VLAN Creation & Troubleshooting: Complete Hands-On Guide with EVE-NG Lab [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
Everything seemed easy on paper until the first trunk port failed, and the whole lab collapsed. That’s when I realized: configuring VLANs is one part, troubleshooting them is another beast altogether. In this post, I’ll walk you through VLAN creation, CLI commands, real-world cases, and yes—how to fix them when things go wrong. Whether you’re studying for CCNA, CCNP, or just upgrading your lab skills, you’ll walk away confident and hands-on.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief: Understanding VLANs
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a logical segmentation of a switch network, allowing different devices to communicate as if they were in separate physical LANs—even if they’re on the same switch.
VLANs help in improving security, reducing broadcast domains, and enhancing network performance. For example, you can have VLAN 10 for HR, VLAN 20 for Finance, and VLAN 30 for IT, each isolated from the other unless you configure routing between them.
Each VLAN is assigned a unique ID (1-4094). Ports on a switch can be either access ports (belong to a single VLAN) or trunk ports (carry traffic for multiple VLANs using tagging protocols like 802.1Q).
In enterprise environments, VLANs are crucial for user segmentation, VoIP, guest access, and multitenant networks. The separation also helps with policy enforcement, limiting broadcast storms, and applying Quality of Service (QoS) rules more effectively.
VLAN Summary: Comparison & Pros and Cons
| Feature/Aspect | Access Port VLAN | Trunk Port VLAN | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Assigned to one VLAN | Carries multiple VLANs | Isolation, security, better broadcast control | Misconfigurations can cause loss of access |
| Used in | End devices (PCs, printers) | Switch-to-switch, switch-to-router | Scalable design, flexibility | Adds complexity in large networks |
| VLAN Tagging | No (untagged) | Yes (802.1Q tagged) | Efficient use of single physical links | Needs careful planning |
| Troubleshooting | Simple (1 VLAN per port) | Requires checking tag configs | Easier to isolate issues | Tagging errors can cause VLAN mismatches |
Essential CLI Commands (Cisco IOS Format)
| Task | CLI Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| View existing VLANs | show vlan brief | Lists all VLANs on switch |
| Create VLAN | vlan 10 + name HR | Creates VLAN with ID and name |
| Assign VLAN to port | interface fa0/1 → switchport access vlan 10 | Assigns port to a VLAN |
| Make port a trunk | switchport mode trunk | Enables trunking on port |
| Check trunk status | show interfaces trunk | Lists active trunk ports |
| Verify VLAN on port | show interface fa0/1 switchport | Shows port VLAN assignment |
| Ping test between VLANs | ping [IP address] | Basic reachability test |
| Troubleshoot STP issues | show spanning-tree vlan 10 | STP info per VLAN |
| Debug VLAN traffic (advanced) | debug sw-vlan packet | Used for packet-level issues |
Real-World Use Case
| Scenario | VLAN Setup | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Office with departments (HR, IT) | VLAN 10 = HR, VLAN 20 = IT, VLAN 30 = Finance | Department isolation, security |
| VoIP deployment | VLAN 40 = Voice, separate from data VLANs | QoS and jitter control |
| Guest Wi-Fi with limited access | VLAN 50 = Guest Network, ACL applied to block internal resources | Secure guest access |
| School/College network | VLAN per lab/classroom to control access and reduce broadcast traffic | Controlled student access |
| Multi-tenant building | VLANs per company with separate subnets and policies | Logical separation without physical isolation |
EVE-NG LAB: Basic VLAN Creation with Troubleshooting
Topology:
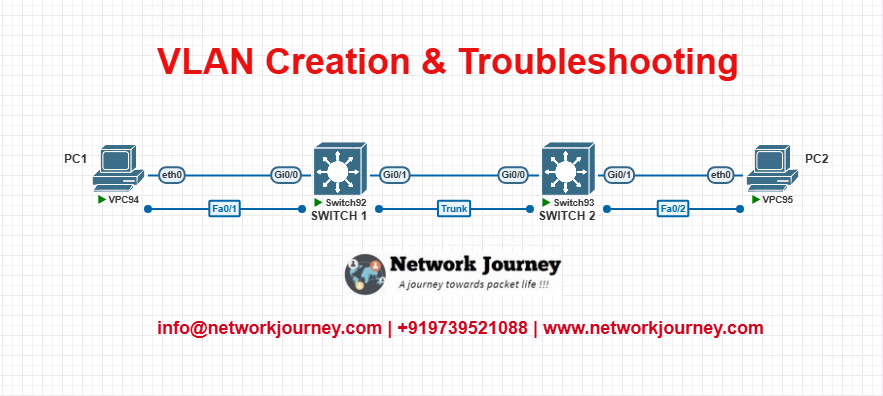
- PC1 = VLAN 10
- PC2 = VLAN 10
- Trunk link between SW1 and SW2
- Ping test from PC1 to PC2
Configuration (Cisco IOS):
SW1
vlan 10 name HR interface fa0/1 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 no shutdown interface fa0/24 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk no shutdown
SW2
vlan 10 name HR interface fa0/2 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 no shutdown interface fa0/24 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk no shutdown
Test:
PC1> ping PC2_IP
Success = VLAN is configured and trunk is passing tags
Failure = Check VLANs, trunk mode, allowed VLANs, interface status
Troubleshooting Tips
| Problem | Likely Cause | Fix or CLI Command |
|---|---|---|
| Devices in same VLAN can’t ping | Trunk not configured or mis-tagged | show interfaces trunk + verify VLAN ID |
| Port not in right VLAN | Wrong access config | show vlan brief + show run int fa0/x |
| VLAN not showing on switch | VLAN not created | vlan <ID> again in config mode |
| Trunk link down | Physical issue or wrong config | show interface status + cabling check |
| VLAN blocked by STP | STP blocking port | show spanning-tree vlan <ID> |
VLAN FAQs
1. What is a VLAN and why is it used in modern networks?
Answer:
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) logically segments a Layer 2 network into multiple broadcast domains.
Benefits include:
- Improved security (isolation of departments)
- Reduced broadcast traffic
- Efficient traffic management
Each VLAN behaves as a separate physical LAN, even though all devices may be connected to the same switch.
2. How do I create a VLAN on a Cisco switch using CLI?
Answer:
configure terminal vlan 10 name SALES exit
This creates VLAN 10 and names it “SALES”.
To assign an interface to this VLAN:
interface fa0/1 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10
3. How do I verify VLAN creation and interface assignments?
Answer:
Use the following commands:
show vlan brief
- Lists all VLANs and their assigned ports
show interfaces switchport
- Shows access/trunk status and VLAN assignment of interfaces
4. What are common reasons VLANs fail to communicate across switches?
Answer:
- Trunk links not configured or misconfigured
- VLAN not allowed on the trunk
- Native VLAN mismatch
- Switchport in the wrong mode (access vs trunk)
- Missing VLAN on one of the switches
Use:
show interfaces trunk show cdp neighbors detail
To diagnose such issues.
5. Can VLANs communicate with each other by default?
Answer:
No. VLANs are isolated Layer 2 domains. To allow communication:
- You need Inter-VLAN Routing, done via:
- A Layer 3 switch
- A router-on-a-stick configuration
Example:
interface g0/0.10 encapsulation dot1Q 10 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
6. How do I troubleshoot when devices in the same VLAN can’t communicate?
Answer:
Check the following:
- Interface assigned to correct VLAN:
show interfaces fa0/1 switchport
- Interface status:
show interfaces fa0/1 status
- MAC address table:
show mac address-table vlan 10
- Ping between end devices to test reachability
7. What is the maximum number of VLANs supported on Cisco switches?
Answer:
Standard VLANs:
- Range: 1–1005
- VLANs 1, 1002–1005 are reserved and cannot be deleted
Extended VLANs (1006–4094) are supported in VTP Transparent or VTP Off modes on some switches.
8. How do I ensure VLANs are consistent across all switches in my topology?
Answer:
Options include:
- Manually creating VLANs on each switch (for smaller networks)
- Using VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) to propagate VLAN info automatically
Verify with:
show vtp status
But be cautious—incorrect VTP configuration can delete VLANs. Back up configs first.
9. How does EVE-NG help with VLAN lab simulation?
Answer:
EVE-NG allows you to:
- Build multi-switch topologies
- Simulate access and trunk ports
- Test VLAN tagging, trunking, and inter-VLAN routing
- Use real Cisco IOS images for hands-on CLI experience
It’s a perfect platform for CCNP labs and troubleshooting practice.
10. What commands are most helpful when troubleshooting VLANs?
Answer:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
show vlan brief | List VLANs and their assigned ports |
show interfaces trunk | Verify trunk links and allowed VLANs |
show mac address-table | See learned MACs in VLANs |
show interfaces switchport | View mode and VLAN of an interface |
ping | Basic Layer 3 connectivity test |
show spanning-tree vlan <id> | Check STP role and status of ports |
These help narrow down port mode, VLAN mismatch, and connectivity issues.
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: VLAN Creation & Troubleshooting: Complete Hands-On Guide with EVE-NG Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement VLAN Creation & Troubleshooting: Complete Hands-On Guide with EVE-NG Lab is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![VLAN Creation_Troubleshooting_Complete Hands-On Guide with EVE-NG Lab_[CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/VLAN-Creation_Troubleshooting_Complete-Hands-On-Guide-with-EVE-NG-Lab_networkjourney.png)
![VRF Lite Explained: Real-World Use Cases, Commands & Troubleshooting [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/VRF-Lite-Explained_networkjourney.png)

![Ticket#3 - VLAN Mismatch: End Users Unable to Reach Gateway – A Real Cisco Fix [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/nj-blog-post-Ticket3.jpg)