VPN 0 and VPN 512 in Cisco SD-WAN: Backbone & Management Explained [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
Today diving deep into a very important, yet often misunderstood part of SD-WAN architecture — VPN 0 and VPN 512.
When you start exploring Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela), you’ll quickly notice the use of different VPNs not just for end-user data, but for control, management, and transport separation. In traditional networking, VPN often means encrypted traffic. But in SD-WAN, it’s a virtual routing and forwarding instance (VRF) that isolates traffic.
Let’s break this down and understand it clearly — with CLI, real-world labs, and common troubleshooting too.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief: What Are VPN 0 and VPN 512?
VPN 0 – Transport VPN
- Responsible for WAN transport connectivity (Internet/MPLS/4G).
- Used for building control connections (DTLS/TLS) between vEdge/vSmart/vBond.
- No service-side data plane (LAN user traffic) passes through it.
VPN 512 – Management VPN
- Provides out-of-band management access (SSH, SNMP, NTP, etc.).
- Typically used to manage vEdge devices via a dedicated interface.
- Doesn’t participate in data or control-plane routing.
VPN Comparison
| Feature | VPN 0 (Transport VPN) | VPN 512 (Management VPN) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Transport connectivity | Device management |
| Data Plane | Yes (control-plane only) | No |
| Routing Role | Control connections | Mgmt. access only |
| Interface Type | WAN (ge0/0, ge0/1) | Mgmt port (mgmt0) |
| Protocols Allowed | BFD, DTLS/TLS | SSH, SNMP, ICMP |
Pros and Cons
| VPN | Pros | Cons |
| VPN 0 | Required for SD-WAN fabric to form | Misconfiguration affects control plane |
| VPN 512 | Secure remote access for out-of-band management | Doesn’t support routing or service traffic |
CLI Commands
| Task | CLI Command |
| Show interfaces in VPN 0 | show interface vpn 0 |
| Show control connections | show control connections |
| Show interface in VPN 512 | show interface vpn 512 |
| Ping from VPN 512 | ping vpn 512 <ip> |
| Show management interface logs | show logging |
| Show system status | show system status |
Real-World Use Cases
| Use Case | VPN Involved | Why It’s Used |
| Control Plane Tunnel Formation | VPN 0 | Connect to vSmart/vBond/vManage over WAN |
| Device Monitoring & SSH | VPN 512 | Manage edge devices securely |
| Routing Internet/MPLS Traffic | VPN 0 | Send data/control packets over underlay |
| Remote Access for NOC Engineers | VPN 512 | Access devices via management plane |
Lab 1: vEdge VPN 0 and 512 Interface Configuration
Topology:
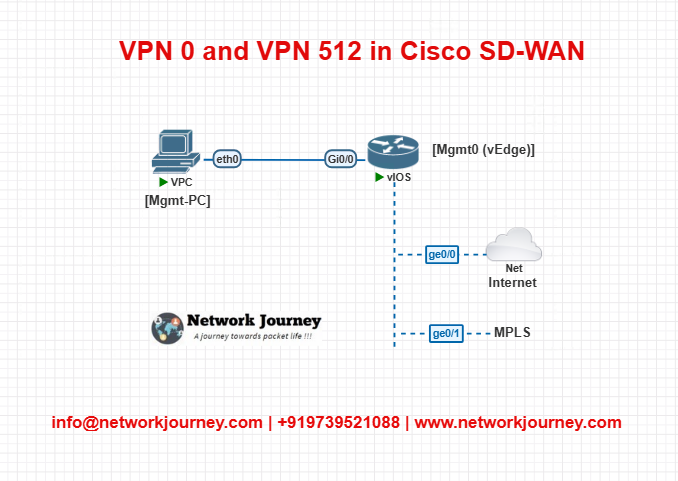
Objective:
- Configure basic VPN 0 (WAN) and VPN 512 (Mgmt) interfaces on vEdge.
Configuration Snippet:
! VPN 0 (WAN) vpn 0 interface ge0/0 ip address 192.0.2.2/30 tunnel-interface encapsulation ipsec color mpls no shutdown ! interface ge0/1 ip address 203.0.113.2/30 tunnel-interface encapsulation ipsec color biz-internet no shutdown ! VPN 512 (Mgmt) vpn 512 interface mgmt0 ip address 10.10.10.2/24 no shutdown
Lab 2: Test VPN 512 SSH Access
Objective:
- Test out-of-band access from Mgmt-PC to vEdge using VPN 512.
Test Steps:
- SSH into vEdge from Mgmt-PC.
- Use
show interface vpn 512to verify connectivity. - Use
ping vpn 512 <gateway-IP>to test reachability.
Lab 3: Break VPN 0 and Observe Control Loss
Scenario:
- Shut down VPN 0 interfaces and watch DTLS sessions drop.
Commands:
interface ge0/0 shutdown ! show control connections
- Notice how control plane collapses when VPN 0 is down.
Troubleshooting Tips
| Issue | Cause | Fix |
| No DTLS/TLS control connection | VPN 0 misconfigured | Check IP, color, encapsulation |
| SSH not working on vEdge | VPN 512 down or wrong IP | Verify mgmt0 interface and IP/subnet |
| No route in VPN 0 | No static/default route set | Add ip route 0.0.0.0/0 <gateway> in VPN 0 |
| Ping fails from VPN 512 | Wrong gateway IP | Use correct management subnet |
FAQs: VPN 0 & VPN 512
1. What is the purpose of VPN 0 in Cisco SD-WAN?
Answer:
VPN 0 is the transport VPN, responsible for establishing control plane connectivity between SD-WAN devices like vEdge, vSmart, and vBond. It carries IPsec tunnels, DTLS/ TLS control connections, and data plane traffic over transport networks like the internet, MPLS, or LTE. No service-side traffic (such as user VLANs) is routed here—it’s strictly for backbone communication.
2. What role does VPN 512 play in Cisco SD-WAN?
Answer:
VPN 512 is the management VPN used for out-of-band (OOB) communication with the local device. It connects to services like vManage, SSH, SNMP, logging, or NTP. Typically, this VPN is configured with a static IP address and default route pointing to a local gateway, often over Ethernet. It does not participate in overlay tunnels.
3. Can VPN 0 and VPN 512 share the same interface?
Answer:
No. Interfaces used in VPN 0 (transport) and VPN 512 (management) must be on separate physical or logical interfaces. This ensures clear separation between data/control-plane transport and device management. Overlapping would cause operational and security issues.
4. Is it mandatory to configure VPN 0 and VPN 512 on every SD-WAN device?
Answer:
Yes. All SD-WAN edge devices (vEdge/C8000v) must have VPN 0 configured to establish secure fabric communication with the controllers. VPN 512 is also required for out-of-band device management and initial onboarding (e.g., when using bootstrap configuration or vBond redirection).
5. What kind of interfaces are typically configured in VPN 0 and VPN 512?
Answer:
- VPN 0: WAN-facing interfaces like GigabitEthernet, cellular, or T1/E1 interfaces, depending on the transport medium.
- VPN 512: Local management ports like GigabitEthernet0, loopback, or dedicated OOB management ports (e.g., MGMT interface on vEdge).
6. How does VPN 0 support multiple transport types in SD-WAN?
Answer:
VPN 0 allows you to configure multiple interfaces, each pointing to a different transport (MPLS, Internet, LTE). These interfaces enable TLOCs (Transport Locators) which are used to build multiple control connections and data tunnels. This is essential for SD-WAN’s application-aware routing and transport redundancy features.
7. Can I route service-side (user) traffic in VPN 0 or VPN 512?
Answer:
No. VPN 0 and 512 are reserved for transport and management respectively. Service-side (user/data) traffic must be routed in VPN 1 and above, typically VPN 1 for most deployments. Routing or policy-based forwarding in VPN 0/512 is not allowed for user traffic.
8. What happens if VPN 0 is misconfigured or down?
Answer:
If VPN 0 is down or misconfigured:
- The control plane will fail (vEdge cannot reach vSmart or vBond).
- No IPsec tunnels can be established.
- Data plane communication with other SD-WAN sites will break.
- The device may appear as ‘down’ or ‘disconnected’ in vManage.
9. Is NAT supported in VPN 0 for internet transport?
Answer:
Yes. VPN 0 supports NAT traversal, especially when using internet transport. You can configure NAT interfaces and use DTLS/TLS with NAT detection to establish control and data plane tunnels. It also supports NAT DIA (Direct Internet Access) for local internet breakout.
10. How can I verify VPN 0 and VPN 512 interface status and configuration?
Answer:
You can use the following CLI commands on vEdge or C8000v:
show interface vpn 0 show interface vpn 512
To view routing in each VPN:
show ip route vpn 0 show ip route vpn 512
These help confirm IP addressing, interface status (up/down), and routes necessary for connectivity to transport or management networks.
Related YouTube Video
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: VPN 0 and VPN 512 in Cisco SD-WAN: Backbone & Management Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Class 4 Traditional Network Topology vs SD Access Simplified
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement VPN 0 and VPN 512 in Cisco SD-WAN: Backbone & Management is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![VPN 0 and VPN 512 in Cisco SD-WAN: Backbone & Management Explained[CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/nj-blog-post-vpn0-vpn512.jpg)

![Mastering Ping and Traceroute: Advanced Options Every Network Engineer Should Know [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Mastering-Ping-and-Traceroute_Advanced-Options-Every-Network-Engineer-Should-Know_networkjourney.png)
