Troubleshooting Multicast in Enterprise – From Chaos to Clarity [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
Today we’ll dive deep into the art and science of troubleshooting multicast in enterprise networks.
This post is for engineers who are tired of “guesswork” and want step-by-step strategies to solve real multicast challenges—whether it’s IPTV not streaming or CCTV video dropouts. We’ll pair concepts with CLI tools, lab configs, and even EVE-NG simulations. Ready? Let’s fix those multicast gremlins!
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief – Understanding Multicast Troubleshooting
Multicast is a one-to-many delivery method that efficiently distributes data like IPTV, video conferencing, and real-time telemetry. But troubleshooting multicast is quite different from unicast or broadcast—it spans multiple OSI layers and protocols, including:
- Layer 2: IGMP Snooping (to prevent flooding)
- Layer 3: PIM (to build multicast routing trees)
- Applications: Streaming clients, source servers, etc.
Why is Multicast Hard to Troubleshoot?
- Silent Fails: Multicast doesn’t retransmit by default like TCP. If it’s not working—there are often no obvious signs.
- Multiple Components: Switches, routers, queriers, PIM routers, and even ACLs may affect delivery.
- Asymmetric Paths: One side may see traffic, another may not.
Common Multicast Issues in Enterprise Networks
- Stream drops after few minutes
- Multicast floods across the LAN
- Devices on different VLANs can’t see the stream
- One region receives multicast, another doesn’t
- IGMP joins not being registered
To troubleshoot these, you need a methodical approach—and that’s what this guide is all about.
Comparision – Troubleshooting Multicast at a Glance
| Component | Potential Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| IGMP Snooping | Not enabled / not filtering | Enable globally & per VLAN |
| Querier | Missing / multiple queriers | Configure switch or router as querier |
| PIM | Not configured or mismatched mode | Use Sparse/DM and match across routers |
| RP (Rendezvous Point) | Not reachable | Ensure RP is reachable; use static or Auto-RP |
| ACLs | Blocking IGMP or PIM | Allow protocols in control/data path |
| Multicast Routing Table | Not populated | Verify joins, neighbors, RPF, PIM neighbors |
| Client | Not sending IGMP Join | Use packet capture or verify config |
Pros and Cons of Multicast
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Efficient for one-to-many transmission | Complex setup |
| Scales well in large networks | Troubleshooting is non-trivial |
| Reduces overall bandwidth | Requires IGMP/PIM configuration |
| Ideal for real-time services | Prone to silent failures |
Essential CLI Commands
| Function | Command |
|---|---|
| Show IGMP snooping | show ip igmp snooping |
| Show IGMP groups | show ip igmp groups |
| Show multicast routes | show ip mroute |
| Show PIM neighbors | show ip pim neighbor |
| Show PIM interfaces | show ip pim interface |
| Debug IGMP packets | debug ip igmp |
| Debug PIM packets | debug ip pim |
| Ping multicast group | ping <multicast-ip> repeat 5 |
| Verify RP mapping | show ip pim rp mapping |
| View RPF info | show ip rpf <source-ip> |
These commands help you identify whether IGMP joins are registered, PIM neighbors are up, and whether the Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) check is passing.
Real-World Use Case – CCTV Streaming Across Branches
| Scenario | Details |
|---|---|
| Problem | HQ multicast CCTV stream not reaching branch office |
| Root Cause | RP not reachable from remote router due to missing PIM route |
| Solution | Added static RP and enabled multicast routing and PIM sparse mode across WAN |
| Result | CCTV feed stable and consistent in both HQ and branch |
| Bonus Fix | IGMP Snooping enabled on access switches to prevent flooding |
EVE-NG Lab – Troubleshooting Multicast
Lab Topology
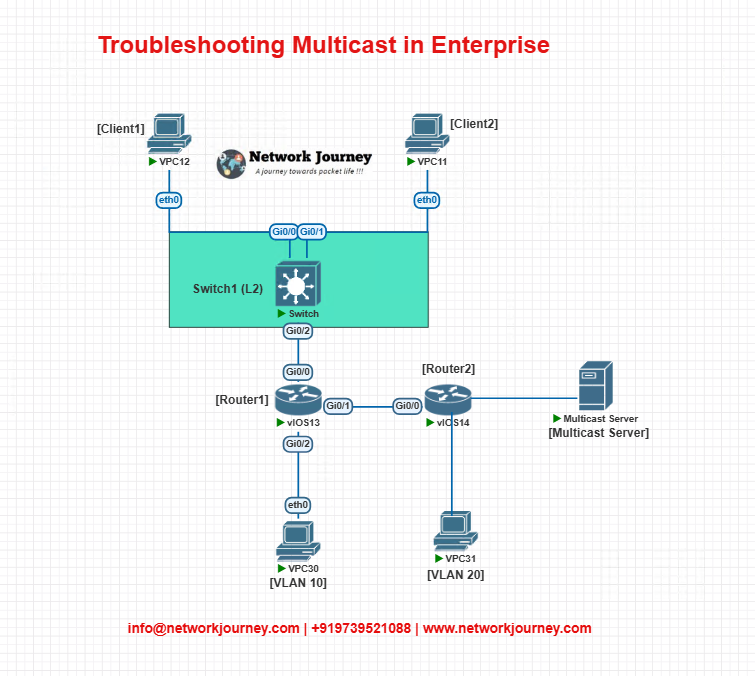
IP Schema
- VLAN 10: 192.168.10.0/24
- VLAN 20: 192.168.20.0/24
- Client1: 192.168.10.10
- Client2: 192.168.10.11
- Server: 192.168.20.100 (sending to group 239.1.1.1)
- RP: Router1 (manually configured)
Configuration Snippets
On Router1 (RP + PIM Config):
ip multicast-routing
interface g0/0
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface g0/1
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
ip pim sparse-mode
ip pim rp-address 10.0.0.1
On Router2 (Branch Router):
ip multicast-routing
interface g0/0
ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface g0/1
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
ip pim sparse-mode
ip pim rp-address 10.0.0.1
On SW1:
ip igmp snooping
vlan 10
ip igmp snooping
ip igmp snooping querier
Verification
# On Router1:
show ip pim neighbor
show ip pim rp mapping
show ip mroute
# On Switch:
show ip igmp snooping groups
Troubleshooting Tips
| Issue | Symptom | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| RP unreachable | Clients not receiving multicast | Verify routing to RP |
| No joins | IGMP join not seen on router | Check IGMP snooping, client config |
| PIM neighbors down | No (*,G) or (S,G) entries | Check PIM config/interface |
| RPF failure | Stream not forwarding | Use show ip rpf <source> |
| Flooding in LAN | All clients receiving multicast | Check IGMP snooping on switch |
FAQ – Troubleshooting Multicast
1. What are the most common reasons multicast traffic fails in enterprise networks?
Answer:
Multicast issues often stem from:
- Missing or incorrect PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast) configuration on routers.
- IGMP Snooping not enabled or misconfigured on switches.
- Lack of an IGMP Querier on the VLAN.
- Missing or incorrect RP (Rendezvous Point) configuration in PIM-SM.
- ACLs or firewalls blocking multicast traffic (224.0.0.0/4).
- Host devices not sending IGMP Join requests.
Start with verifying the control plane: IGMP messages, PIM neighbors, and multicast routing tables. Then check the data plane path hop-by-hop.
2. How can I verify if multicast routing is working on a Cisco router?
Answer:
Use the following commands:
R1# show ip mroute
R1# show ip pim neighbor
R1# show ip igmp groups
show ip mroute: Checks multicast routing table and (*,G) or (S,G) entries.show ip pim neighbor: Ensures PIM adjacency with other routers.show ip igmp groups: Verifies which groups are being joined on local interfaces.
If you see no entries in these outputs, there’s likely an issue with PIM or IGMP.
3. What is the role of IGMP in multicast troubleshooting?
Answer:
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) allows hosts to tell multicast routers they want to receive specific multicast streams. If hosts don’t send IGMP Join messages, or switches don’t forward them correctly due to missing IGMP Snooping, multicast routers will assume no receivers exist. Use packet captures or debug ip igmp to verify IGMP messaging from clients.
4. What is a Rendezvous Point (RP), and how do I know if it’s working properly in PIM-SM?
Answer:
In PIM Sparse Mode, the RP acts as the shared meeting point for multicast senders and receivers. If RP is misconfigured or unreachable, receivers won’t receive streams.
To check RP status:
R1# show ip pim rp mapping
R1# show ip pim rp-hash <multicast-group>
Verify consistency across routers and ensure the RP IP is reachable from all PIM routers.
5. How do I test end-to-end multicast connectivity in an enterprise network?
Answer:
Use ping or iperf with multicast options, or simulate a multicast sender and receiver setup. On Cisco IOS, use:
R1# ping 239.1.1.1 repeat 10
But more effectively:
- Use VLC, iperf, or multicast test tools between two endpoints.
- Run
netstat -gnon Windows/Linux to verify group joins. - Use Wireshark to confirm IGMP Report and multicast traffic flows.
6. How can I check if multicast packets are being dropped on the switch?
Answer:
Check the IGMP Snooping status:
Switch# show ip igmp snooping vlan <id>
Switch# show mac address-table multicast
Ensure:
- IGMP Snooping is enabled.
- Querier exists in the VLAN.
- Receivers are shown in the snooping group.
If you see no multicast MAC entries or output interfaces, traffic is likely dropped or flooded incorrectly.
7. What should I look for in Wireshark to troubleshoot multicast issues?
Answer:
In Wireshark:
- Look for IGMP Membership Reports (IGMPv2 or v3) from clients.
- Verify that multicast packets (e.g., UDP to 239.x.x.x) are arriving at the receiver.
- Check TTL (Time-To-Live) values — if TTL is too low, packets may get dropped before reaching the receiver.
- Inspect Source IP and Group Address (S,G) details.
If multicast packets are missing at any point, trace back to the last hop where they were seen.
8. How do PIM modes (Sparse vs Dense) impact multicast behavior and troubleshooting?
Answer:
- PIM Sparse Mode (SM): Requires RP and Join messages. Traffic flows only when requested. Good for scalable enterprise networks.
- PIM Dense Mode (DM): Assumes everyone wants multicast. Flood-and-prune model. Easy to set up but inefficient.
Troubleshooting SM involves checking RP and Join paths, while DM involves checking if pruning or flooding is occurring as expected.
9. Why is multicast working in one VLAN but not in another?
Answer:
Possible reasons:
- VLAN missing IGMP Snooping config or Querier.
- VLAN not trunked correctly between switches.
- Multicast router not active in the second VLAN.
- RP not reachable from the second VLAN’s subnet.
- Incorrect Layer 3 interface or ACL blocking multicast.
Run:
Switch# show vlan brief
Switch# show ip igmp snooping vlan <id>
Router# show ip mroute
Compare outputs between working and non-working VLANs.
10. How can I monitor or log multicast issues proactively?
Answer:
You can:
- Enable SNMP traps for multicast events (like PIM neighbor down).
- Use NetFlow or Model-Driven Telemetry (MDT) to track multicast flows.
- Use
debug ip igmp,debug ip pim, anddebug ip mpacketfor real-time logs. - Set up logging to syslog servers or use DNA Center / Prime Infrastructure for multicast-aware monitoring.
YouTube Video Link
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implement Troubleshooting Multicast in Enterprise – From Chaos to Clarity is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![Troubleshooting Multicast in Enterprise – From Chaos to Clarity [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Troubleshooting-Multicast-in-Enterprise-–-From-Chaos-to-Clarity.png)
![Mastering STP Tuning: Optimizing Priority & Path Cost for Smarter Network Redundancy [CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Mastering-STP-Tuning_Optimizing-Priority_Path-Cost-for-Smarter-Network-Redundancy_networkjourney.png)
![On-Prem vs Cloud Controllers – Which One Powers Your Network Better? [CCNP Enterprise]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/On-Prem-vs-Cloud-Controllers_networkjourney.png)
![How to Lock Down Cisco Switch Ports with Port Security (2025 Guide)[CCNP ENTERPRISE]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/nj-blog-post-portsec-switchport.jpg)