IGMP Snooping and Configuration – Mastering Multicast Efficiency [CCNP ENTERPRISE]
Today’s article is all about IGMP Snooping—a crucial Layer 2 switch feature that ensures multicast traffic only reaches the devices that actually asked for it. Whether you’re preparing for CCNP or managing an enterprise network, understanding IGMP Snooping is a must. Let’s break it down in a way that’s as real-world as it is exam-ready.
Table of Contents
Theory in Brief – What is IGMP Snooping?
Multicast is an efficient method of delivering a single stream of traffic (like IPTV or video conferencing) to multiple clients. But multicast traffic doesn’t work like unicast or broadcast. It needs a system in place to know which devices want which stream.
Enter IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol). It operates between hosts (like PCs or IP TVs) and routers to manage multicast group memberships. IGMP messages tell the network: “Hey, I want to join or leave this multicast group.”
Now, here’s the twist. Layer 2 switches don’t normally inspect Layer 3 packets. So if no controls are applied, multicast packets are flooded out all switch ports—even to devices that didn’t ask for them!
That’s where IGMP Snooping comes in.
IGMP Snooping allows the switch to listen in on (or “snoop”) IGMP messages exchanged between hosts and routers. This way, it builds a table mapping multicast groups to specific switch ports. As a result, multicast streams go only where they’re needed—not everywhere.
Why IGMP Snooping Matters?
Imagine 100 users on your VLAN. Only 5 need a multicast stream (say, CCTV feed). Without IGMP Snooping, all 100 get flooded. Waste of bandwidth, right? With IGMP Snooping, the switch filters traffic intelligently, reducing congestion and improving efficiency.
Where is IGMP Snooping Used?
- IPTV streaming networks
- Corporate video conferencing
- CCTV surveillance systems
- Live video feeds in universities
- Multicast-based software distribution
It’s a backbone of enterprise AV over IP setups and is critical in wireless multicast environments.
Comparision : IGMP Snooping at a Glance
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | IGMP (v1, v2, v3) |
| Function | Prevents multicast flooding by mapping group traffic to requesting ports |
| Layer | Layer 2 |
| Switch Requirement | Must support IGMP Snooping |
| Required with | Multicast networks |
| Snooping on | IGMP Join/Leave/Query messages |
| Optional Feature | IGMP Snooping Querier (in absence of multicast router) |
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Efficient multicast forwarding | Slight CPU/memory overhead |
| Reduces unnecessary bandwidth use | Misconfigurations may block needed traffic |
| Enhances video/audio stream quality | Requires proper router/snooping querier configuration |
| Improves network stability in multicast deployments | May need tuning for high-scale environments |
Essential CLI Commands
| Purpose | Command |
|---|---|
| Enable IGMP snooping globally | Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping |
| Disable globally (not recommended) | Switch(config)# no ip igmp snooping |
| Enable on specific VLAN | Switch(config)# vlan 10Switch(config-vlan)# ip igmp snooping |
| Check IGMP snooping status | Switch# show ip igmp snooping |
| Check multicast group memberships | Switch# show ip igmp snooping groups |
| Enable querier on VLAN | Switch(config)# vlan 10Switch(config-vlan)# ip igmp snooping querier |
| Debug IGMP packets (router) | Router# debug ip igmp |
| View group stats | Switch# show ip igmp snooping mrouter |
Real-World Use Case – IPTV Streaming in Enterprise Network
| Scenario | Details |
|---|---|
| Environment | Large enterprise office with IPTV feeds from HQ |
| Problem | All VLAN users receiving multicast even if not watching |
| Solution | Enable IGMP Snooping on VLAN where IPTV receivers exist |
| Result | Only ports with IPTV clients receive the stream |
| Bonus | Improved bandwidth usage, reduced complaints from non-IPTV users |
EVE-NG Lab Topology
LAB TOPOLOGY
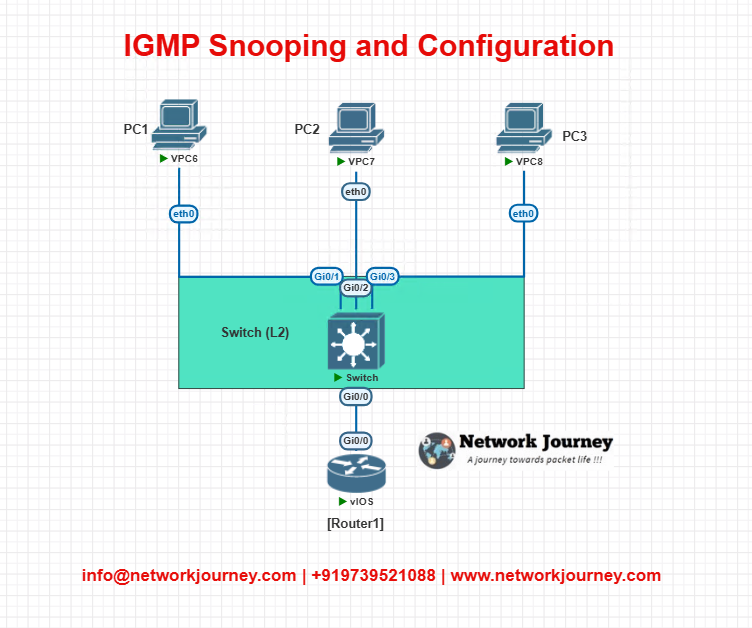
IP Schema
- VLAN 10: 192.168.10.0/24
- PC1: 192.168.10.101
- PC2: 192.168.10.102 (IPTV client)
- PC3: 192.168.10.103 (IPTV client)
- Router1: 192.168.10.1 (Multicast Router)
Lab Configuration (Cisco IOS)
Switch
conf t
vlan 10
name IPTV
exit
interface range fa0/1 - 3
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan 10
exit
ip igmp snooping
vlan 10
ip igmp snooping
ip igmp snooping querier
exit
Router
interface fa0/0
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
ip pim sparse-mode
exit
ip multicast-routing
Verification
Switch# show ip igmp snooping groups
Switch# show ip igmp snooping mrouter
Router# show ip mroute
Troubleshooting Tips
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Multicast traffic still flooding | IGMP Snooping disabled | Enable snooping on VLAN |
| Hosts not receiving stream | Querier not configured | Enable querier or ensure multicast router is present |
| Multicast drops after few minutes | IGMP Membership timeout | Tune snooping timers |
| Switch not learning groups | IGMP messages blocked | Check access-lists or port security |
| High CPU on switch | Too many multicast streams | Consider hardware support for multicast or VLAN design |
Most Asked FAQs on IGMP Snooping
1. What is IGMP Snooping, and why is it used in networks?
Answer:
IGMP Snooping is a Layer 2 feature that listens to Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) messages exchanged between hosts and routers to intelligently forward multicast traffic. Without IGMP Snooping, switches flood multicast traffic out of all ports in a VLAN, which wastes bandwidth. IGMP Snooping ensures multicast traffic is only sent to ports with interested receivers—this drastically improves multicast efficiency, especially in large networks like enterprise LANs, campus setups, or IPTV deployments.
2. How does IGMP Snooping work behind the scenes?
Answer:
When a host sends an IGMP Join or Leave message to a multicast group, the switch “snoops” or inspects the packet and builds a forwarding table based on which port requested which multicast group. Similarly, it monitors IGMP Report and Leave messages to update this table. The switch thus acts as a passive listener and avoids unnecessary flooding. The control plane isn’t burdened much—it’s handled mostly in hardware (ASICs) on modern switches.
3. What are the different IGMP versions, and which one should I configure for IGMP Snooping?
Answer:
There are three versions of IGMP:
- IGMPv1 – Simple, but lacks Leave messages.
- IGMPv2 – Adds Leave messages for faster pruning.
- IGMPv3 – Supports Source-Specific Multicast (SSM).
For most enterprise environments, IGMPv2 is commonly used because it offers a good balance between compatibility and efficiency. However, if you’re doing SSM or using modern applications, IGMPv3 might be needed. IGMP Snooping itself supports all versions, but your multicast router and host configurations must align.
4. What is the role of a querier in IGMP Snooping?
Answer:
In multicast networks, the IGMP Querier is responsible for periodically asking hosts if they still want to receive multicast traffic. This helps maintain up-to-date group memberships. In networks without a multicast router (like a Layer 3 switch), the IGMP Snooping Querier can be enabled on the switch to take over that function. This ensures the IGMP Snooping table remains refreshed and accurate, preventing stale entries and traffic black-holing.
5. What happens if IGMP Snooping is disabled on a switch?
Answer:
If IGMP Snooping is disabled, multicast traffic will be flooded to all ports within the VLAN—even if only one host requested it. This can severely degrade performance, especially in video streaming or VOIP multicast scenarios, because all endpoints receive unnecessary traffic. It essentially treats multicast like broadcast. For efficient and secure multicast delivery, it’s best practice to always enable IGMP Snooping on switches where multicast is used.
6. How do I configure IGMP Snooping on a Cisco switch?
Answer:
Basic configuration is straightforward. Here’s a quick example:
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 10
To configure a querier on a VLAN:
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 10 querier
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping querier address 192.168.10.1
This enables IGMP Snooping globally and for VLAN 10, and configures a querier with a specified IP address.
7. What is IGMP Snooping Proxy, and when is it used?
Answer:
IGMP Snooping Proxy is a feature used in more complex environments where multicast traffic needs to be forwarded across VLANs or when switches act as intermediaries between hosts and multicast routers. It summarizes IGMP reports from multiple clients and sends a single membership report upstream. This reduces overhead and enhances scalability, especially in large Layer 2 networks or IPTV scenarios. It’s typically used in provider networks or large enterprise video networks.
8. How do I troubleshoot multicast traffic not reaching clients despite IGMP Snooping being enabled?
Answer:
Here’s a checklist:
- Ensure clients are sending IGMP Join messages (use Wireshark or debug IGMP).
- Check if the querier is active—without it, group entries will expire.
- Verify that IGMP Snooping is enabled globally and per VLAN.
- Confirm PIM or multicast routing is configured on upstream routers.
- Ensure no IGMP filtering or ACLs are blocking group joins.
- Use
show ip igmp snooping groupsorshow mac address-table multicastto verify multicast forwarding tables.
9. Does IGMP Snooping affect broadcast or unicast traffic in any way?
Answer:
No, IGMP Snooping is purely concerned with multicast traffic. It does not impact unicast or broadcast forwarding. That said, if misconfigured, it may lead to multicast being treated as broadcast, which can result in unnecessary bandwidth consumption. However, for proper IGMP configuration, multicast is efficiently isolated and forwarded only to interested receivers.
10. Can IGMP Snooping be used in wireless networks or is it only for wired LANs?
Answer:
While IGMP Snooping is primarily a Layer 2 wired LAN feature, wireless controllers (like Cisco WLCs) have similar multicast optimization techniques. They don’t technically do IGMP Snooping, but they do handle multicast-to-unicast conversions or use multicast direct features for efficient delivery. In wired LANs, you always want IGMP Snooping enabled where multicast flows are expected. In wireless, look for multicast optimization under QoS or WLAN profiles.
YouTube Video Link
Final Note
Understanding how to differentiate and implementIGMP Snooping and Configuration – Mastering Multicast Efficiency is critical for anyone pursuing CCNP Enterprise (ENCOR) certification or working in enterprise network roles. Use this guide in your practice labs, real-world projects, and interviews to show a solid grasp of architectural planning and CLI-level configuration skills.
If you found this article helpful and want to take your skills to the next level, I invite you to join my Instructor-Led Weekend Batch for:
CCNP Enterprise to CCIE Enterprise – Covering ENCOR, ENARSI, SD-WAN, and more!
Get hands-on labs, real-world projects, and industry-grade training that strengthens your Routing & Switching foundations while preparing you for advanced certifications and job roles.
Email: info@networkjourney.com
WhatsApp / Call: +91 97395 21088
Upskill now and future-proof your networking career!
![IGMP Snooping and Configuration – Mastering Multicast Efficiency [CCNP ENTERPRISE]_networkjourney](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/IGMP-Snooping-and-Configuration-–-Mastering-Multicast-Efficiency.png)
![[Day #21 Pyats Series] VLAN database validation before/after changes using pyATS for Cisco](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Day21-PyATS-Series-VLAN-Database-Validation-Before_After-Changes-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco.png)
![[Day #84 PyATS Series] Multi-Vendor Golden Image Compliance Testing Using pyATS for Cisco [Python for Network Engineer]](https://networkjourney.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Day-84-PyATS-Series-Multi-Vendor-Golden-Image-Compliance-Testing-Using-pyATS-for-Cisco-Python-for-Network-Engineer-470x274.png)
