[Day 55] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: EAP-TLS Wireless Certificate Authentication
Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s enterprise networks, passwords are the weakest link. They get reused, stolen, phished, and brute-forced — and once they’re compromised, your wireless network is wide open. Even with strong 802.1X + EAP-PEAP deployments, a single credential leak can let an attacker in from your parking lot.
EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol – Transport Layer Security) changes the game. Instead of usernames and passwords, it uses digital certificates for mutual authentication between the client and Cisco ISE. That means:
- No passwords to steal
- Device binding so only approved hardware gets on the network
- Compliance-ready security for frameworks like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and ISO 27001
With EAP-TLS, your wireless access is locked down with the same cryptographic trust model used in online banking and HTTPS websites — except here, it’s applied at the network edge.
In this session, we’ll go way beyond theory. You’ll:
- Integrate ISE with a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Configure a Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) for certificate-based authentication
- Build policy sets in ISE that authorize access based on certificate attributes
- Validate every stage with both GUI and CLI so you can prove it’s working in your lab and in production.
By the end of this, you won’t just understand EAP-TLS — you’ll have a bulletproof wireless authentication method ready to deploy in any secure environment.
Problem Statement
In many organizations, traditional 802.1X deployments rely on EAP-PEAP or EAP-TTLS with passwords. These methods face issues:
- Weak security posture — stolen credentials can still authenticate.
- No device binding — any device with credentials can connect.
- High management overhead — password resets, expirations, and lockouts cause support tickets.
- Compliance risks — certain regulatory frameworks (PCI DSS, HIPAA) demand certificate-based access.
The challenge: Deploy a password-less, certificate-driven wireless authentication that’s scalable, centrally managed, and easy for users — while integrating seamlessly with Cisco ISE and existing infrastructure.
Solution Overview
Cisco ISE solves this with EAP-TLS:
- Uses mutual TLS authentication — client verifies ISE’s certificate, ISE verifies client’s certificate.
- Integrates with an internal or external CA (Microsoft AD CS, SCEP, or ISE’s internal CA).
- Automates certificate provisioning via SCEP or MDM integration.
- Policies in ISE allow granular access control based on certificate attributes (OU, SAN, CN).
- Works seamlessly with WLC and 802.1X SSIDs.
Sample Lab Topology
Lab Setup:
- VMware ESXi hosting:
- Cisco ISE 3.x (Policy Service Node)
- Windows Server (AD, DNS, NTP, Enterprise CA)
- Cisco WLC (9800 or 3504)
- Cisco Catalyst Switch (for wired testing & trunk uplinks)
- Wireless Access Point (CAPWAP joined to WLC)
- Test endpoints: Windows 10, macOS, iOS with valid certificates
- EVE-NG alternative topology possible
Topology Layout:
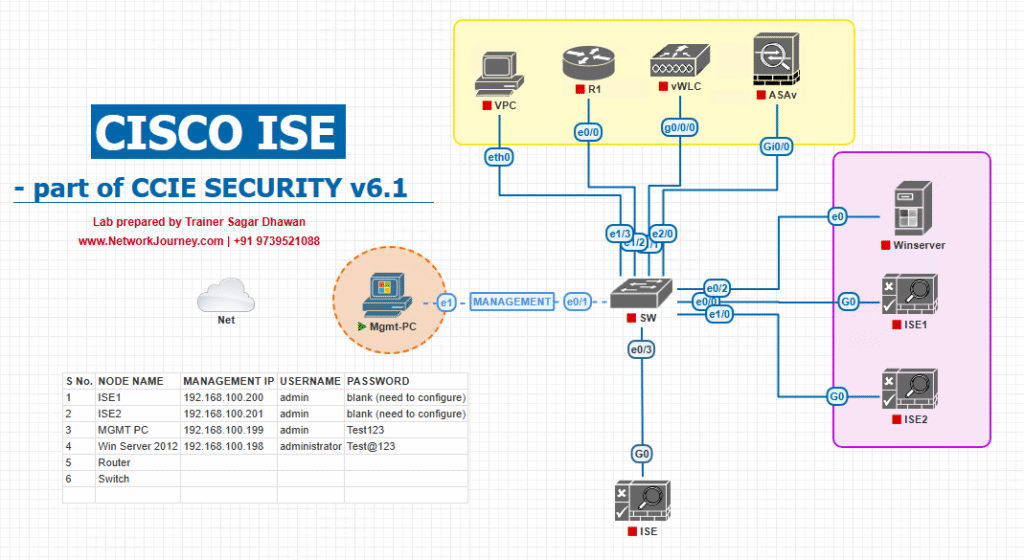
- All clients authenticate to SSID “Secure-EAPTLS” using 802.1X with EAP-TLS.
- ISE communicates with AD for group policy matching.
- Certificates are issued from the Enterprise CA and installed on endpoints.
Step-by-Step GUI Configuration Guide
Step 1 – Prepare PKI
- On the Windows Server CA, configure an User/Computer Certificate Template for EAP-TLS.
- Enable Auto-Enrollment for domain-joined devices via Group Policy.
- Verify certificate issuance with
certmgr.mscon a test machine.- [Screenshot: Issued certificate with Client Authentication EKU]
Step 2 – Configure ISE for EAP-TLS
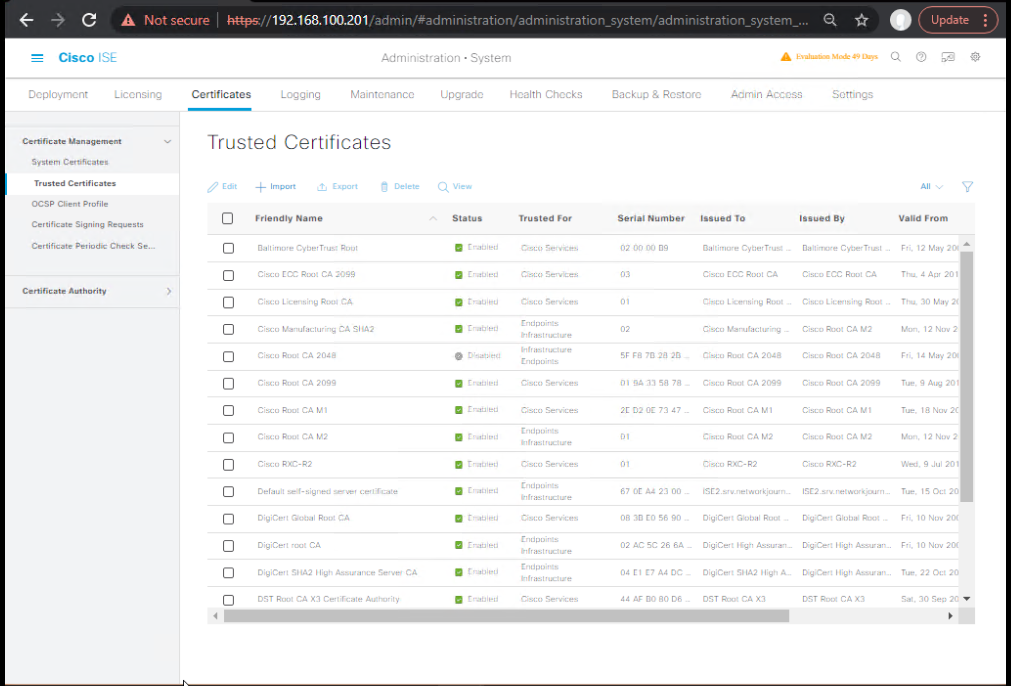
- Import CA Chain into ISE
- Navigate:
Administration > System > Certificates > Trusted Certificates - Import the Root CA and any intermediate CAs.
- Enable Trust for client authentication.
- [Screenshot: ISE Trusted Certificate List]
- Navigate:
- Ensure ISE has a valid server certificate issued by the same or trusted CA.
Administration > System > Certificates > System Certificates- Assign the certificate for EAP Authentication.
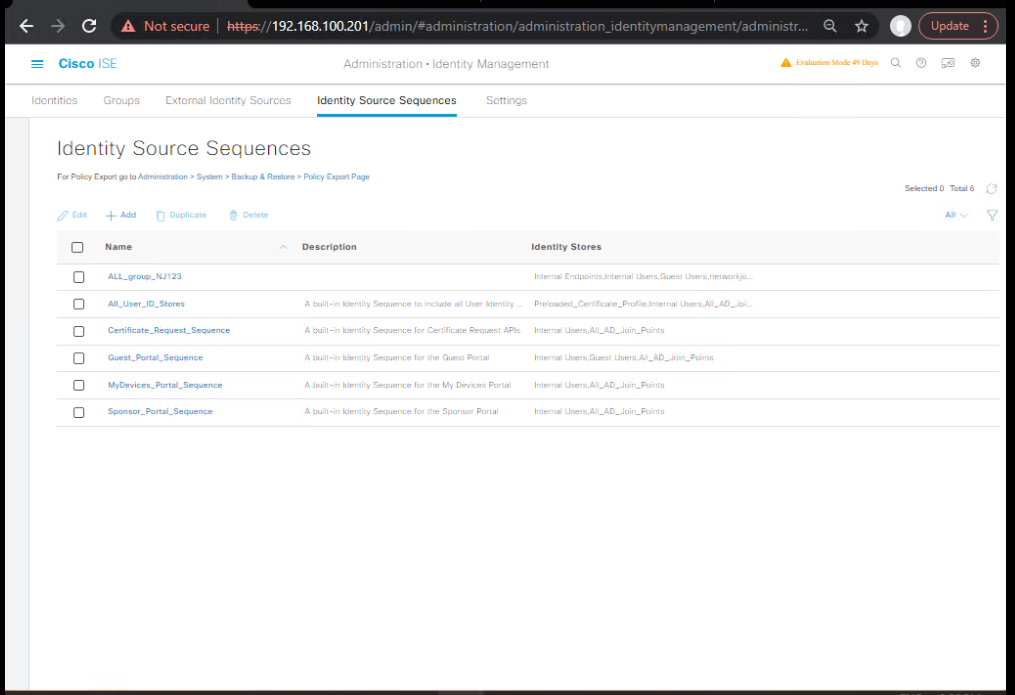
Step 3 – Configure Identity Source Sequence
- Go to:
Administration > Identity Management > Identity Source Sequences - Create a sequence including Internal Endpoints or AD if mapping attributes.
Step 4 – Create Wireless SSID on WLC
- On WLC GUI:
- Create SSID “Secure-EAPTLS”
- Security → Layer 2: WPA2/WPA3 Enterprise
- Auth Key Mgmt: 802.1X
- Point RADIUS to ISE.
- [Screenshot: WLC WLAN Security Settings]
CLI Example (9800 WLC):
wlan Secure-EAPTLS 1 Secure-EAPTLS security wpa security wpa akm 802.1x no shutdown
Step 5 – Configure ISE Policy Set
- Create Policy Set “Wireless EAP-TLS”
- Conditions:
RADIUS:NAS-Port-Type == Wireless - IEEE 802.11EAP-Tunnel == EAP-TLS
- Authorization Policy:
- If certificate OU = “Staff”, permit full access VLAN 10.
- Else if certificate OU = “Guest”, apply restricted VLAN.
- [Screenshot: ISE Policy Set Screen]
Step 6 – Validation
GUI Validation:
- In ISE:
Operations > RADIUS > Live Logs - Look for AuthC: EAP-TLS and AuthZ: PermitAccess.
- [Screenshot: Successful EAP-TLS Log Entry]
CLI Validation (WLC):
show client detail <MAC> show wlan summary show aaa servers
Ensure PMKID and AAA-Override are correct.
FAQs
1. What is EAP-TLS and why is it considered the most secure 802.1X method?
EAP-TLS is an authentication framework that uses mutual certificate-based authentication instead of usernames and passwords. The client presents its digital certificate to the server (Cisco ISE), and ISE presents its own certificate back to the client. Because no passwords are exchanged and authentication relies on public key cryptography, it’s immune to phishing, brute-force, and password replay attacks.
2. Do I need a PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) to implement EAP-TLS?
Yes. EAP-TLS requires a Certificate Authority (CA) to issue and manage digital certificates for clients and the ISE server. You can use:
- Microsoft AD CS for internal enterprise deployments
- ISE’s built-in CA (for labs or small-scale deployments)
- Public CAs for external-facing scenarios
3. Can EAP-TLS work without Active Directory integration?
Yes, but with limitations. You can authenticate devices purely based on certificate trust without AD lookup. However, in most enterprise setups, you still integrate ISE with AD to use certificate attributes (e.g., SAN fields or CN) for group-based policy decisions.
4. How do I distribute certificates to endpoints securely?
Options include:
- Group Policy (GPO) for Windows domain-joined machines
- SCEP (Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol) for mobile devices
- Manual enrollment (not recommended for large deployments)
- MDM integration (Intune, Jamf, etc.) for BYOD and corporate-owned devices
5. Which certificate fields does ISE check during EAP-TLS authentication?
ISE typically validates:
- Certificate validity (date range, signature, revocation check)
- Issuer (must be from a trusted CA)
- Subject CN or SAN (used in policy rules for user/device mapping)
- Extended Key Usage (EKU)
6. How do I handle certificate expiration in EAP-TLS deployments?
Plan a renewal strategy:
- Automate renewals via GPO or MDM before expiration
- Use shorter validity periods for security but ensure auto-renew works
- Monitor certificates in ISE Reports > Certificates for upcoming expirations
7. What WLC configuration is required for EAP-TLS?
On the WLC:
- Enable 802.1X on the WLAN
- Configure the AAA server (ISE)
- Enable Management over HTTPS for RADIUS DTLS if desired
- Ensure the WLAN security is set to WPA2/WPA3-Enterprise
8. How do I troubleshoot failed EAP-TLS authentications?
Steps:
- Check ISE Live Logs for authentication failure reasons
- Use
debug client <mac>on WLC CLI for handshake details - Verify certificate trust on both client and ISE
- Confirm CRL/OCSP checks if revocation is enabled
9. Can I combine EAP-TLS with posture assessment in ISE?
Yes. EAP-TLS can be the primary authentication method, and ISE can still apply posture checks after authentication to ensure device compliance before granting full access.
10. What happens if a device’s certificate is revoked?
If CRL or OCSP checking is enabled in ISE, a revoked certificate will cause the authentication to fail immediately. This is critical for disabling lost or compromised devices without needing to modify WLAN or AD configurations.
YouTube Link
For more in-depth Cisco ISE Mastery Training, subscribe to my YouTube channel Network Journey and join my instructor-led classes for hands-on, real-world ISE experience
Closing Notes
EAP-TLS in Cisco ISE provides strong, scalable, and phishing-resistant authentication for wireless clients. By removing password reliance, you cut down on helpdesk tickets and improve security posture. When paired with endpoint management automation, EAP-TLS becomes nearly transparent to end users, yet airtight against unauthorized access.
Upgrade Your Skills – Start Today
“If you want to deploy enterprise-grade NAC like this in production — not just in labs — you need structured, hands-on guidance. I’m running a 4-month, instructor-led CCIE Security Mastery Program that covers ISE, ASA/FTD, VPN, and advanced network security topics in depth.
- 100% Lab-Driven
- Real-World Scenarios
- Direct Trainer Mentoring
Next batch starting soon. Seats are limited.
Reserve your spot now: https://course.networkjourney.com/ccie-security/
Don’t just watch — master it. Your next security deployment could depend on it.”
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day 55] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: EAP-TLS Wireless Certificate Authentication](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-55-–-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-EAP‑TLS-Wireless-Certificate-Authentication.png)
![[Day 22] Cisco ISE Mastery Training: MAB (MAC Authentication Bypass) Configuration](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-22-Cisco-ISE-Mastery-Training-MAB-MAC-Authentication-Bypass-Configuration.png)

