From Zero to Secure: 802.1X + MAB CLI Walkthrough with Labs [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
I am going to simplify one of the most powerful port-based access control mechanisms in enterprise networking — 802.1X with MAB (MAC Authentication Bypass). When configured properly, it ensures secure access for both corporate-managed devices and non-802.1X-capable endpoints like printers, IP phones, or legacy hardware.
Let’s walk through the theory, configuration, and labs that make this topic easy to implement and hard to forget.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief: What is 802.1X and MAB?
802.1X is a network access control protocol that authenticates devices before allowing them onto the network using credentials verified by a RADIUS server. It’s like a bouncer checking ID before someone enters a party.
MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) is the backup plan. If a device doesn’t support 802.1X (like a printer), the switch falls back to using its MAC address to authenticate with the RADIUS server.
Why Combine Them?
- 802.1X offers strong identity-based access control.
- MAB ensures legacy devices still get access — securely.
The combination ensures zero trust onboarding with flexibility.
802.1X vs MAB
| Feature | 802.1X | MAB (MAC Authentication Bypass) |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | Username/Password (EAP/RADIUS) | MAC Address sent to RADIUS |
| Device Support | Corporate laptops, PCs | Printers, IP phones, IoT devices |
| Security Level | High | Moderate |
| Timeout Control | Yes (authentication timer) | Yes (authentication delay) |
| Use Case | Primary Authentication Method | Backup if 802.1X fails or unsupported |
Pros and Cons
| Benefits | Limitations |
| Granular device access control | Complex initial configuration |
| Seamless fallback for legacy devices | MAB can be spoofed if MAC filtering isn’t strict |
| Integrates with ISE / AAA systems | Requires solid RADIUS policy design |
CLI Commands
| Task | CLI Command |
| Enable AAA | aaa new-model |
| Define RADIUS server | radius-server host <ip> key <key> |
| Enable 802.1X globally | dot1x system-auth-control |
| Configure port for 802.1X + MAB | See interface config below |
| Show authentication sessions | show authentication sessions |
| View session interface status | show dot1x interface <int> detail |
| Debug MAB/802.1X issues | debug dot1x, debug authentication |
Real-World Use Cases
| Scenario | How 802.1X + MAB Helps |
| Corporate laptop onboarding | Uses 802.1X with domain credentials |
| IP phone with no 802.1X | Authenticated via MAB using MAC lookup in ISE |
| Secure guest network entry | 802.1X + MAB enables device-based VLAN assignment via policy |
Lab 1: Basic 802.1X + MAB Configuration
Topology:
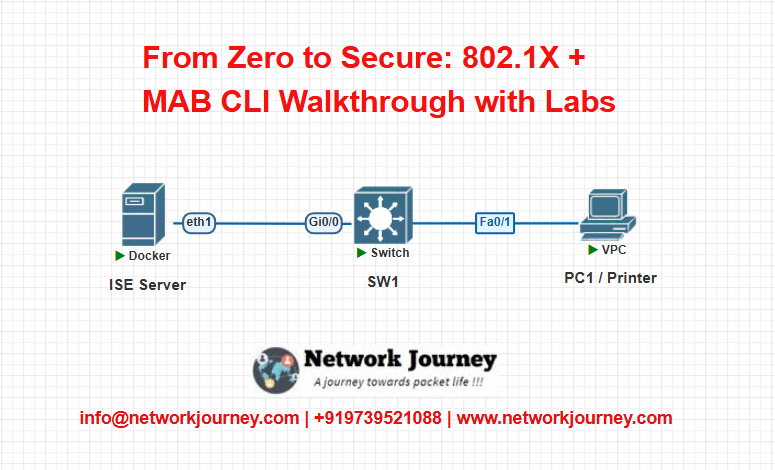
Objective:
Configure a switchport for 802.1X with MAB fallback and authenticate against an ISE or simulated RADIUS server.
Switch Configuration:
aaa new-model radius-server host 192.168.1.100 key cisco123 ! interface Fa0/1 switchport mode access authentication port-control auto mab dot1x pae authenticator dot1x timeout tx-period 10 dot1x max-req 3 authentication order dot1x mab authentication priority dot1x mab spanning-tree portfast ! dot1x system-auth-control
Lab 2: Dynamic VLAN Assignment
Objective:
Assign different VLANs based on identity (802.1X users get VLAN 10, MAB devices get VLAN 20).
ISE Policy:
- Create Authorization Profiles for VLANs
- Match Endpoint MAC or Username group
Switch Configuration:
Add this under interface config:
authentication event server dead action authorize vlan 999 authentication event server alive action reinitialize
Lab 3: Session Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Commands to Use:
show authentication sessions interface Fa0/1 show dot1x interface Fa0/1 detail debug dot1x all debug authentication
This helps verify:
- Which method succeeded (dot1x or MAB)
- Session ID, VLAN assigned
- Any timeouts or policy rejections
Troubleshooting Tips
| Issue | Possible Cause | Fix |
| Device not authenticated | No response to EAP requests | Check supplicant or fallback to MAB |
| Always falls to MAB | Client not 802.1X capable or misconfigured | Validate dot1x config on client |
| ISE doesn’t assign VLAN | Missing authorization profile or policy | Create appropriate VLAN policy in ISE |
| Port stuck in unauthorized | MAC not recognized or RADIUS reject | Add MAC to ISE, check policy results |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is 802.1X and how does it enhance network security?
Answer:
802.1X is a port-based Network Access Control (PNAC) protocol that enforces authentication before a device is allowed onto a LAN or WLAN. It uses three components:
- Supplicant (e.g., PC or IP phone)
- Authenticator (e.g., switch)
- Authentication server (e.g., RADIUS server like Cisco ISE or FreeRADIUS)
By requiring user or device credentials before granting access, 802.1X helps prevent unauthorized access and strengthens endpoint security.
2. What is MAB and how is it different from 802.1X?
Answer:
MAB (MAC Authentication Bypass) is a fallback method used when a device doesn’t support 802.1X (like printers or IP phones). Instead of credentials, the switch uses the device’s MAC address to authenticate it through the RADIUS server.
Key differences:
- 802.1X: Uses user/device credentials with EAP
- MAB: Uses MAC address as identity
MAB is less secure than 802.1X but necessary for legacy or non-802.1X devices.
3. Can 802.1X and MAB be used together on the same port?
Answer:
Yes. In fact, it’s a common practice called “802.1X with MAB fallback.”
Here’s how it works:
- The switch tries 802.1X first.
- If no EAPoL packets are received (meaning the device doesn’t support 802.1X), it falls back to MAB.
This ensures both secure and legacy devices can connect while maintaining network access control.
4. What are the prerequisites to implement 802.1X + MAB on a Cisco switch?
Answer:
To enable 802.1X and MAB, you need:
- A configured RADIUS server (e.g., Cisco ISE or FreeRADIUS)
- AAA authentication enabled on the switch
- Dot1x system-auth-control globally
- Switchport configuration per interface for
dot1xandmab - Proper VLAN assignments for authenticated/unauthenticated access
5. What command enables 802.1X globally on a Cisco switch?
Answer:
The global command is:
dot1x system-auth-control
Without this, interface-level authentication port-control settings won’t take effect.
6. How can I verify if a device is authenticated using 802.1X or MAB?
Answer:
Use the command:
show authentication sessions interface [interface-id]
This displays:
- Method of authentication (
dot1x,mab, etc.) - Status (Authorized or Unauth)
- MAC address
- VLAN assignment
You can also add details to the command for deeper insight.
7. How do I configure an interface for both 802.1X and MAB?
Answer:
Here’s a sample config:
interface Gig1/0/1 switchport mode access authentication port-control auto mab dot1x pae authenticator authentication order dot1x mab authentication priority dot1x mab authentication event fail action next-method
This enables dot1x first, and if it fails or times out, MAB kicks in.
8. What happens when an unauthorized device tries to connect?
Answer:
If the device fails both 802.1X and MAB (or isn’t allowed by the RADIUS server), the switch can:
- Assign it to a guest VLAN
- Restrict access completely (no VLAN)
- Apply an ACL blocking access
These behaviors depend on your configuration (authentication violation restrict/shutdown).
9. How can I simulate and test 802.1X + MAB in a lab environment like EVE-NG?
Answer:
You can use:
- A Cisco switch or IOU image
- A RADIUS server VM (e.g., FreeRADIUS, Cisco ISE)
- Linux/Windows VMs with supplicant software
Simulate various devices:
- Use
wpa_supplicanton Linux for 802.1X - Use a MAC-only client (or disable supplicant) to trigger MAB
Then capture EAPoL and RADIUS traffic using Wireshark to verify flow.
10. Is MAB secure enough for production environments?
Answer:
No. MAB is inherently weak, as MAC addresses can be spoofed. It’s recommended to:
- Use MAB only as fallback
- Combine it with port-security or Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI)
- Apply downloadable ACLs (dACLs) or profiling in Cisco ISE
This reduces risk by limiting what MAB-authenticated devices can access.
Related YouTube Video
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement From Zero to Secure: 802.1X + MAB CLI Walkthrough in Modern Networks is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![From Zero to Secure: 802.1X + MAB CLI Walkthrough with Labs[CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/nj-blog-post-802.1.jpg)

![NETCONF vs RESTCONF – Choosing the Right Protocol for Network Automation [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/NETCONF-vs-RESTCONF-–-Choosing-the-Right-Protocol-for-Network-Automation-1.png)
![Mastering Layer 2 Troubleshooting Commands: A Complete Guide with CLI & EVE-NG Labs [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Mastering-Layer-2-Troubleshooting-Commands_networkjourney.png)