Mastering Layer 2 Troubleshooting Commands: A Complete Guide with CLI & EVE-NG Labs [CCNP Enterprise]
Today we’re diving into something every network engineer must master—Layer 2 Troubleshooting. Whether you’re preparing for CCNP or resolving critical enterprise network issues, knowing the right CLI commands can make all the difference. In this post, we’ll walk through key Layer 2 concepts, explore essential commands, test real-world use cases, and build a compact EVE-NG lab to practice everything hands-on.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief
What is Layer 2 in Networking?
Layer 2, also known as the Data Link Layer, handles frame transmission within the same network segment. It involves MAC addressing, switching, VLANs, and protocols like STP (Spanning Tree Protocol).
Why Troubleshoot Layer 2?
Most network issues—like loops, broadcast storms, or VLAN mismatches—originate at Layer 2. Quick diagnostics can save hours of downtime.
What You Need to Know
To troubleshoot effectively, you must understand:
- MAC Address Table
- Spanning Tree States
- Port Security
- VLAN Configuration
- Interface and Trunking Modes
Comparison: Common Layer 2 Issues
| Issue Type | Symptoms | CLI for Detection | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VLAN Mismatch | No connectivity | show vlan, show int trunk | Quick to fix | Can break inter-VLAN routing |
| STP Loop | Broadcast storm, slow net | show spanning-tree | Protects from loops | Misconfig = blocked ports |
| Port Security | Port shut down unexpectedly | show port-security | Prevents MAC flooding | Can block legit users |
| Duplex Mismatch | Packet drops, low throughput | show interface | Easy to detect | Performance issues |
| MAC Table Issues | Flapping or stale entries | show mac address-table | Pinpoints MAC movement | Doesn’t show physical path |
Essential CLI Commands
| Purpose | CLI Command |
| Check interface status | show interfaces status |
| Verify VLAN configuration | show vlan brief |
| Inspect port mode | show interfaces switchport |
| Review MAC address table | show mac address-table |
| Check trunking interfaces | show interfaces trunk |
| Display STP details | show spanning-tree |
| Examine port security | show port-security interface |
| Debug Layer 2 issues | debug spanning-tree events |
| View BPDU traffic | debug spanning-tree bpdu receive |
| Clear MAC table | clear mac address-table dynamic |
Real-World Use Cases
| Scenario | Common Commands Used |
| Access port not forwarding traffic | show interfaces switchport, show vlan |
| User intermittently disconnected | show port-security, show mac address |
| Slow network during file transfer | show interface, show spanning-tree |
| No ping between devices on same VLAN | show vlan, show int trunk, show mac |
| Loop detected in network | show spanning-tree, debug spanning-tree |
EVE-NG LAB Setup
Topology Diagram:
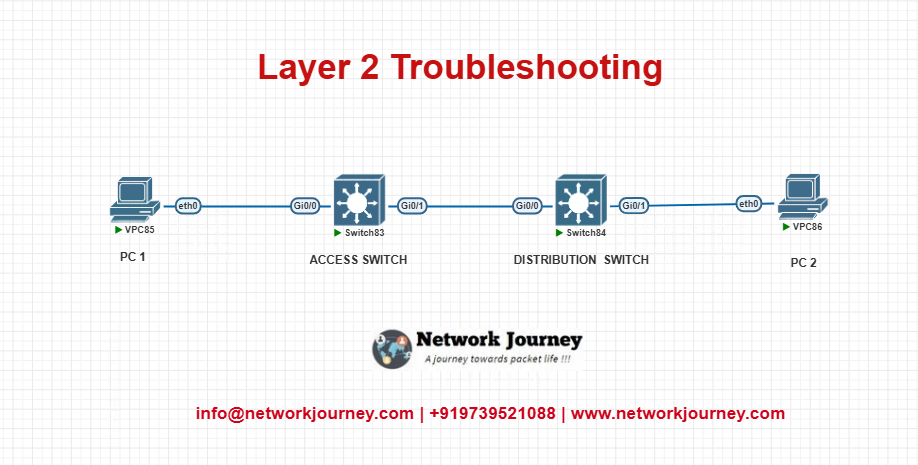
Configuration Samples:
Access Switch:
hostname SW1 interface range fa0/1 - 2 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 spanning-tree portfast no shutdown interface vlan 10 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
Distribution Switch:
hostname SW2 interface fa0/1 switchport mode trunk interface fa0/2 switchport mode trunk vlan 10 name Users
Troubleshooting Tips
| Problem | Likely Cause | Suggested Action |
| Port in err-disabled state | Port security violation | Use errdisable recovery or re-enable |
| STP blocking legitimate port | Wrong root bridge config | Change STP priority |
| No MAC entry for device | VLAN not assigned | Check show vlan, assign correct VLAN |
| Trunk link not forwarding VLANs | VLAN not allowed | Add VLANs to trunk with switchport trunk allowed vlan |
| End device can’t ping gateway | SVI down or VLAN issue | Check interface vlan <id>, VLAN status |
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are the most commonly used Layer 2 troubleshooting commands on a Cisco switch?
Answer:
The essential Layer 2 troubleshooting commands include:
show mac address-table– View MAC learningshow vlan brief– Verify VLAN existence and assignmentshow interfaces status– Check interface link and modeshow spanning-tree– Check STP state and port rolesshow cdp neighbors– Discover directly connected Cisco devices
These commands provide a quick snapshot of switch health and Layer 2 status.
2. How do I identify VLAN misconfigurations on a switch?
Answer:
Use:
show vlan brief
This command shows:
- All configured VLANs
- Ports assigned to each VLAN
If a port is not in the correct VLAN or a VLAN is missing, it may cause devices in the same subnet to fail to communicate.
3. How can I verify MAC address learning on a switch port?
Answer:
Run:
show mac address-table interface <interface>
Example:
show mac address-table interface Gig0/1
This displays all MACs learned on that port. If none are listed and the port is up, it may indicate a connectivity issue or wrong VLAN.
4. What command shows if a switch port is blocking due to STP?
Answer:
Use:
show spanning-tree interface <interface>
It shows the STP state of the port—forwarding, blocking, or learning. If a port is blocking, it may be due to a loop or incorrect STP priority settings.
5. How do I find physical layer issues on a switch port?
Answer:
Use:
show interfaces <interface>
Look for:
- CRC errors
- Input/output errors
- Duplex mismatches
These indicators help pinpoint physical cabling or speed/duplex negotiation issues.
6. How can I detect Layer 2 loops in a switched network?
Answer:
Look for:
- High CPU usage on switches
- MAC flapping (same MAC appearing on multiple ports)
Use:
show mac address-table | include <MAC> show logging | include LOOP
Also check STP status using:
show spanning-tree
7. What does the “err-disabled” port status mean and how do I recover it?
Answer:
A port in err-disabled state has been shut down automatically due to a violation (e.g., BPDU guard, port-security, loopback).
Check with:
show interfaces status err-disabled show errdisable recovery
To recover manually:
shutdown no shutdown
Or enable automatic recovery:
errdisable recovery cause all
8. How do I verify trunk link configurations?
Answer:
Use:
show interfaces trunk
It displays:
- Trunking interfaces
- Allowed VLANs
- Native VLAN
Mismatched trunk settings can cause VLAN leakage or dropped frames.
9. How can I verify Layer 2 connectivity between switches?
Answer:
Use:
show cdp neighbors
It shows directly connected Cisco devices and their interfaces. To test Layer 2 reachability, also verify matching VLANs and STP status on trunk links.
10. What are some Layer 2 issues that can break inter-VLAN routing or gateway reachability?
Answer:
Common causes include:
- Host port assigned to wrong VLAN
- Trunk link missing allowed VLANs
- Native VLAN mismatch
- STP blocking key uplink ports
- MAC address not being learned due to port-security
To troubleshoot: - Use
show vlan,show interfaces trunk, andshow spanning-tree - Confirm the gateway IP is reachable using
pingfrom different VLANs
YouTube Link
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: Mastering Layer 2 Troubleshooting Commands: A Complete Guide with CLI & EVE-NG Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Mastering Layer 2 Troubleshooting Commands: A Complete Guide with CLI is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Mastering Layer 2 Troubleshooting Commands: A Complete Guide with CLI & EVE-NG Labs [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Mastering-Layer-2-Troubleshooting-Commands_networkjourney.png)
![Git and GitHub for Network Engineers – Version Control Made Easy [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Git-and-GitHub-for-Network-Engineers-–-Version-Control-Made-Easy-1.png)
![Mastering Next-Hop Reachability: A Guide to Smarter Routing Decisions [ CCNP ENTERPRISE ]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Mastering-Next-Hop-Reachability-A-Guide-to-Smarter-Routing-Decisions.png)
