[Day #55 Pyats Series] Using Cisco/Arista/Paloalto/Fortigate with pyATS using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction on the Key Points
As networks become increasingly hybrid and multi-vendor, vendor-agnostic automation becomes not just a good-to-have skill, but a must-have. Whether you’re working with Cisco routers, Arista switches, Palo Alto firewalls, or Fortigate appliances—your automation framework needs to talk to all of them, uniformly and efficiently.
That’s exactly where Cisco pyATS (Python Automated Test System) comes into play. Originally built for Cisco internal testing, pyATS is now open to engineers everywhere. In this article, we’ll explore how to use pyATS with Cisco, Arista, Palo Alto, and Fortigate devices—proving how vendor-agnostic automation is possible today.
If you’re learning Python for Network Engineer, this hands-on guide is for you. You’ll learn:
- How pyATS works across multiple vendors
- A working multi-vendor testbed
- A reusable script to check device reachability and software versions
- Real CLI outputs to compare validation results
Topology Overview
Here’s the logical view of our lab environment:
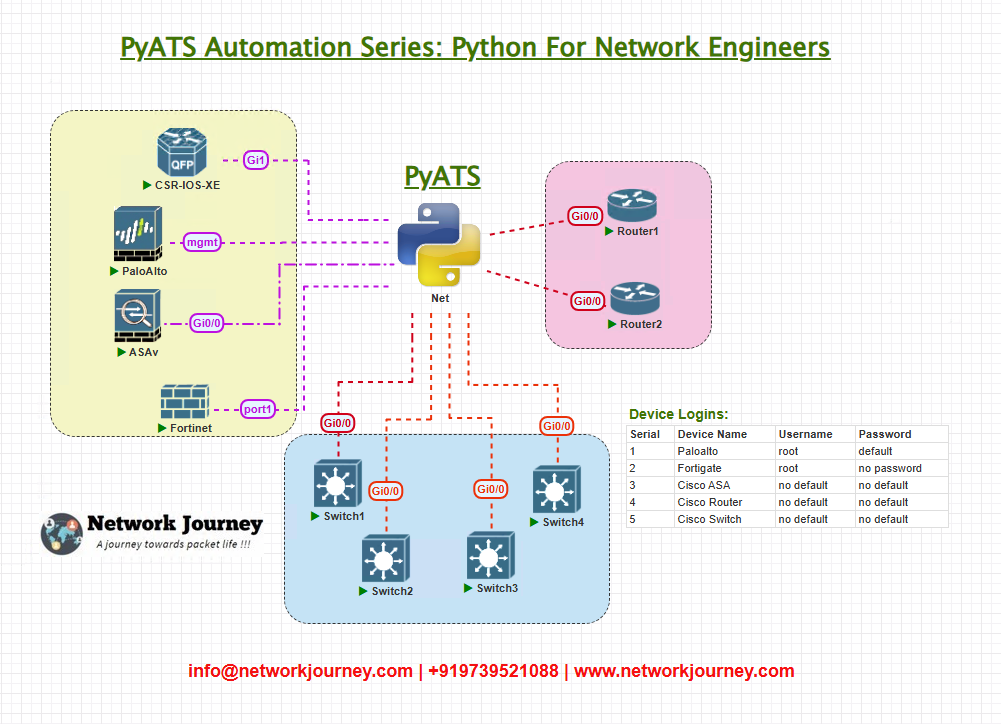
Each device supports some form of SSH or API communication. We’ll use Unicon (SSH) for Cisco and Arista, and paramiko/custom CLI for Palo Alto and Fortigate, depending on what’s supported.
Topology & Communications
| Device Type | OS | Access Type | Protocol | pyATS Support | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco Router | IOS-XE | SSH | SSH/NETCONF/RESTCONF | Official Support | Full support using Unicon |
| Arista Switch | EOS | SSH | SSH/JSON-RPC | Unofficial via CLI | Works well with Unicon |
| Palo Alto FW | PAN-OS | CLI/API | SSH/API | CLI + REST API | pyATS with customization |
| Fortigate FW | FortiOS | CLI/API | SSH/API | CLI + REST API | Requires tuning |
pyATS does not natively support Palo Alto and Fortigate in the same way it supports Cisco, but you can still integrate them for CLI automation and testing using the CLI (Unicon) or custom libraries.
Workflow Script
Below is a sample multi-vendor validation script to:
- Connect to each device
- Run
show version(or equivalent) - Output vendor, model, and version
from genie.testbed import load
import logging
# Suppress warnings
logging.getLogger("unicon").setLevel(logging.CRITICAL)
# Load the testbed
testbed = load('testbed.yml')
# Define devices to test
devices = ['cisco_iosxe', 'arista_eos', 'palo_alto', 'fortigate']
# Loop through devices
for dev_name in devices:
device = testbed.devices[dev_name]
print(f"\n--- Connecting to {device.name} ---")
try:
device.connect(log_stdout=False)
print(f"[CONNECTED] {device.name}")
# Run OS-specific show command
if device.os == "iosxe":
output = device.parse("show version")
print(f"Hostname: {output['hostname']}")
print(f"Version: {output['version']}")
elif device.os == "eos":
output = device.execute("show version")
print(output)
elif device.os == "panos":
output = device.execute("show system info")
print(output)
elif device.os == "fortios":
output = device.execute("get system status")
print(output)
device.disconnect()
except Exception as e:
print(f"[FAILED] Could not connect to {device.name} - {e}")
Explanation by Line
load('testbed.yml'): Loads all device credentials and access methods.device.connect(): Uses Unicon (SSH) to log in.- Device OS types help us decide which command to run.
device.execute(...)anddevice.parse(...): Run commands and extract data.- Disconnects after every session to cleanly manage resources.
This script is highly reusable and scalable across devices.
testbed.yml Example (Multi-Vendor)
devices:
cisco_iosxe:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.100.10
port: 22
username: admin
password: cisco123
arista_eos:
os: eos
type: switch
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.100.11
port: 22
username: admin
password: arista123
palo_alto:
os: panos
type: firewall
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.100.12
port: 22
username: admin
password: palo123
fortigate:
os: fortios
type: firewall
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.100.13
port: 22
username: admin
password: forti123
Note: Adjust class and os depending on support/custom drivers.
Post-validation CLI Screenshots
Cisco IOS-XE
R1# show version Cisco IOS XE Software, Version 17.03.01a Hostname: R1 Model: ISR4331/K9
Arista EOS
arista# show version Software image version: 4.25.4M Architecture: x86_64 Model Name: DCS-7050TX-64
Palo Alto
> show system info hostname: PA-VM model: PA-VM sw-version: 10.1.5
Fortigate
# get system status Version: FortiOS v6.4.7 Hostname: FG60E Serial-Number: FG60E1XXXXXXXX
These outputs help you visually compare and log version consistency across vendors.
FAQs
1. Can I use pyATS with Cisco, Arista, Palo Alto, and FortiGate devices?
Yes, pyATS is vendor-agnostic and can work across Cisco (IOS-XE/XR/NX-OS), Arista (EOS), Palo Alto (PAN-OS), and FortiGate (FortiOS) devices.
Support varies based on:
- Connection method (
ssh,telnet,netconf, orrest) - Parsing availability (Cisco/Arista have richer Genie support; Palo Alto/Fortinet use custom parsers)
- Testbed schema compatibility
For less supported platforms like FortiGate and Palo Alto, you can use:
- Unstructured command outputs (parsed using regex or TextFSM)
- Custom
pyats parserplugins - REST APIs for config/state retrieval
2. What connection protocols does pyATS support for multi-vendor platforms?
| Vendor | Protocol Options | pyATS Support |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco | SSH, Telnet, NETCONF, RESTCONF | Native with Genie parsers |
| Arista | SSH, eAPI (HTTPS), NETCONF | Strong support |
| Palo Alto | SSH (CLI), REST/XML API | Use custom APIs or scripts |
| FortiGate | SSH (CLI), REST API | Limited parsing, CLI output scraping needed |
For Palo Alto & FortiGate, using API tokens or structured XML/JSON from APIs is more stable than CLI scraping.
3. How do I define a pyATS testbed file for multi-vendor devices?
Sample testbed.yaml structure:
devices:
cisco_router:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
defaults:
class: unicon.Unicon
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.10.10.1
arista_switch:
os: eos
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.10.20.1
palo_ngfw:
os: panos
type: firewall
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.10.30.1
fortigate_fw:
os: fortinet
type: firewall
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 10.10.40.1
Add username and password or use environment variables.
You can override command prompts via settings block for Palo/Forti.
4. Does pyATS Genie support parsing for all vendors equally?
No. Genie parsers are most mature for Cisco IOS-XE/XR/NX-OS and Arista EOS.
| Vendor | Genie Parser Availability | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco | Full CLI + YANG | Hundreds of commands supported |
| Arista | Growing parser library | show version, interfaces, vlans etc. |
| Palo Alto | No native parsers | Use api or ssh + regex parsing |
| FortiGate | No native parsers | Use CLI or REST API + custom scripts |
You can write custom parsers using pyats parser create or convert CLI output into Python dictionaries manually.
5. How can I validate firewall rules or policies on Palo Alto and FortiGate using pyATS?
Since Palo Alto and FortiGate don’t have built-in Genie parsers, use REST/XML APIs:
Palo Alto XML API Example:
https://<fw-ip>/api/?type=config&action=show&xpath=/config/devices/entry/vsys/entry/rulebase/security&key=<API_KEY>
FortiGate REST API Example:
GET https://<fw-ip>/api/v2/cmdb/firewall/policy Headers: Authorization: Bearer <token>
Parse the JSON/XML response in Python, then:
- Validate rule names, source/destination IPs, zones
- Compare current vs. baseline policy
Use pyATS test cases with rest.connector or Python’s requests module.
6. How do I handle CLI prompts or inconsistent outputs for FortiGate or Palo Alto?
Fortinet and Palo Alto CLI outputs can be inconsistent due to:
- Dynamic prompts
- Extra banners
- Variable output formatting
Mitigation tips:
- Use
commandanddialogoptions in pyATS - Set
prompt_recoveryto false - Use
log_level: debugto troubleshoot prompt handling - Clean and normalize outputs with regex before parsing
Example:
output = device.execute("show system interface")
interfaces = parse_forti_output(output) # custom parser
7. Can I use pyATS to compare config/state between Cisco and Arista devices?
Yes! You can:
- Use
genie learn <feature>to collect data from both - Normalize the output into JSON/dicts
- Compare values such as:
- Interface status
- VLAN assignments
- Routing table entries
Example:
genie learn interface --testbed-file testbed.yaml --devices cisco1 arista1 --output learn_output/
Then compare outputs using diff tools or pyATS custom testcases.
8. What’s the best practice for vendor-agnostic validation in production with pyATS?
A:
- Normalize data using custom parsers or YANG models.
- Avoid hardcoding CLI – use API or model-driven outputs if available.
- Use common test templates with Jinja2 or templates for assertion logic.
- Organize test scripts by feature (e.g., interface, ACL, routing).
- Build baseline snapshots of config/state and compare dynamically.
- Log all test outcomes using pyATS native logging for CI/CD pipelines.
Bonus: Integrate with Git, Jenkins, or NetBox for automation workflows.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: Using Cisco/Arista/Paloalto/Fortigate with pyATS using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
Are you serious about mastering Python for Network Engineer, automation tools like pyATS, Ansible, RESTCONF/NETCONF, and becoming multi-vendor-ready?
Join our 3-month instructor-led program conducted by Trainer Sagar Dhawan (14+ years experience) and become industry-ready.
- Work on Cisco, Arista, Palo Alto, and Fortigate real labs
- Build job-ready automation workflows
- Hands-on Git, API, YAML, pyATS, Ansible, and more
Check the full course syllabus now:
https://course.networkjourney.com/python-ansible-api-cisco-devnet-for-network-engineers/
This is the ultimate program for Python for Network Engineer aspirants. Let’s start automating!
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #55 Pyats Series] Using Cisco/Arista/Paloalto/Fortigate with pyATS using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Using-CiscoAristaPaloaltoFortigate-with-pyATS-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![[Day #34 PyATS Series] DHCP Snooping & Binding Table Verification Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-34-PyATS-Series-DHCP-Snooping-Binding-Table-Verification-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![Introduction to JSON & YANG – The Foundation of Network Automation [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Introduction-to-JSON_YANG–The-Foundation-of-Network-Automation_networkjourney.png)
![[Day #30 PyATS Series] Checking STP Root Bridge Across Cisco Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-30-PyATS-Series-Checking-STP-Root-Bridge-Across-Cisco-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)