Performance Routing (PfR) Basics: Optimize Traffic Like a Pro [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
Today’s article, we’ll dive into one of the most powerful yet underrated features in enterprise networks — Performance Routing (PfR). While traditional routing protocols like OSPF or BGP make decisions based on shortest path or metrics like cost, PfR goes beyond. It chooses the best path based on live performance metrics, such as jitter, loss, latency, or even app policies.
If you’ve ever faced a situation where one WAN link was technically “up” but barely usable, this article is for you. Let’s explore how PfR helps networks make smarter decisions.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief: Understanding Performance Routing
What is PfR?
PfR (Performance Routing) is a Cisco technology that dynamically selects the best outbound path for traffic based on performance metrics, not just traditional routing tables.
- It’s like a traffic controller that reroutes packets on-the-fly.
- Integrated with IP SLA probes to measure latency, loss, and jitter.
- Works well for voice/video traffic where QoS is crucial.
How it Works:
PfR operates in two modes:
- Passive Monitoring (Learning Mode) – Gathers data on traffic flows.
- Active Policy Enforcement – Takes real-time action based on policies.
PfR uses the Master Controller (MC) and Border Routers (BR) architecture:
- MC makes routing decisions.
- BR implements those decisions and routes traffic accordingly.
Use Case Relevance:
Even with SD-WAN, PfR-style logic is used under the hood (like application-aware routing or policy-based traffic engineering).
PfR vs Traditional Routing
| Feature | Traditional Routing | Performance Routing (PfR) |
|---|---|---|
| Basis for Decision | Hop Count / Cost | Latency, Loss, Jitter, Policy |
| Path Failover | Only when down | Based on SLA / thresholds |
| Application-Awareness | No | Yes |
| Control Plane | Distributed | Centralized (MC/BR) |
| Integration | Static / OSPF / BGP | With IP SLA, NBAR, QoS |
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| Intelligent routing based on real metrics | Requires more configuration and planning |
| Improves performance for voice/video apps | Limited to Cisco IOS routers |
| SLA-aware with fallback options | Complexity in large networks |
| Dynamic failover | May require IP SLA licenses on some devices |
CLI Commands
| Task | Command |
| Check PfR Status | show pfr master |
| View Active PfR Routes | show pfr border |
| Debug SLA Events | debug ip sla trace |
| View IP SLA Statistics | show ip sla statistics |
| Monitor Application Routing | show pfr traffic |
| Check MC to BR Communication | show pfr master detail |
Use Cases
| Scenario | What PfR Does | Outcome |
| VoIP calls experiencing jitter | Reroutes via lower-jitter backup path | Clearer voice quality |
| Primary link is up but slow | Fails over to secondary path | Better user experience |
| Internet link flap detection | Detects SLA threshold violations | Auto path switch |
| App-specific routing (e.g., Zoom on MPLS) | Routes apps via policy-based logic | Better control for business-critical apps |
Lab 1: Basic PfR with Two WAN Links
Lab Topology:
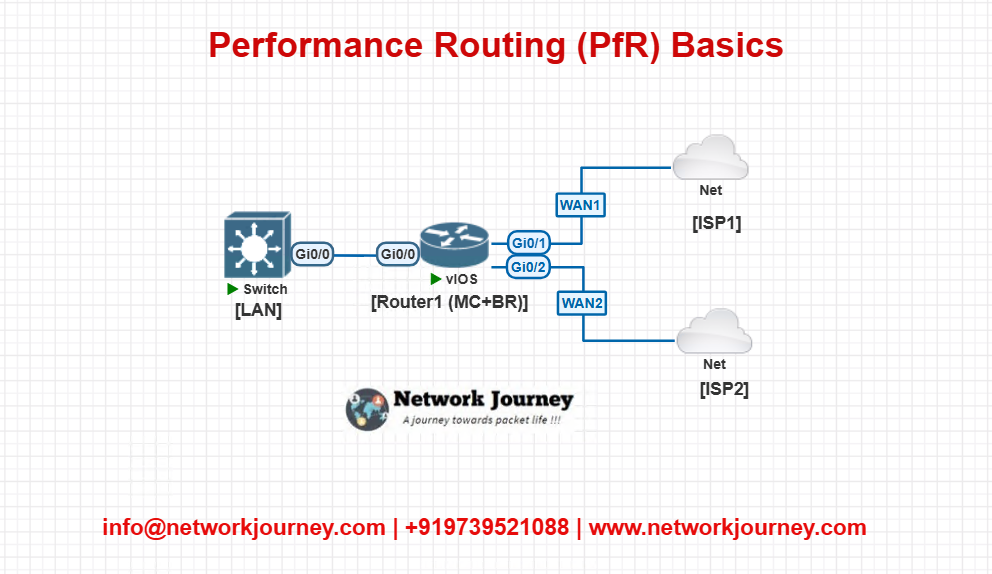
Goal:
Test PfR failover when WAN1 experiences high latency or loss.
Config Snippets:
Define IP SLA:
ip sla 1 icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source-interface Gig0/1 frequency 10 ip sla schedule 1 life forever start-time now
Enable PfR:
pfr master max-routes 10000 border 10.1.1.1 exit pfr border master 10.1.1.1 exit
Lab 2: PfR with Application Routing
Scenario:
- Route voice/video via MPLS (low latency)
- Route bulk data via Internet
Define NBAR App Policy:
class-map match-any VOICE-TRAFFIC match protocol rtp ! policy-map ROUTE-APP class VOICE-TRAFFIC set ip next-hop <MPLS-NEXT-HOP> class class-default set ip next-hop <INET-NEXT-HOP>
Apply this under the PfR policy configuration.
Lab 3: Dual Hub PfR Deployment
Objective:
Simulate dual MC/BR routers with policy-based decision making across multiple branches.
Topology:
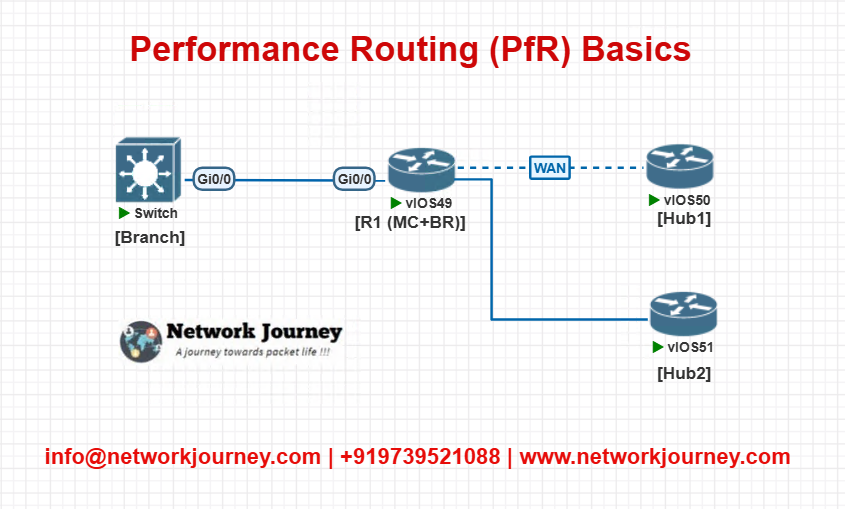
- Load balance branches across both hubs using policies
- Prioritize one link for VoIP, another for bulk transfer
Troubleshooting Tips
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Fix |
| PfR not rerouting traffic | SLA threshold not met | Adjust IP SLA and thresholds |
No traffic seen in show pfr | MC/BR communication issue | Check config and IP reachability |
| App not routed via right path | NBAR or Policy misconfigured | Verify class-map and match conditions |
| IP SLA showing 0 success | Source interface down | Use correct source-interface |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Hub-and-Spoke topology in WAN architecture?
Hub-and-Spoke is a network topology where remote sites (spokes) communicate through a central site (hub). All data flows between spokes must pass through the hub. It’s simple to deploy and manage but may introduce latency and bandwidth bottlenecks at the hub.
2. Why was the Hub-and-Spoke model so popular in traditional enterprise WANs?
This model centralized security, routing, and WAN optimization, making it easier for IT teams to enforce policies and monitor traffic. It also aligned well with MPLS-based WANs where the hub (usually HQ or data center) hosted most of the applications and services.
3. How does SD-WAN challenge the traditional Hub-and-Spoke approach?
SD-WAN introduces Direct Internet Access (DIA) and dynamic path selection. It allows branch-to-branch or branch-to-cloud communication without relying solely on the hub, improving performance, reliability, and reducing latency.
4. Is Hub-and-Spoke topology still relevant in 2025?
Yes, but with a hybrid twist. While full-mesh SD-WAN is ideal for high-availability environments, Hub-and-Spoke is still used for regulatory compliance, security inspection, and centralized services. Many organizations adopt partial mesh or dual-hub models for better scalability.
5. What are the limitations of Hub-and-Spoke in modern WANs?
Key limitations include:
- Increased latency for spoke-to-spoke traffic
- Hub becomes a single point of failure or congestion
- Limited scalability when traffic patterns shift to cloud-first or hybrid applications
6. Can I use Hub-and-Spoke with Cloud Connectivity (like Azure or AWS)?
Yes, cloud providers offer Virtual WAN and Transit Gateways that mimic Hub-and-Spoke. However, for performance-sensitive workloads, direct spoke-to-cloud or spoke-to-spoke paths (enabled by SD-WAN) are often recommended.
7. How does Hub-and-Spoke impact security policy enforcement?
It simplifies security since all traffic flows through a centralized firewall or IPS/IDS system at the hub. But in modern networks with local breakouts, security must be distributed via cloud-delivered firewalls or Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) frameworks.
8. Is Hub-and-Spoke better than full mesh for remote branch offices?
It depends. For a few branches with predictable traffic patterns, Hub-and-Spoke is cost-effective and easier to manage. But for latency-sensitive apps or high branch-to-branch traffic, a full mesh or hybrid SD-WAN approach is more efficient.
9. What role does redundancy play in Hub-and-Spoke WANs?
Redundancy is critical. Dual-hub designs or backup VPNs between spokes can help mitigate the impact of a hub failure. SD-WAN solutions can also provide automated failover and path resiliency to enhance availability.
10. How do I transition from a legacy Hub-and-Spoke to a modern SD-WAN model?
Start with hybrid deployments: keep the hub for centralized control and add DIA and cloud breakout at the spoke level. Gradually phase in features like path selection, app-aware routing, and cloud integration. Choose an SD-WAN vendor that supports flexible topology options.
YouTube Video
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: Performance Routing (PfR) Basics: Optimize Traffic Like a Pro Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Performance Routing (PfR) Basics: Optimize Traffic Like a Pro is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Performance Routing (PfR) Basics: Optimize Traffic Like a Pro [CCNP ENTERPRISE] networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/nj-blog-post-PFR.jpg)
![Mastering BGP Peering and Authentication – A Complete Guide [ CCNP ENTERPRISE ]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Mastering-BGP-Peering-and-Authentication-–-A-Complete-Guide.png)

![[Day #46 Pyats Series] Validate QoS policy configurations using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Validate-QoS-policy-configurations-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)