Ticket#20 – Default Route Not Propagating in BGP: Missing Network Statement Fixed [CCNP Enterprise]
Table of Contents
Problem Summary
In a multi-site enterprise setup running eBGP, the edge router was configured with a static default route pointing to the internet. However, this default route was not being advertised to downstream routers via BGP.
Remote sites relied on the HQ BGP router to learn the default route. But when the static route was configured, the admin forgot to include it in the BGP advertisements. As a result, remote sites couldn’t reach the internet, even though the HQ router could.
Symptoms Observed
- HQ router had internet access (static route to ISP worked)
- Remote branches had no default route in their routing table
show ip bgpon branch showed no 0.0.0.0/0- BGP session was up and healthy
- No filtering or route-maps applied
- Static route present, but not seen in BGP table on HQ
Root Cause Analysis
The issue boiled down to BGP not advertising the default route, because:
- BGP only advertises networks explicitly mentioned using the
networkcommand - The static route for
0.0.0.0/0was present in the RIB (Routing Table) but not in the BGP table - No
network 0.0.0.0statement = no BGP advertisement
Remember: BGP does NOT “automatically” advertise static or connected routes like IGPs do!
The Fix
On the HQ router (BGP speaker), add the network statement with mask:
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <next-hop-IP>
router bgp 65000
network 0.0.0.0
This tells BGP:
“If you see this route in your routing table, advertise it to peers.”
Alternative (if using route-maps):
neighbor x.x.x.x default-originate
Use this only if you’re intending to force a default route to a peer, regardless of local availability.
EVE-NG Lab Topology
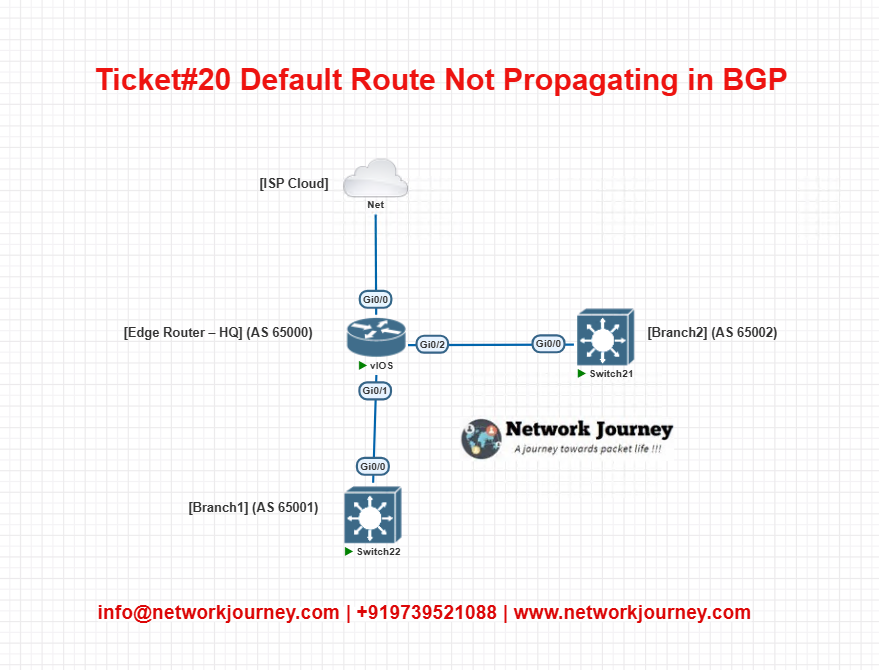
- HQ has a static default route to ISP
- Branches have eBGP peering with HQ
- Default route not advertised from HQ until
network 0.0.0.0added
Verification
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
show ip bgp | Check advertised prefixes |
show ip route | Confirm default route in RIB |
show ip bgp neighbors <ip> advertised-routes | Confirm default route is sent |
debug ip bgp | Observe BGP updates live |
| `show run | section bgp` |
Key Takeaways
- BGP requires explicit
networkcommands to advertise prefixes - A static route alone is not enough
- Always verify both RIB and BGP table
- Use
default-originatecarefully—good for forced default push - Lab it out before applying in production!
Best Practices / Design Tips
- Use
network 0.0.0.0in HQ if default route exists in RIB - Avoid unnecessary redistribution unless required
- Prefer route-maps with conditional
default-originatefor flexibility - Monitor BGP advertisements with: bashCopyEdit
show ip bgp neighbors x.x.x.x advertised-routes - Automate verification via EEM or CLI scripts in critical environments
FAQs
- Why didn’t BGP advertise the default route automatically?
Because BGP doesn’t auto-advertise any route—it needs anetworkcommand explicitly configured. - Does
network 0.0.0.0work without a static default route?
No. The route must exist in the RIB, or BGP won’t advertise it. - How do I verify if BGP is advertising the default route?
Use:show ip bgp neighbors <peer-IP> advertised-routes - Can I use
redistribute staticinstead?
Yes, but it’s not recommended unless you’re filtering properly—it can flood BGP with all static routes. - What is the difference between
networkanddefault-originate?network: Advertises prefix if it exists in RIBdefault-originate: Pushes 0.0.0.0/0 even if it doesn’t exist locally
- Can I advertise default route via route-map?
Yes, usingneighbor x.x.x.x default-originate route-map <name>with conditions. - Is this behavior same in iBGP and eBGP?
Yes. In both, default route must be manually advertised. - What’s the impact of not having a default route on branch routers?
They won’t know where to send internet-bound traffic, causing “destination unreachable” errors. - Can I use
aggregate-address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0?
Technically yes, but it’s less common and requires special handling—networkordefault-originateis preferred. - What is the requirement for the
networkcommand to work?
The prefix must exactly match a route in the routing table. - Why didn’t
redistribute staticwork immediately?
It might’ve worked, but without a proper route-map, you risk injecting all static routes, which is dangerous. - Should the default originate be used on all routers?
No—only the router with external connectivity (typically edge/HQ). - What does the branch router see if default route is advertised?
In the BGP table:
t*> 0.0.0.0/0 [20/0] via x.x.x.x
- Can MPLS VPN customers receive default this way?
Yes, using BGP default-originate under VRFs—common in MPLS L3VPN scenarios. - How to simulate this in EVE-NG?
Build 3 routers (HQ, Branch, ISP), configure static default at HQ, BGP peering with branches, and observe default propagation.
YouTube Video
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Default Route Not Propagating in BGP: Missing Network Statement Fixed is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career
![Ticket#20 – Default Route Not Propagating in BGP: Missing Network Statement Fixed [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Ticket20_Default-Route-Not-Propagating-in-BGP_Missing-Network-Statement-Fixed_networkjourney.png)
![[Day #59 PyATS Series] Detect Split-Horizon Issues in Large Networks Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Day-59-PyATS-Series-Detect-Split-Horizon-Issues-in-Large-Networks-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![[Day #44 Pyats Series] Cross-check BGP route attributes (AS path, next hop) using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Cross-check-BGP-route-attributes-AS-path-next-hop-using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![BGP Prefix Filtering – Control What You Advertise and Accept [ CCNP ENTERPRISE ]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/BGP-Prefix-Filtering-–-Control-What-You-Advertise-and-Accept-CCNP-ENTERPRISE-.png)