[Day 38] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Wired Supplicant Configuration for Windows
Table of Contents
Introduction
In enterprise networks, 802.1X authentication is the backbone of Network Access Control (NAC). For a wired connection, the device’s built-in supplicant — a client software that handles authentication — is the bridge between the endpoint and Cisco ISE.
Windows systems come with a native 802.1X supplicant that can be configured to perform EAP authentication (EAP-TLS, PEAP-MSCHAPv2, etc.), enabling seamless wired access control without third-party agents.
In Cisco ISE deployments, configuring the Windows supplicant correctly is critical — a single misconfigured checkbox can cause hours of troubleshooting. In this lab, we’ll configure Windows wired supplicants for 802.1X, validate with ISE, and use CLI & GUI to confirm the results.
Problem Statement
Without proper supplicant configuration:
- Endpoints bypass 802.1X by falling back to open or MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) modes.
- Users see “Network authentication failed” errors without clear guidance.
- Certificates aren’t presented correctly, breaking EAP-TLS setups.
- Large deployments face inconsistencies if manual setup is used instead of automation (GPO/Intune).
This results in security gaps where unauthorized devices can plug into wall jacks and gain access — something NAC is designed to prevent.
Solution Overview
Cisco ISE ensures that only properly authenticated endpoints are allowed on the network. The Windows wired supplicant is the client side of this process:
- For EAP-TLS: The supplicant presents a client certificate to ISE.
- For PEAP: The supplicant uses username/password credentials (usually from Active Directory).
- ISE enforces access policies based on authentication + authorization results.
The solution involves:
- Enabling the Wired AutoConfig service on Windows.
- Configuring the wired network interface for 802.1X.
- Choosing the correct EAP method (PEAP or EAP-TLS).
- Testing and validating via ISE Live Logs and switch CLI.
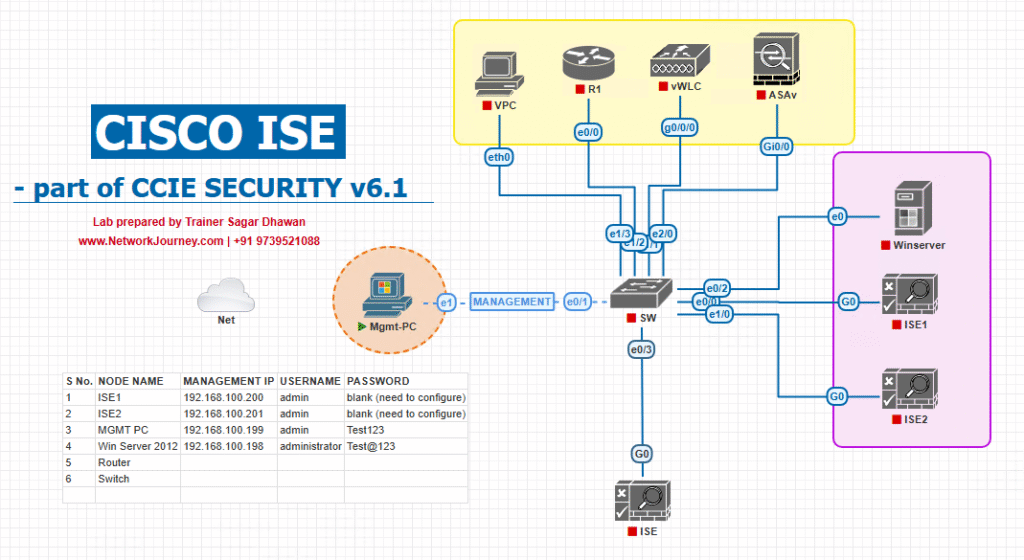
Sample Lab Topology
Lab Environment Components:
- Cisco ISE: v3.x (VMware Workstation/EVE-NG)
- Access Switch: Catalyst 9300 (EVE-NG or physical)
- Windows 10/11 Endpoint: Physical or VMware bridged to wired interface
- AD/DNS/CA Server: Windows Server 2019 (for domain join and certificates)
- Management PC: For ISE GUI access
Logical Diagram:
Step-by-Step GUI + CLI Configuration Guide
Part A – Switch Configuration (CLI)
conf t ! aaa new-model aaa authentication dot1x default group radius aaa authorization network default group radius radius server ISE1 address ipv4 10.10.10.10 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key cisco123 ! ip device tracking dot1x system-auth-control ! interface Gi1/0/10 switchport mode access authentication order dot1x mab authentication priority dot1x mab authentication port-control auto mab dot1x pae authenticator spanning-tree portfast ! end wr mem
Validation Command:
show authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/10 details
Look for Authc Success and method dot1x.
Part B – Windows Endpoint Configuration (GUI)
Step 1 – Enable Wired AutoConfig Service
- Open Services.msc.
- Locate Wired AutoConfig.
- Set Startup type to Automatic.
- Click Start.
Step 2 – Configure 802.1X on Ethernet Interface
- Go to Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings.
- Right-click Ethernet > Properties.
- Go to Authentication tab.
[Screenshot: Ethernet Authentication Tab] - Check Enable IEEE 802.1X authentication.
Step 3 – Choose EAP Method
- For PEAP: Select Microsoft: Protected EAP (PEAP), click Settings, uncheck Validate server certificate (for lab), choose MSCHAPv2.
- For EAP-TLS: Select Smart Card or other certificate, choose the correct machine certificate.
Step 4 – Save & Reconnect
- Disconnect & reconnect Ethernet cable to trigger authentication.
- On success, ISE Live Logs should show:
- Authc: Passed
- Authz: Assigned VLAN / dACL as per policy.
Part C – ISE Configuration (GUI)
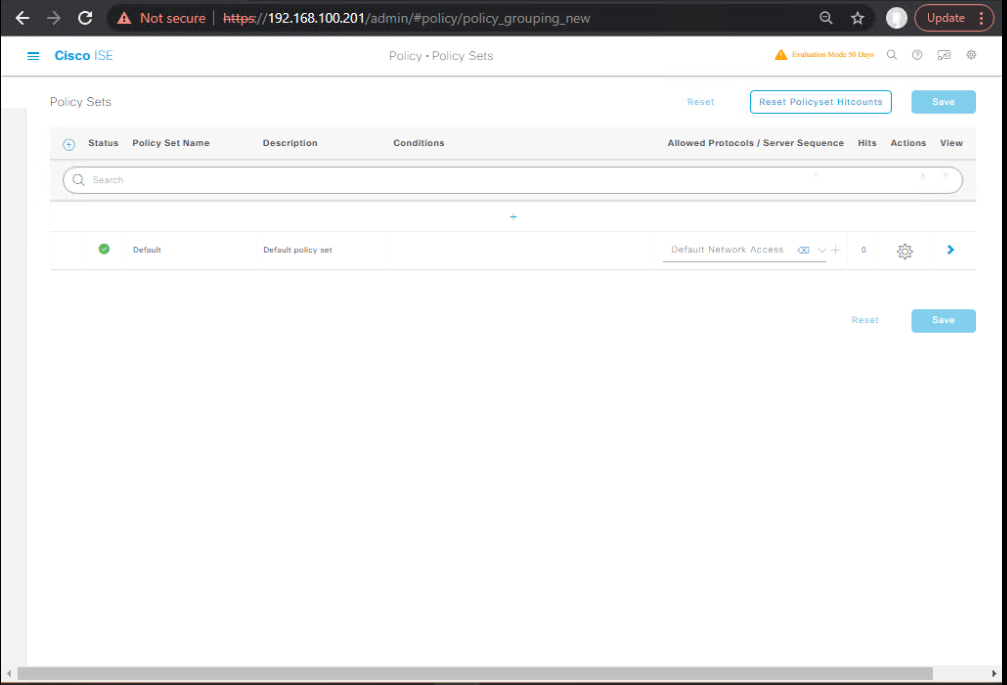
Step 1 – Add Endpoint Group/Conditions
- Navigate to Policy > Policy Sets.
- Create a new Policy Set for Wired 802.1X.
[Screenshot: ISE Policy Set Screen]
Step 2 – Authentication Policy
- Condition: Wired_802.1X
- Allowed Protocols: PEAP, EAP-TLS.
Step 3 – Authorization Policy
- If AD user in Domain Users: PermitAccess.
- If Cert CN matches: Assign VLAN 10.
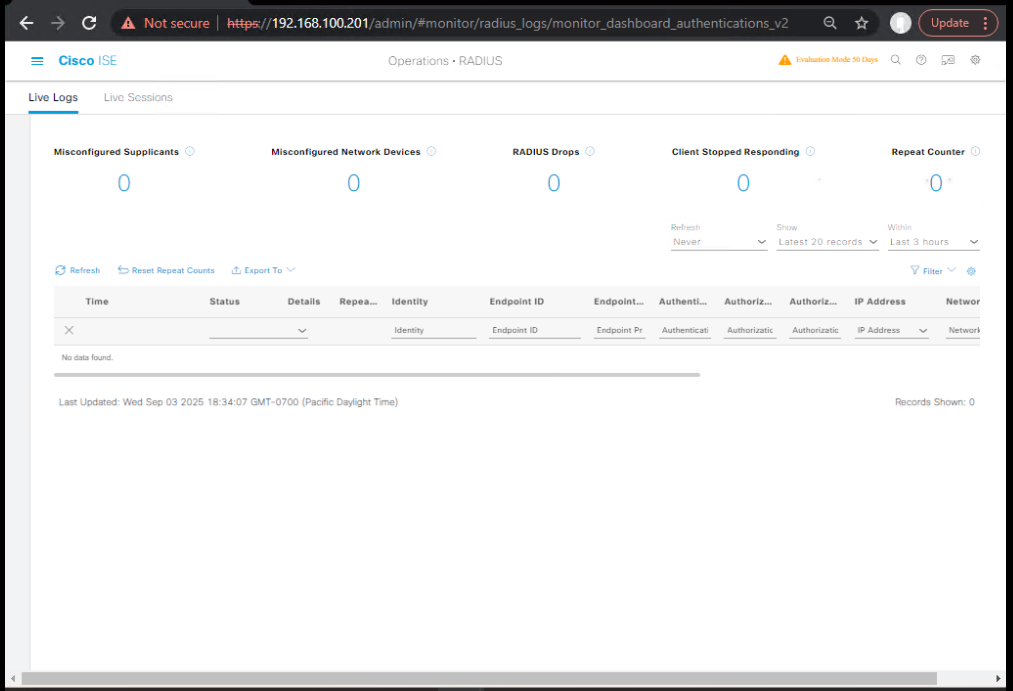
Step 4 – Validate in Live Logs
- Go to Operations > RADIUS > Live Logs.
- Confirm “Wired 802.1X” session shows SUCCESS.
FAQs
1. Do I need to install any extra software for Windows wired 802.1X authentication?
No. Windows has a native supplicant built in — all you need is to enable the Wired AutoConfig service. However, in enterprise deployments, admins often push configuration through Group Policy (GPO) so that no manual user intervention is required.
2. Should I use PEAP-MSCHAPv2 or EAP-TLS in production?
- EAP-TLS is preferred in production because it uses certificates, offering mutual authentication and stronger security.
- PEAP-MSCHAPv2 is simpler to deploy but relies on usernames/passwords, which can be phished or cracked.
3. How can I check if the Windows machine actually sent 802.1X authentication?
- On the switch CLI:
show authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/10 details - On Windows: Check Event Viewer → Windows Logs > Security for 802.1X events.
4. My ISE Live Logs show “Authentication failed” for a Windows endpoint — what’s the first thing to check?
Verify that:
- Wired AutoConfig service is running.
- Correct EAP type is configured.
- Certificate (for EAP-TLS) exists and is valid.
- User or machine credentials are correct (for PEAP).
5. Can I configure both machine and user authentication?
Yes — in Windows supplicant settings, enable “Authenticate as computer when computer information is available” to allow machine-auth before login, then user-auth after login.
6. How can I mass-deploy Windows supplicant settings?
Use Active Directory Group Policy or Microsoft Intune to push 802.1X settings to all domain-joined endpoints, ensuring consistent configuration.
7. What happens if the ISE server is unreachable?
If switch ports are set to fail-open, the endpoint may get access without authentication.
If set to fail-closed, the endpoint will be denied.
You can configure a Critical VLAN on the switch for restricted access during outages.
8. Why do I keep getting authentication loops?
Common causes include:
- Wrong EAP type selected.
- Expired or missing certificate.
- Supplicant not set to “Remember my credentials”.
- Switch misconfiguration (dot1x priority or MAB fallback loop).
9. Can I bypass authentication for special devices like printers or IP phones?
Yes — configure MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) on the switch and add the device MAC addresses in ISE under an Endpoint Identity Group.
10. How can I confirm which certificate the Windows supplicant is presenting to ISE?
- Open
certmgr.mscon Windows. - Check Personal > Certificates for the machine/user certificate.
- Ensure it matches the authentication policy in ISE.
YouTube Link
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to my YouTube channel Network Journey and join my instructor-led classes for hands-on, real-world ISE experience
Closing Notes
A properly configured Windows wired supplicant is essential for 802.1X success in ISE environments.
Inconsistent supplicant settings are one of the top causes of NAC project delays.
Mastering both GUI and CLI validation ensures smooth deployments, fewer support tickets, and better security posture.
Fast-Track to Cisco ISE Mastery Pro
Take your Cisco ISE skills from lab to production.
I run a focused 4-Month CCIE Security Instructor-Led Mastery Program — an immersive, hands-on journey covering ISE, ASA/FTD, VPN, SD-WAN, and more.
Learn in real enterprise topologies, get lifetime lab access, and train directly with an industry expert who has mentored thousands of engineers.
Limited seats — secure your spot today: https://course.networkjourney.com/ccie-security/
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day 38] – Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Wired Supplicant Configuration for Windows](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-38-–-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Wired-Supplicant-Configuration-for-Windows.png)
![[Day 31] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Wired Posture Assessment Overview](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-31-–-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Wired-Posture-Assessment-Overview-1.png)
![[Day 14] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Setting Up a Test Switch for Authentication](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-14-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-Setting-Up-a-Test-Switch-for-Authentication.png)
