Default Route Propagation – Your Gateway to the World [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
Today, let’s talk about something deceptively simple but absolutely mission-critical in enterprise routing — Default Route Propagation.
You know, in my CCNP classes, I often start the routing discussions with: “What happens when a router doesn’t know where to send a packet?” And the answer is simple — it sends it to the default route, a.k.a. the gateway of last resort. But in real-world enterprise setups, just configuring a static default route isn’t enough. You need that route to propagate throughout the network so every router — from core to edge — knows where to send unknown traffic.
Let’s dive into this from concept to CLI, from lab to real-world troubleshooting. Grab your coffee and packet tracer — we’re going deep.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief – What is Default Route Propagation?
A default route (0.0.0.0/0) tells the router where to forward packets when no specific route exists in its routing table.
In small setups, it’s okay to configure this statically on each device. But in enterprise or ISP-grade networks, default route propagation is used so the default route is advertised dynamically using routing protocols like:
- OSPF
- EIGRP
- BGP
- RIP
Why Propagate It?
Imagine you have multiple branch offices, and only the HQ has an internet connection. Rather than setting static 0.0.0.0/0 routes on every branch router, you can inject the default route from HQ dynamically.
Default Route Injection Methods
- Use
default-information originatein OSPF - Use
redistribute staticwith a static 0.0.0.0/0 route - Use
network 0.0.0.0in BGP - Use
ip default-networkin older protocols like RIP
Once injected, the routing protocol takes care of propagating the default route to all downstream routers.
Comparison – Default Route Propagation Methods
| Protocol | Method Used | Requires Existing Default? | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| OSPF | default-information originate | Yes | Controlled and secure injection |
| EIGRP | redistribute static | Yes | Needs route-map for fine control |
| BGP | network 0.0.0.0 or default-originate | Yes or No (depends) | Often used at the ISP edge |
| RIP | ip default-network | Yes | Legacy method, less granular control |
Essential CLI Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
show ip route | View current routes including default |
show ip protocols | See what’s being advertised |
show ip ospf database | Confirm LSA types, including default LSA |
show ip eigrp topology | Check EIGRP propagated default route |
debug ip routing | Trace route installation/removal in real time |
show bgp ipv4 unicast | View default route in BGP table |
show ip bgp neighbors | See if default-originate is enabled |
Real-World Use Case: Internet Access via HQ
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| Topology | HQ (with ISP link) and multiple branch offices |
| Goal | Allow branches to reach internet via HQ |
| Problem | Branches don’t know where to send non-local traffic |
| Solution | Inject default route at HQ and propagate via OSPF |
| Benefit | Simplifies configuration, enables central control |
| Key Commands | ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0, default-information originate in OSPF |
Small EVE-NG Lab – Diagram + Configuration
Lab Topology
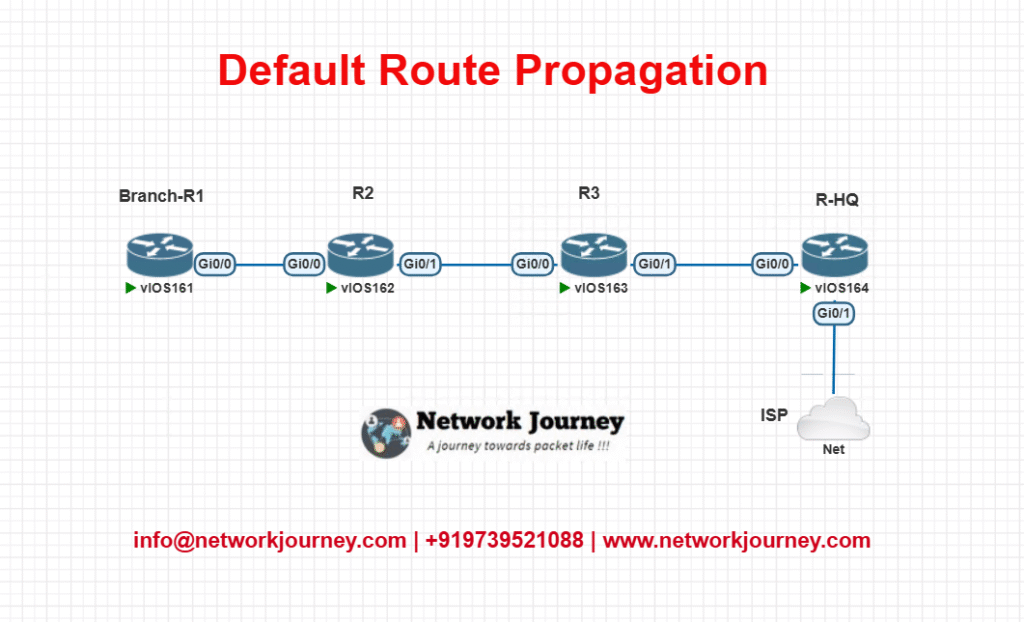
- R-HQ: Connected to ISP, generates default route.
- R3, R2, Branch-R1: Internal routers using OSPF.
Basic Configuration Snippet
On R-HQ:
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <ISP-NEXT-HOP>
!
router ospf 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
default-information originate
On R3, R2, Branch-R1:
router ospf 1
network <interfaces> area 0
Verification:
Branch-R1# show ip route
...
O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 192.168.1.1, 00:00:03, Gig0/1
You’ll see the default route with O*E2, meaning it’s OSPF External Type 2.
Troubleshooting Tips
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Default route not appearing | No static default on injecting router | Add ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 x.x.x.x |
| OSPF router doesn’t advertise default | default-information originate missing | Configure it in router ospf |
| Route received but not installed | Administrative distance conflict | Check with show ip route and AD values |
| EIGRP doesn’t propagate default | Missing redistribution | Use redistribute static |
| BGP peer doesn’t get default | Missing default-originate | Add in router bgp under neighbor config |
FAQ – Default Route Propagation
1. What is a default route and why do we need it?
Answer: A default route (0.0.0.0/0) is used when no specific route matches a packet’s destination. It acts like a “catch-all” route. Essential for accessing unknown networks (like the internet).
2. Can I configure a default route statically and still propagate it dynamically?
Answer: Yes! Most routing protocols require that the static default route already exist on the router before it can be advertised.
3. How does OSPF propagate a default route?
Answer: Using the command:
default-information originate
This tells OSPF to generate a Type 5 LSA for 0.0.0.0/0, provided a default route already exists.
4. What is the difference between always and normal originate in OSPF?
Answer:
- Without
always: OSPF advertises the default only if a default route exists in the routing table. - With
always: OSPF advertises it regardless of the static route’s presence.
default-information originate always
5. Can I propagate a default route in EIGRP?
Answer: Yes. You must:
- Create a static default route.
- Use
redistribute staticunder EIGRP. - (Optional) Use a route-map to control the advertisement.
6. How does BGP handle default routes?
Answer:
You can either:
- Advertise 0.0.0.0/0 using
network 0.0.0.0(if in BGP table). - Use
neighbor x.x.x.x default-originateto inject default to a specific neighbor.
7. Is it possible to filter default route propagation?
Answer: Absolutely. You can use route-maps, prefix-lists, and distribute-lists to prevent unwanted default route learning or advertising.
8. What does the O*E2 mean in show ip route?
Answer:
O= Learned via OSPF*= Candidate defaultE2= External type 2 LSA (default cost, does not increment)
9. Should I advertise default routes in all routing domains?
Answer: No — advertise only where necessary. For example, you may not want to advertise a default route into DMZs or internal-only networks. Use filtering wisely.
10. What’s the risk of improper default propagation?
Answer:
- Routing loops
- Black-holing traffic
- Security vulnerabilities
Always ensure that default routes are advertised with clear intent and proper filtering in place.
YouTube Video
Watch the Complete CCNP Enterprise: Default Route Propagation – Your Gateway to the World Lab Demo & Explanation on our channel:
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Default Route Propagation – Your Gateway to the World is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Default Route Propagation – Your Gateway to the World [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Default-Route-Propagation-–-Your-Gateway-to-the-World-CCNP-ENTERPRISE.png)
![Wireless QoS Settings – Prioritizing Your Wireless Traffic Like a Pro[CCNP Enterprise]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Wireless-QoS-Settings-–-Prioritizing-Your-Wireless-Traffic-Like-a-Pro-CCNP-Enterprise.png)
![Mastering DHCP Snooping and Binding Table: Secure Your Layer 2 Network Like a Pro [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/nj-blog-post-dhcp-snooping-binding-table.jpg)
![Ticket#8 - VOIP Choppy Audio – DSCP Marking Mismatch Fixed [QoS Real World] [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/nj-blog-post-Ticket-8.jpg)