[Day 39] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: Wired Supplicant Configuration for macOS/Linux
Table of Contents
Introduction
In enterprise NAC deployments, 802.1X authentication on wired ports is not just for Windows machines — it’s equally critical for macOS and Linux endpoints. Whether it’s a corporate MacBook on the marketing team’s desk or a Linux workstation in an R&D lab, Cisco ISE must enforce identity-based access control for all wired devices.
This session focuses on configuring native supplicants in macOS and Linux NetworkManager/WPA Supplicant to work seamlessly with Cisco ISE for secure wired access.
Problem Statement
Many organizations mistakenly assume that macOS and Linux devices will “just work” with the same switch and ISE settings as Windows machines.
The reality:
- macOS hides advanced 802.1X wired settings deep in Network Preferences, making it confusing for end-users.
- Linux often requires manual configuration via NetworkManager GUI or
wpa_supplicant.conf. - Without proper supplicant setup, ISE logs will show authentication failures or devices will fall back to MAB.
This creates a blind spot in NAC enforcement and opens the door to unauthorized access.
Solution Overview
Cisco ISE fully supports 802.1X authentication for both macOS and Linux wired endpoints using EAP methods such as EAP-TLS and PEAP-MSCHAPv2.
The solution involves:
- Enabling 802.1X on the wired NIC in macOS/Linux.
- Selecting the correct EAP method and certificate profile.
- Ensuring switchport configuration matches the authentication policy in ISE.
- Testing and validating via CLI (switch) + GUI (ISE Live Logs).
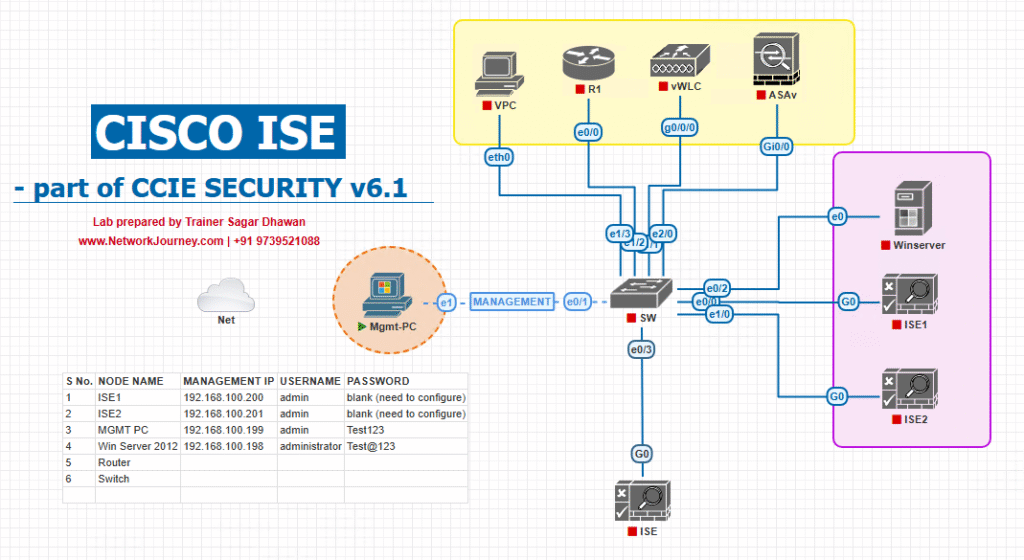
Sample Lab Topology
Components:
- ISE Server: v3.2 on VMware
- Switch: Catalyst 9300 in EVE-NG or physical lab
- Endpoints:
- macOS Ventura laptop
- Ubuntu 22.04 workstation
- AD Server: Windows Server 2019 for user/machine auth (optional)
- WLC: Optional for hybrid testing
Diagram Description:
Step-by-Step Configuration Guide
A. Switch CLI Configuration
interface Gi1/0/10 switchport mode access authentication port-control auto mab dot1x pae authenticator spanning-tree portfast
interface Gi1/0/11 switchport mode access authentication port-control auto mab dot1x pae authenticator spanning-tree portfast
B. macOS 802.1X Wired Supplicant
- Open Network Preferences → Select the wired interface (e.g., USB Ethernet or Thunderbolt Ethernet).
- Click Advanced… → 802.1X tab.
- Click + → Create new profile (e.g.,
ISE-EAP-TLS). - Authentication Type: Select TLS or PEAP.
- If TLS, choose the correct identity certificate from the keychain.
- Apply and save settings.
- Disable and re-enable the Ethernet connection to trigger authentication.
- [Screenshot: macOS 802.1X Wired Settings Screen]
C. Linux (Ubuntu with NetworkManager)
- Open Settings → Network → Wired connection → Settings (gear icon).
- Go to Security tab.
- Authentication: Choose 802.1X security.
- Method:
- TLS → select client certificate and private key file.
- PEAP → enter username/password and CA certificate if required.
- Save and reconnect the interface.
- [Screenshot: Linux NetworkManager 802.1X Configuration]
D. Linux (CLI with WPA Supplicant)
- Create
/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf:
network={
key_mgmt=IEEE8021X
eap=TLS
identity="user@domain.com"
ca_cert="/etc/certs/ca.pem"
client_cert="/etc/certs/client.pem"
private_key="/etc/certs/client.key"
}
- Start service:
sudo wpa_supplicant -D wired -i eth0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
E. ISE Policy Configuration
- Policy Sets → Create new Wired 802.1X policy for macOS/Linux.
- Condition:
DEVICE:OScontainsMac OS XorLinux. - Authentication Policy: Allow EAP-TLS / PEAP.
- Authorization Policy: Place into VLAN or ACL based on posture/compliance.
- [Screenshot: ISE Policy Set Screen]
F. Validation
- Switch CLI:
show authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/10 details
- ISE GUI: Operations → RADIUS Live Logs → Filter by endpoint MAC.
- Confirm successful 802.1X authentication event with correct EAP method.
FAQs for Wired Supplicant Configuration (macOS/Linux)
1. My macOS device doesn’t prompt for 802.1X authentication on wired ports. Why?
Cause: macOS requires manual enabling of 802.1X for wired interfaces — it’s not on by default.
Solution:
- Go to System Preferences → Network → Ethernet → Advanced → 802.1X tab.
- Ensure a profile is selected and set to Connect automatically.
- Disconnect/reconnect the cable to trigger re-authentication.
2. Where are macOS wired 802.1X logs stored for troubleshooting?
- Open Console.app → Filter by
eapolclient. - Or in Terminal:
log show --predicate 'process == "eapolclient"' --last 1h
- Look for EAP handshake status, certificate errors, or wrong credentials.
3. My macOS 802.1X EAP-TLS authentication fails, but the certificate is installed.
Possible issues:
- Wrong Keychain: Certificate should be in System keychain, not login keychain.
- Missing private key pairing.
Fix: - Import the
.p12file with both cert + private key. - Set Always Trust for the ISE CA in the certificate settings.
4. How do I configure 802.1X on Linux without a GUI (headless server)?
Use wpa_supplicant:
network={
key_mgmt=IEEE8021X
eap=TLS
identity="user@domain.com"
ca_cert="/etc/certs/ca.pem"
client_cert="/etc/certs/client.pem"
private_key="/etc/certs/client.key"
}
Start:
sudo wpa_supplicant -D wired -i eth0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf -B
Check logs:
sudo tail -f /var/log/syslog
5. Linux 802.1X works with PEAP but fails with EAP-TLS — why?
Likely cause: Missing or mismatched certificate chain.
Fix:
- Install full CA chain including intermediate CAs.
- Verify file permissions:
sudo chmod 600 /etc/certs/*
- Ensure
private_keyformat is PEM, not PKCS#12 unless supported.
6. ISE shows “RADIUS request dropped” for macOS/Linux endpoints.
Causes:
- Endpoint not sending EAP-Start (supplicant not active).
- Switchport misconfigured (missing
dot1x pae authenticator).
Check on switch:
show authentication sessions interface Gi1/0/10 details
Look for Authc Success status.
7. How do I quickly verify if 802.1X is running on Linux?
Run:
nmcli connection show
Look for 802-1x fields in the wired profile.
Or check active processes:
ps -ef | grep wpa_supplicant
8. Can I use the same ISE policy set for Windows, macOS, and Linux wired endpoints?
Yes, but best practice is to have separate conditions based on OS for easier troubleshooting.
Example condition in ISE:
Endpoint:OS equals Mac OS X OR Endpoint:OS equals Linux
This helps you tailor authorization profiles per OS type.
9. What’s the default wired 802.1X timeout on macOS and can I change it?
Default EAPOL handshake timeout is short (~30 seconds). You can modify using:
sudo defaults write /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/com.apple.eapolclient.plist EAPOLClientUserFlags -int 0
(Change cautiously — not typically required unless network latency is high.)
10. How do I capture 802.1X packets on macOS/Linux for deep troubleshooting?
- macOS:
sudo tcpdump -i en0 ether proto 0x888e
- Linux:
sudo tcpdump -i eth0 ether proto 0x888e -vv
Look for EAPOL-Start, Identity, and TLS handshake frames.
YouTube Link
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to my YouTube channel Network Journey and join my instructor-led classes for hands-on, real-world ISE experience
Closing Notes
A properly configured macOS/Linux wired supplicant ensures uniform NAC policy enforcement across heterogeneous environments. With ISE, you can manage these devices with the same granularity and security standards as Windows endpoints.
Neglecting these endpoints leaves gaps in access control and compliance.
Fast-Track to Cisco ISE Mastery Pro
Ready to go from ISE beginner to deployment expert?
Join 4-Month Instructor-Led Cisco ISE & CCIE Security Mastery Program — the most practical, lab-intensive training available today.
Learn every ISE use case step-by-step, with real lab topologies, config validations, and job-ready skills.
Next batch starts soon! Reserve your spot now → https://course.networkjourney.com/ccie-security/
Bonus: Access lifetime recordings, lab topologies, and dedicated 1-on-1 mentorship to fast-track your NAC expertise.
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088


![[Day 22] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: MAB (MAC Authentication Bypass) Configuration](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-22-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-MAB-MAC-Authentication-Bypass-Configuration.png)
