Route Redistribution with Tagging – Mastering Controlled Routing Across Protocols [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
Today we’re diving deep into a topic that often haunts network engineers during real-world implementations and certifications like CCNP or CCIE — Route Redistribution with Tagging. I still remember a consulting project where a simple redistribution misstep created routing loops and service disruption across multiple branches. That’s when I realized — it’s not just about redistributing routes between protocols, it’s about doing it smartly, and tagging plays a huge role in that. So, if you want to prevent routing loops, filter precisely, and maintain control — this guide is your goldmine!
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief: Understanding Route Redistribution with Tagging
What is Route Redistribution?
Route redistribution allows different routing protocols (like OSPF, EIGRP, RIP, or BGP) to share routing information between each other. It’s especially useful when you’re dealing with multi-protocol environments or merging networks after acquisitions.
Example: Your enterprise runs OSPF internally, but your data center uses EIGRP. You’ll need redistribution at the boundary router to ensure both sides can communicate.
The Challenge – Routing Loops and Route Feedback
Without proper control, redistribution can create issues like:
- Routing loops
- Route feedback (routes being re-advertised back into their source protocol)
- Metric conflicts
This is where Route Tagging comes in as a powerful solution.
What is Route Tagging?
Route tagging is the process of attaching a numerical or string label (tag) to routes as they’re redistributed. These tags don’t affect routing decisions but can be used to filter or match routes when redistributing them again or preventing loops.
Comparison-Pros & Cons
| Feature | Route Redistribution | Route Tagging |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Share routes across different protocols | Add metadata to routes for filtering |
| Prevents Loops | Not by default | Yes, when used correctly |
| Metric Handling | Required for redistribution | Not required but helps with filtering |
| Complexity | Moderate | Slightly more complex but worth it |
| Common Protocols | OSPF ↔ EIGRP, OSPF ↔ BGP, etc. | Works with all routing protocols |
| Use in Policies | Not applicable | Can be matched in route-maps |
| Visibility in Routing Table | Yes | Tags are hidden, used in policies |
Pros and Cons
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Redistribution | Enables communication across protocol boundaries | Can cause loops, requires careful metric configuration |
| Tagging | Helps prevent loops, enables intelligent route filtering | Needs policy planning, not always visible in routing table |
Essential CLI Commands (Cisco IOS)
| Task | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Configure Redistribution | redistribute ospf 1 metric 100 | Redistributes OSPF into another protocol |
| Apply Route-Map | redistribute eigrp 100 route-map TAG-INTO-OSPF | Uses route-map during redistribution |
| Tag Routes in Route-Map | set tag 100 | Adds tag to a route in route-map |
| Match Routes by Tag | match tag 100 | Matches previously tagged routes |
| View IP Routing Table | show ip route | Displays the routing table |
| View Tags in Routes (IOS XE) | `show ip route | include tag` |
| Debug Redistribution | debug ip routing | Monitors real-time changes in the routing table |
| Check BGP/OSPF/EIGRP neighbors | show ip ospf neighbor, show ip eigrp neighbor | Verifies adjacency before redistribution |
| Verify Route Map | show route-map | Displays route-map configuration |
| Show Redistributed Routes | show ip protocols | Verifies redistribution configuration |
Real-World Use Case – Route Tagging in Action
| Scenario | Redistribution Strategy | Tagging Usage |
|---|---|---|
| OSPF to EIGRP in Enterprise Core | Redistribute OSPF into EIGRP with metric | Tag OSPF routes entering EIGRP to prevent loops |
| EIGRP to BGP in Cloud Edge | Redistribute EIGRP into BGP | Tag EIGRP routes; block them from re-entry |
| OSPF <-> OSPF (Multiple Areas or Processes) | Redistribute between OSPF processes | Tag routes to prevent re-injection |
| Branch routers connected to two ISPs | Redistribute BGP to OSPF | Tag ISP-learned routes for tracking or backup use |
| MPLS PE-CE Redistribution | OSPF ↔ BGP Redistribution | Use tags for tenant isolation and loop prevention |
SMALL EVE-NG LAB – Route Redistribution with Tagging
LAB TOPOLOGY:
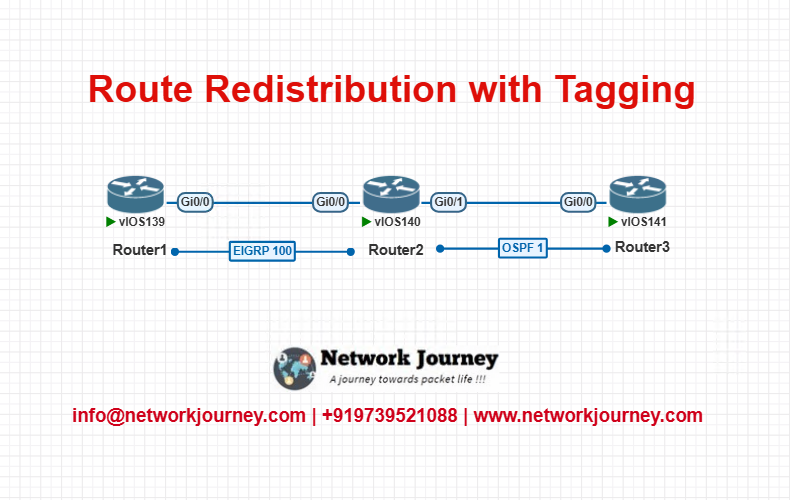
- Router1 runs EIGRP
- Router3 runs OSPF
- Router2 redistributes between both using Route-Map with Tagging
CLI CONFIGURATION
Router1 (EIGRP)
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.255
router eigrp 100
network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255
Router3 (OSPF)
interface Loopback0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255
router ospf 1
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router2 (Redistribution with Tagging)
router eigrp 100
network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255
redistribute ospf 1 metric 10000 100 255 1 1500 route-map FROM-OSPF
router ospf 1
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
redistribute eigrp 100 subnets route-map FROM-EIGRP
route-map FROM-OSPF permit 10
set tag 111
route-map FROM-EIGRP permit 10
match tag 111
set tag 222
Troubleshooting Tips
| Issue | Cause | Solution / Command |
|---|---|---|
| Routes not appearing after redistribution | Protocol mismatch, metric missing | Use show ip protocols, verify metrics |
| Routing loops seen | Improper use of route-maps or missing tags | Use tagging to filter re-injected routes |
| Redistribution working only one-way | No return route or filters blocking reverse traffic | Add bidirectional route-maps |
| Routes not tagged | Route-map missing or improperly applied | Check show route-map, show ip protocols |
| Metric too high causing route rejection | Incorrect metric configuration in redistribution | Adjust metric values for correct preference |
FAQ – Route Redistribution with Tagging
1. What is route redistribution and why is it used?
Answer:
Route redistribution allows you to exchange routing information between different routing protocols, such as OSPF, EIGRP, BGP, and RIP. It’s used when:
- Merging different network domains.
- Transitioning from one protocol to another.
- Connecting enterprise and partner/customer networks.
Redistribution makes networks interoperable — but if done incorrectly, it can create routing loops and instability.
2. What is route tagging in the context of redistribution?
Answer:
Route tagging is the process of assigning an identifying value (a tag) to redistributed routes. It helps to:
- Track the origin of a route.
- Prevent loops (especially in mutual redistribution scenarios).
- Enforce route control policies.
Think of tags like “sticky notes” — you attach one to each route to say where it came from or what to do with it.
3. What is mutual redistribution, and why is tagging critical in that case?
Answer:
Mutual redistribution happens when two routing protocols redistribute into each other (e.g., OSPF into EIGRP and EIGRP into OSPF).
Without tagging, a route might:
- Leave Protocol A,
- Enter Protocol B,
- Then get re-injected back into A — creating a loop.
Route tags help block re-injection by identifying already redistributed routes.
4. How do I tag routes during redistribution in Cisco IOS?
Answer:
Use a route-map to set a tag:
route-map TAG_OSPF_TO_EIGRP permit 10
set tag 100
router eigrp 1
redistribute ospf 1 route-map TAG_OSPF_TO_EIGRP
This sets tag 100 for any OSPF route going into EIGRP. You can then filter or track it later using this tag.
5. How can I filter routes based on tags?
Answer:
Use the match tag statement in your route-map:
route-map BLOCK_RETAGGED_ROUTES deny 10
match tag 100
This will deny any route with tag 100 (previously tagged during redistribution) — helping prevent loops or re-injection.
6. What is the syntax for verifying route tags in the routing table?
Answer:
Use the following command:
show ip route <protocol>
Look for output like this:
nginxCopyEditO E2 10.10.10.0/24 [110/20] via 192.168.1.1, tag 100
You can also view tag info with:
show ip protocols
or
show route-map
7. What’s the difference between route tags and route-maps?
Answer:
| Feature | Route Tags | Route Maps |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Label routes during redistribution | Control routing policy |
| Usage | Identify source protocol or path | Match/set based on prefix, tag, metrics |
| Works With | OSPF, EIGRP, BGP, RIP | Prefix-lists, ACLs, tags, metrics |
| Common Scenario | Loop prevention | Conditional redistribution, tagging |
They’re complementary — tags are values, route-maps are tools that use those values.
8. Can route tags be used for policy-based routing or traffic engineering?
Answer:
Yes — especially in BGP or advanced IGP setups, route tags (or extended communities in BGP) can help:
- Influence route selection
- Apply QoS policies
- Direct traffic over backup paths
In enterprise environments, tags often trigger routing policies or redistribution rules.
9. Is route tagging the same in OSPF and EIGRP?
Answer:
Yes in concept, but OSPF stores the tag in external routes only (Type 5 or Type 7 LSAs). Internal OSPF routes don’t carry tags.
In EIGRP, tags are preserved across redistributed routes.
So, for tagging to work in OSPF:
- Route must be external.
- Tagging is ignored for intra-area or inter-area routes.
10. Can you give a real-world use case of route redistribution with tagging?
Answer:
Scenario:
You have EIGRP in your internal network and OSPF in the DMZ. You need to redistribute routes between them, but prevent loops.
Solution:
- Tag routes going from EIGRP to OSPF: bashCopyEdit
route-map TAG_EIGRP_TO_OSPF permit 10 set tag 200 router ospf 1 redistribute eigrp 100 subnets route-map TAG_EIGRP_TO_OSPF - Block these tagged routes from re-entering EIGRP: bashCopyEdit
route-map BLOCK_TAG200 deny 10 match tag 200 route-map BLOCK_TAG200 permit 20 router eigrp 100 redistribute ospf 1 route-map BLOCK_TAG200
This way, redistributed routes don’t loop back into their source protocol.
YouTube Video Link
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: Route Redistribution with Tagging – Mastering Controlled Routing Across Protocols Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Route Redistribution with Tagging – Mastering Controlled Routing Across Protocols is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Route Redistribution with Tagging – Mastering Controlled Routing Across Protocols [ CCNP ENTERPRISE ]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Route-Redistribution-with-Tagging-–-Mastering-Controlled-Routing-Across-Protocols-CCNP-ENTERPRISE-.png)

![Redundancy Unleashed: Keeping Enterprise Networks Always-On [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Redundancy-Unleashed_-Keeping-Enterprise-Networks-Always-On_networkjourney.png)
![[Day #18 Pyats Series] Building test case hierarchy with Section, CommonSetup using pyATS for Cisco](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Building-test-case-hierarchy-with-Section-CommonSetup-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)