[Day #90 PyATS Series] GitOps for Network Automation (pyATS + GitHub Actions) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]
Table of Contents
Introduction on the Key Points
In modern network automation practices, GitOps has emerged as a powerful methodology to manage infrastructure as code. It bridges the gap between development and operations by leveraging Git as the single source of truth, allowing automation pipelines to trigger infrastructure validation and deployment processes automatically.
Today, in this Article, we will dive deep into automating network validations using pyATS + GitHub Actions, forming a GitOps-driven workflow specifically for Cisco environments. As part of this guide, you will gain hands-on experience in designing production-ready, automated validation pipelines that run seamlessly with GitHub Actions.
This article is designed for serious Python for Network Engineer practitioners who want to move from manual validation to fully automated GitOps-driven workflows, blending CLI and GUI validation techniques for end-to-end reliability.
Topology Overview
I will work with a simple yet scalable lab topology to simulate a data center network, using Cisco devices such as IOS-XE routers and Nexus switches. The environment consists of the following components:’
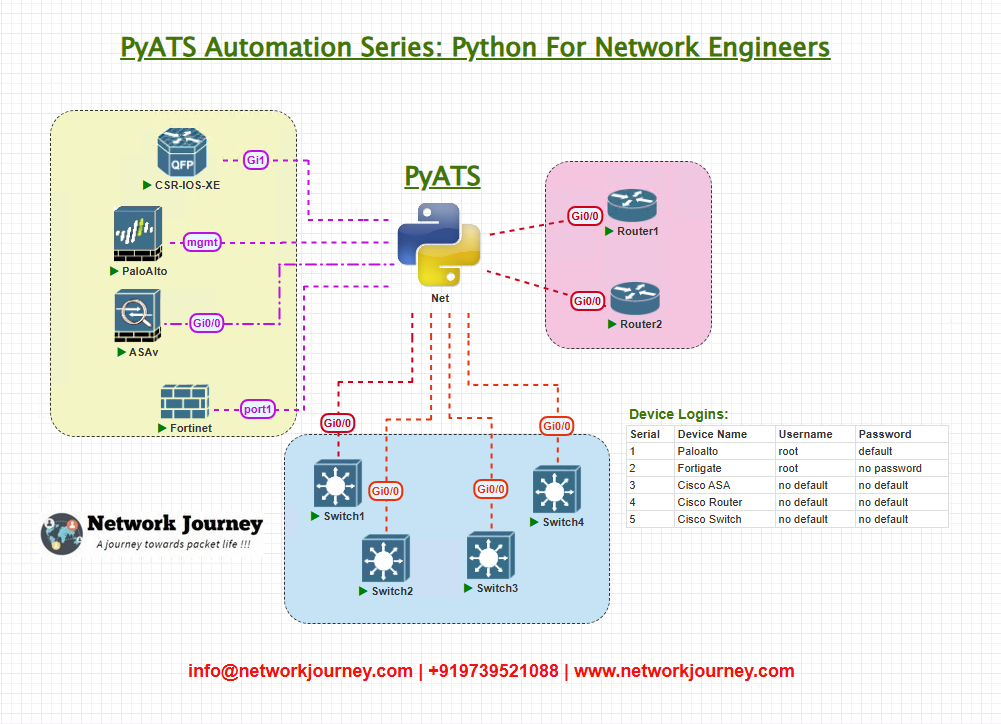
- Cisco IOS-XE Router (R1, R2) – Acts as core routers for routing and management.
- Cisco Nexus Switch (SW1, SW2) – Acts as the data center leaf-spine fabric.
- APIC Controller – Used to manage ACI configurations.
- GitHub Repository – Hosts pyATS test scripts and configurations.
- GitHub Actions – Executes validation jobs automatically when code is pushed or pull requests are raised.
This setup allows us to validate interfaces, routing, and policy configurations across devices after changes are committed to the Git repository.
Topology & Communications
| Device | Management IP | Role | OS Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 192.168.1.1 | IOS-XE Router | IOS-XE 17.x |
| R2 | 192.168.1.2 | IOS-XE Router | IOS-XE 17.x |
| SW1 | 192.168.1.3 | Nexus Leaf Switch | NX-OS 9.x |
| SW2 | 192.168.1.4 | Nexus Spine Switch | NX-OS 9.x |
- Management traffic is routed via 192.168.1.0/24 subnet.
- SSH and HTTPS are used for device management.
- GitHub Actions run tests against this environment through the pyATS testbed file.
Workflow Script
Our GitOps workflow leverages GitHub Actions to automatically run validation jobs whenever code is committed or a pull request is created.
Workflow Trigger
name: pyATS Validation Pipeline
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
jobs:
validate-config:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Git Repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: 3.10
- name: Install Dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install pyats genie
- name: Run pyATS Test Script
run: |
pyats run job jobs/validate_config.py --testbed-file testbed.yml
Explanation by Line
on: push / pull_request: Triggers validation on every commit or pull request to themainbranch.actions/checkout@v3: Checks out the repository code into the runner workspace.actions/setup-python@v4: Ensures Python 3.10 is installed for the environment.- Dependency installation uses
pip install pyats genieto set up the pyATS framework. - The key action is running the
pyats run jobcommand with the custom validation job and thetestbed.yml.
testbed.yml Example
testbed:
name: data_center_lab
devices:
R1:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.1
port: 22
R2:
os: iosxe
type: router
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.2
port: 22
SW1:
os: nxos
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.3
port: 22
SW2:
os: nxos
type: switch
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.1.4
port: 22
Post-validation CLI (Real Expected Output)
After the validation job runs, you should see structured output:
=========================== pyATS Job Execution Results =========================== Test: Validate Interface Status -------------------------------- Device: R1 Interface GigabitEthernet0/0 is UP - PASSED Device: R2 Interface GigabitEthernet0/0 is UP - PASSED Device: SW1 Interface Ethernet1/1 is UP - PASSED Device: SW2 Interface Ethernet1/1 is UP - PASSED Test: Validate Routing Protocol -------------------------------- OSPF neighbor state on R1: FULL - PASSED OSPF neighbor state on R2: FULL - PASSED -------------------------------- Overall Status: PASSED
Additionally, the GitHub Actions console will show a green check mark on successful jobs and detailed logs.
FAQs
Q1. What is GitOps and why should network engineers use it with pyATS?
A1. GitOps is a paradigm where Git is used as the single source of truth for infrastructure and automation workflows. It enables declarative version-controlled changes, automated CI/CD pipelines, and enhanced auditability of network configurations using pyATS.
Q2. How do GitHub Actions fit into a GitOps workflow for network automation?
A2. GitHub Actions automatically execute jobs on every commit or pull request. By integrating pyATS jobs, you achieve continuous validation of network configurations before deployment, ensuring consistency and reducing risk.
Q3. Is it possible to run the same workflow across multiple network environments?
A3. Absolutely. The testbed.yml is designed to be modular and reusable. By parameterizing device IPs and credentials, the same GitHub Action can validate multiple environments (e.g., staging, production).
Q4. Can we combine GUI-based validations in the GitOps workflow?
A4. Yes. Tools like Selenium or pyATS Genie can be used to automate GUI validations as part of the test suite, ensuring that not just CLI, but also web-based interfaces are verified.
Q5. How do we handle secrets like device credentials securely in this workflow?
A5. GitHub Actions supports encrypted Secrets. Credentials (like SSH keys or passwords) are stored securely in GitHub Secrets and injected into the workflow at runtime using environment variables.
Q6. How does this solution support rollback in case of failed validations?
A6. While GitOps emphasizes forward-only commits, integrating validation jobs prevents invalid configurations from being merged into main branches. For rollbacks, automation can use git tags and revert changes or run playbooks to reset devices to known good states.
Q7. Can pyATS job failures be integrated with alerting tools?
A7. Yes. Failed jobs can trigger webhooks, Slack notifications, or integration with monitoring systems like PagerDuty, ensuring real-time alerts on configuration drift or validation failures.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete Python for Network Engineer: GitOps for Network Automation (pyATS + GitHub Actions) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer] Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Join Our Training
Transform your career by mastering production-grade Python for Network Engineer automation practices.
Join Trainer Sagar Dhawan’s 3-month instructor-led course and learn real-world network automation workflows, deep-dive into Python, Ansible, APIs, pyATS, and GitOps with hands-on labs and use cases.
Join Now – Python for Network Engineer Training
Enroll Now & Future‑Proof Your Career
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
![[Day #90 PyATS Series] GitOps for Network Automation (pyATS + GitHub Actions) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-90-PyATS-Series-GitOps-for-Network-Automation-pyATS-GitHub-Actions-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)
![Introduction to JSON & YANG – The Foundation of Network Automation [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Introduction-to-JSON_YANG–The-Foundation-of-Network-Automation_networkjourney.png)
![[Day #86 PyATS Series] Automated RMA Device Onboarding (Multi-Vendor) Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-86-PyATS-Series-Automated-RMA-Device-Onboarding-Multi-Vendor-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer-470x274.png)
![[DAY#6 PyATS Series] Using pyATS CLI tools: pyats learn, pyats parse using PyATS [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/DAY6-PyATS-Series-Using-pyATS-CLI-tools-pyats-learn-pyats-parse-using-PyATS-Python-for-Network-Engineer.png)