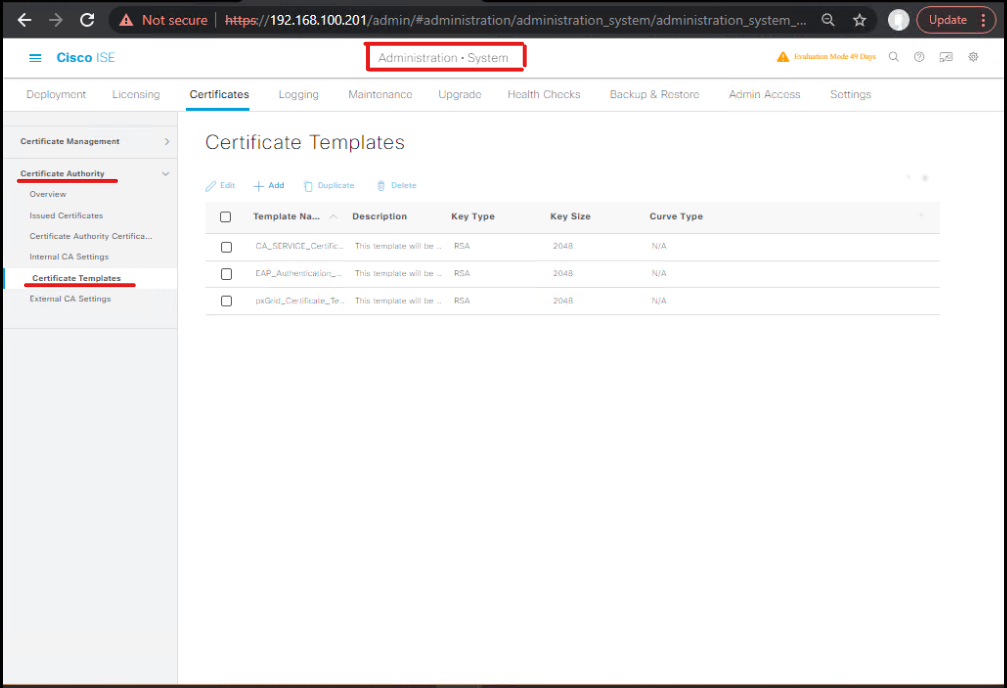
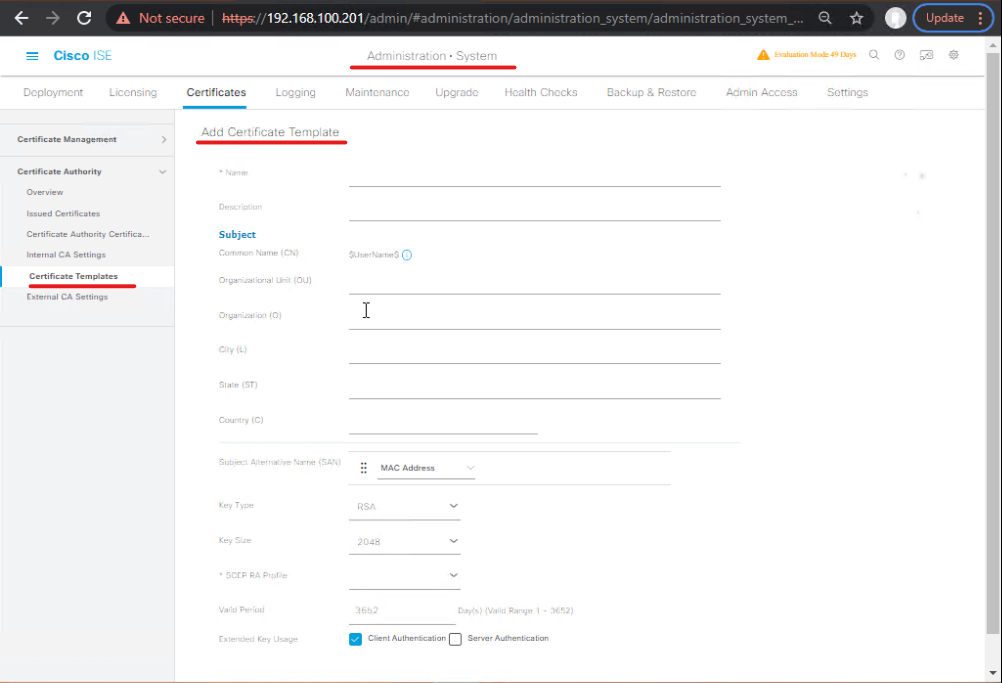
A.1 — ADCS: create Certificate Template for BYOD
- On CA server → Certification Authority → Certificate Templates → Manage.
- Duplicate the User template or Computer template depending on device type, name it
ISE-BYOD(ensure Key Usage includes Client Authentication). - Set Security: give NDES service account Enroll rights.
- Publish the template on the CA (right-click Certificate Templates → New → Certificate Template to Issue → select
ISE-BYOD).- Validation: In CA console the template should appear under Certificate Templates. (Windows CA docs).
A.2 — NDES (Windows Server) installation & recommended registry tweak
- Install Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES) role (part of ADCS). Configure the NDES service account and RA (Registration Authority) certificates.
- Cisco recommends disabling the SCEP challenge password requirement for self-service BYOD (set
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\MSCEP\EnforcePassword= 0) so endpoints can enroll without manual challenge input. (Follow security policy!).
A.3 — Configure HTTPS for NDES (IIS binding)
- Create/obtain an IIS server certificate (Web Server template), bind to Default Web Site on port 443 (recommended). Cisco has a guide to configure NDES over HTTPS to work with ISE SCEP proxy.
Phase B — Configure SCEP RA Profile in ISE (SCEP proxy)
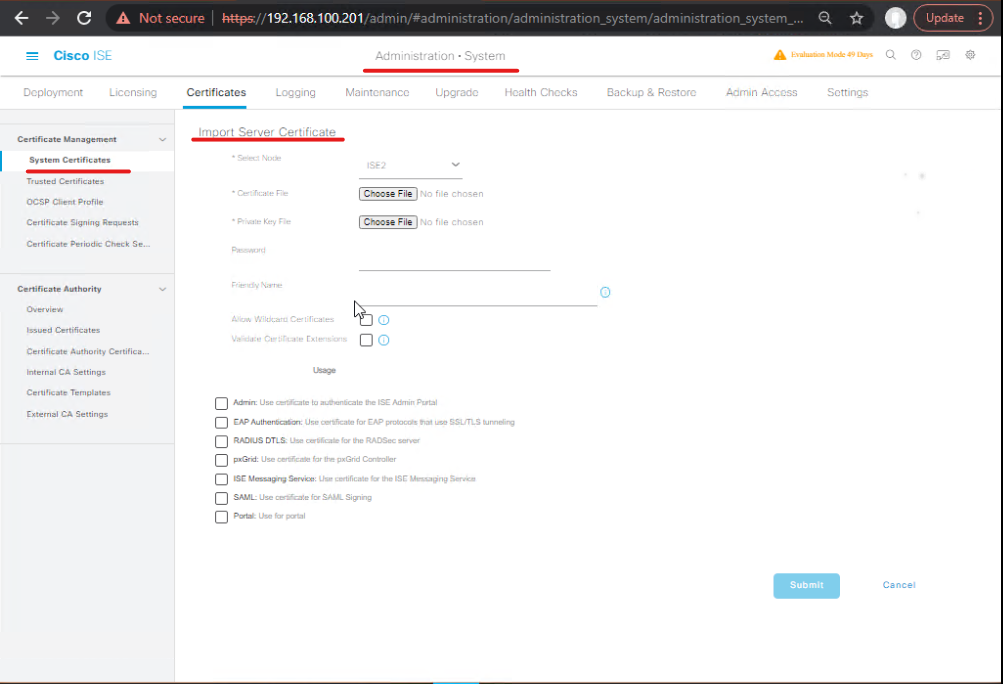
B.1 — Import CA chain into ISE
- ISE GUI:
Administration > System > Certificates > Certificate Store→ Import the CA chain from the AD CS (root + sub CA). Validate the chain appears.
B.2 — Create SCEP RA Profile
- ISE GUI:
Administration > System > Certificates > SCEP RA Profiles→ Add.- Name: NDES-SCEP
- SCEP URL:
http(s)://<NDES_IP_or_FQDN>/certsrv/mscep/(https preferred). - Click Test Connectivity → ISE should retrieve RA certificate chain and import RA cert into Certificate Store.
- [ISE SCEP RA Profiles — Add]
Validation: ISE console shows RA cert in Administration > System > Certificates > Certificate Store. Test connectivity must succeed.
Phase C — Configure Endpoint Profiles / Certificate Authentication in ISE
C.1 — Create Certificate Authentication Profile
- ISE GUI:
Administration > Identity Management > External Identity Sources > Certificate Authentication Profiles→ Add new profile (e.g.,CertAuth_BYOD).- Choose Certificate Subject Mapping rules (e.g., use
Subject CNorSANto map toNetwork Access:Guestor Active Directory user). - [Certificate Authentication Profile]
- Validation: create a test certificate and use
Administration > Identity Management > External Identity Sources > Certificate Authenticationtest tools to verify mapping. (Scribd)
- Choose Certificate Subject Mapping rules (e.g., use
C.2 — Create Endpoint Identity Group & Endpoint Profile
Work Centers > BYOD > Configure > Endpoint Identity Group→ Add groups (e.g.,BYOD_Devices,Corporate_Devices).
Work Centers > BYOD > Configure > Endpoint Profiles→ Create or edit an endpoint profile with EAP-TLS and associated certificate template. Select the SCEP RA profile for certificate provisioning. [ BYOD Endpoint Profile]
Phase D — Enable BYOD Services & Portals (ISE GUI)
D.1 — Enable BYOD Services
Work Centers > BYOD > Onboarding→ Enable BYOD and enable Certificate Provisioning. Configure the portal type: Single-SSID or Dual-SSID onboarding (choose based on your design). [ BYOD Onboarding Enable]
D.2 — Create BYOD Portal (Self Onboard)
Work Centers > Guest & BYOD > Portals & Components→ Create a BYOD portal or customize default BYOD portal pages. Ensure the portal uses the endpoint profile that references the SCEP RA profile. [ BYOD Portal Page]
- Test the portal URL with a browser from the test client (this confirms page load & TLS chain if external).
Phase E — Configure Network Devices for 802.1X EAP-TLS (Switch + WLC CLI)
E.1 — Switch (Catalyst 9300) — sample commands
conf t aaa new-model aaa authentication dot1x default group radius aaa authorization network default group radius radius server ISE address ipv4 10.10.10.11 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key ISE_SECRET ! aaa server radius dynamic-author client 10.10.10.11 server-key ISE_SECRET port 3799 ! dot1x system-auth-control interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 110 authentication port-control auto mab dot1x pae authenticator spanning-tree portfast end
Validation CLI checks
show authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/10 details show dot1x all show aaa servers show radius statistics
E.2 — 9800 WLC (if used): add ISE RADIUS servers with CoA / dynamic author enabled and create WLAN with Security → Layer 2 EAP-TLS, server certificate settings, and dynamic interface mapping. Validate via show wireless client mac <mac> and WLC GUI client page. (Cisco 9800 SCEP/LSC and EAP-TLS docs).
Phase F — BYOD Enrollment Lab Walkthrough (Windows 10 example) — step-by-step with validation
F.1 — Start point: client on open guest VLAN or unauthenticated network (redirect to BYOD portal).
F.2 — On endpoint (automatic flow):
- User navigates to
https://byod.company.com(BYOD portal) — portal detects device OS. [BYOD Portal] - User completes form (Accept policy). Portal presents option Install certificate or Enroll device.
- ISE SCEP proxy process: ISE receives enrollment request → ISE uses configured SCEP RA Profile to call NDES/ADCS → Certificate is issued and returned to ISE → ISE provisions the cert to the endpoint (via OTA mechanisms or via instructions for user to install).
F.3 — Endpoint config / supplicant: (Windows) the portal may install a WLAN profile with EAP-TLS and attach certificate to user/machine store. For iOS/Android, use the native OTA profile or MDM to deliver trust anchor + certificate. [Client certificate store showing issued cert]
F.4 — Authentication validation:
- Attempt to join SSID
Corp-8021x— supplicant uses EAP-TLS; ISE receives certificate & validates chain. - On ISE:
Operations > RADIUS > Live Logs→ Look for Access-Request with EAP type = EAP-TLS and Authorization Profile = BYOD_Employee. [ISE Live Logs – EAP-TLS Success] - On switch:
show authentication sessions mac <mac>→ session stateAuthorized, VLAN 10 (corporate), dACL assigned. - On endpoint:
certutil -store myshows certificate installed and valid (Windows CLI). - Optional packet capture: capture EAPOL and confirm TLS handshake and successful server certificate verification.
Troubleshooting & Diagnostics
T1 — SCEP/NDES Connectivity Failures
- Symptom: ISE Test Connectivity fails on SCEP RA profile.
- Checkpoints:
- From ISE PSN,
curl -vk https://<NDES_FQDN>/certsrv/mscep(use automation host if direct is blocked) — confirm reachability and TLS chain. - In IIS on NDES: verify SCEP virtual directory exists and HTTPS binding uses a valid cert. Cisco has a step-by-step for configuring HTTPS SCEP.
- If using HTTP, ensure firewall rules allow port 80/443 between ISE and NDES.
- Validate
EnforcePasswordregistry setting if using self-service flows (see Cisco guide).
- From ISE PSN,
T2 — Enrollment returns certificate but supplicant fails to use it
- Check: certificate private key presence in user/machine store, correct Key Usage & EKU (Client Authentication).
- Windows:
certutil -store myand check template and EKU. If missing EKU or wrong template, adjust CA template (duplicate with Client Authentication EKU).
T3 — EAP-TLS auth fails (certificate chain or revocation issues)
- On ISE, check
Administration > System > Certificates > Certificate Storefor full chain and CRL/OCSP reachable. - Verify ISE Trust for CA chain. For OCSP:
Administration > System > Settings > OCSPsettings. If ISE cannot fetch CRL/OCSP, EAP-TLS may fail.
T4 — Post-enrollment: device not placed in correct Endpoint Identity Group
- Verify mapping rules in Certificate Authentication Profile and Endpoint Profiling (subject CN, SAN, device UUID). Use
Operations > Endpointsto search endpoint attributes returned by MAB/EAP.
T5 — MDM conditional access issues (Intune example)
- Confirm Intune/SCEP connector correctly configured, that device is marked Compliant, and that ISE is querying MDM for compliance (via pxGrid or API). Validate with ISE device posture and MDM logs. Microsoft docs for SCEP + Intune are helpful. (Microsoft Learn)
Packet capture tips
- Capture EAP traffic on the switch port and RADIUS packets between NAD and ISE. Filter Wireshark:
eap || radius || tcp.port==443 && ip.addr==10.10.20.10
- Look for EAP-TLS handshake and RADIUS Access-Accept attributes (Tunnel-Private-Group-ID for VLAN, Cisco-DACL attributes).
Lab Walkthroughs with Validation (two scenarios)
Lab 1 — Windows 10 BYOD (Self-Onboard + SCEP)
- Boot Windows client (clean state). Connect to a provisioning network or open SSID that redirects to BYOD portal.
- Browse to BYOD portal, accept T&Cs, click Enroll. Portal uses ISE SCEP proxy to call NDES → cert issued.
- Portal installs cert and WLAN profile (EAP-TLS) on the client.
- Client connects to Corp SSID → EAP-TLS handshake → ISE authorizes → VLAN/dACL applied.
- Verify:
show authentication sessions mac <mac>on switch + ISE Live Logs show EAP-TLS success.
Validation checklist:
- Certificate present in
certmgr.msc(Personal/Certificates). - ISE Live Logs show Access-Accept with authorization profile and certificate attributes.
- switch
show access-sessionshows Authorized.
Lab 2 — iOS OTA enrollment (over the air)
- On iOS, open Safari to BYOD portal URL → follow instructions to install provisioning profile (MDM optional).
- If portal uses SCEP + OTA, iOS will request certificate provisioning; NDES issues cert via ISE SCEP proxy.
- After cert installed, iOS connects to SSID with EAP-TLS.
- Validate with ISE Live Logs & WLC
show client detail. (Mobile-specific quirks: ensure proper UDID/SAN mapping and that iOS trusts CA root). (DCLessons)
Expert Level Use Cases
Use Case 1 — Zero-Touch Corporate BYOD Onboarding (scale)
- Design: Single-SSID onboarding with BYOD portal; SCEP proxy to NDES; MDM optional.
- Steps: configure SCEP RA profile, endpoint profile with EAP-TLS, BYOD portal; create onboarding policy.
- Validation: enroll 10 devices concurrently; watch NDES & ISE PSN CPU, check for race conditions; monitor CA issuance latency.
- Troubleshoot: use ISE Test Connectivity to SCEP RA and NDES logs to find failures.
Use Case 2 — Posture-gated certificate issue (compliance enforced)
- Device hits BYOD portal → initial limited access assigned.
- Run posture checks (Antivirus, Patches). If compliant, trigger SCEP enrollment via portal and issue cert.
- After cert issuance, device auto-connects using EAP-TLS and receives full access.
- Validate: ISE Live Logs show posture, SCEP enrollment, and EAP-TLS Access-Accept sequentially.
Use Case 3 — Revoke & Reissue for Compromised Device
- SOC flags device → revoke cert in AD CS + remove endpoint in ISE.
- If device comes back, require re-onboarding via BYOD portal which triggers fresh SCEP flow.
- Verify: revoked cert is listed in CRL; ISE denies EAP-TLS with revoked cert; re-enroll new cert and retest.
FAQs – Cisco ISE Advanced BYOD Flow with Certificates
Q1. Why do we need certificates in BYOD onboarding instead of just usernames/passwords?
Answer:
- Password-based access is vulnerable (phishing, reuse, brute force).
- Certificates provide device identity + user identity (two-level trust).
- They allow seamless re-authentication without user prompts.
Validation: - On endpoint → check installed profile & cert (Windows:
mmc.exe → Certificates → Personal). - On ISE → Operations > RADIUS > Live Logs → confirm “EAP-TLS” with valid CN.
Q2. How does Cisco ISE provision a certificate during BYOD onboarding?
Answer:
- Device first joins with limited access (registration VLAN/dACL).
- ISE redirects HTTP → to BYOD portal.
- User authenticates (AD/LDAP).
- ISE + SCEP (Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol) issues a cert via internal CA or external CA (MS PKI).
- ISE installs certificate + supplicant config (via AnyConnect NAM/Apple MDM).
Validation: - On ISE → Operations > Reports > Endpoint Certificates Issued.
- CLI (switch):
show authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/10 detailsLook forEAP-TLSandSSLcert CN.
Q3. What happens if a user deletes the BYOD certificate from their device?
Answer:
- Next re-auth → fails (no cert).
- ISE moves device back to registration policy → user forced to go through BYOD portal again.
Validation: - On ISE Live Logs → you’ll see
EAP-TLS failed – no valid certificate. - On client → no cert in personal store.
Q4. Can a single user register multiple devices in BYOD flow?
Answer:
Yes, depending on policy:
- Default: 3 devices per user (configurable in ISE → Administration > Identity Management > Settings > Portal Settings).
- Each device gets its own certificate tied to endpoint ID + user ID.
Validation: - ISE → Context Visibility > Endpoints → filter by username, see all devices.
Q5. How do we ensure that only company-approved BYOD devices get access, not random personal ones?
Answer:
- Use certificate profile mapping (OU=BYOD, CN=DeviceID).
- Combine with Endpoint Identity Group (BYOD-Registered).
- Optionally → integrate MDM for posture/device compliance.
Validation: - In ISE Policy Set → check if AuthZ rule matches BYOD-Registered.
- Switch CLI:
show authentication sessions→ Confirm dACL applied.
Q6. How does BYOD flow differ for iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS?
Answer:
- iOS/Android → ISE BYOD portal delivers MDM profile or SCEP profile via Safari/Chrome.
- Windows/macOS → AnyConnect/Native Supplicant Provisioning (NSP) configures Wi-Fi/EAP-TLS profile.
Validation: - On ISE → Operations > Live Logs → check device type in
Called-Station-ID. - On endpoint → Wi-Fi profile auto-created under “Trusted Certificates.”
Q7. How do we troubleshoot when BYOD onboarding portal does not redirect?
Answer:
- Verify switchport ACL:
show access-session interface Gi1/0/10 detailsMust showredirect-url. - Ensure client browser is not using cached HTTPS.
- Debug NAD:
debug ip http all debug aaa authorization
Q8. Can we use BYOD certificates for VPN or wired access as well?
Answer:
Yes. Once device cert is issued, it can be trusted across:
- Wired 802.1X
- Wireless 802.1X
- VPN (ASA/FTD/ISE integration).
Validation: - On ASA/FTD VPN → configure EAP-TLS with trusted CA.
- Test VPN connection using BYOD device cert.
Q9. How do we revoke a BYOD certificate if a device is lost or stolen?
Answer:
- If using ISE Internal CA → Administration > Certificates > Certificate Management → revoke.
- If using MS PKI/External CA → revoke in CA CRL/OCSP.
- Push reauth via CoA → device blocked instantly.
Validation: - Attempt reconnect → fails with “revoked certificate”.
Q10. How do we monitor BYOD success rate and failures in ISE?
Answer:
- Use ISE built-in reports:
- Reports > Endpoints and Users > BYOD Endpoint Provisioning Report
- Reports > Authentication > Authentication Summary
- Monitor failures → reasons like redirect fail, cert not installed, SCEP timeout.
Validation: - Run
show loggingon switch for redirect errors. - On ISE → filter Live Logs for
BYODkeyword.
YouTube Link
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to my YouTube channel Network Journey and join my instructor-led classes for hands-on, real-world ISE experience
Closing Notes (key takeaways)
- Automated certificate provisioning (SCEP/EST) + EAP-TLS = strongest BYOD identity and best UX.
- SCEP via NDES is common in AD shops — but requires careful NDES/IIS config (HTTPS, RA certs) and ISE SCEP proxy configuration.
- Time sync, CA chain and CRL/OCSP reachability, and correct template EKUs are the three most common failure points. Always validate these first.
Upgrade Your Skills – Start Today
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to Network Journey on YouTube and join my instructor-led classes.
Fast-Track to Cisco ISE Mastery Pro (4-month instructor-led) — I run a hands-on program that converts engineers into ISE architects (EVE-NG/VMware labs, live troubleshooting, CCIE-grade scenarios).
Grab the free labpack and reserve a seat: https://course.networkjourney.com/ccie-security/
Join the training here and take your first step towards becoming a CCIE Security expert.
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088



